[Paper Review] Contextnet: Improving convolutional neural networks for automatic speech recognition with global context
Contextnet: Improving convolutional neural networks for automatic speech recognition with global context
Han, Wei, et al. “Contextnet: Improving convolutional neural networks for automatic speech recognition with global context.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.03191 (2020).
Abstract
end-to-end 음성 인식에서 CNN이 좋은 성능을 보여왔지만, 여전히 RNN/Transformer 기반 모델들 보다 성능이 떨어짐
본 논문에서는 이러한 성능 격차를 어떻게 해결할 수 있을지 연구하고, 새로운 CNN-RNN-transducer 구조인 ContextNet 제안
ContextNet은 squeeze-and-excitation 모듈을 추가함으로써 global context 정보를 convolution layers에 통합하는 fully convolutional encoder로 구성
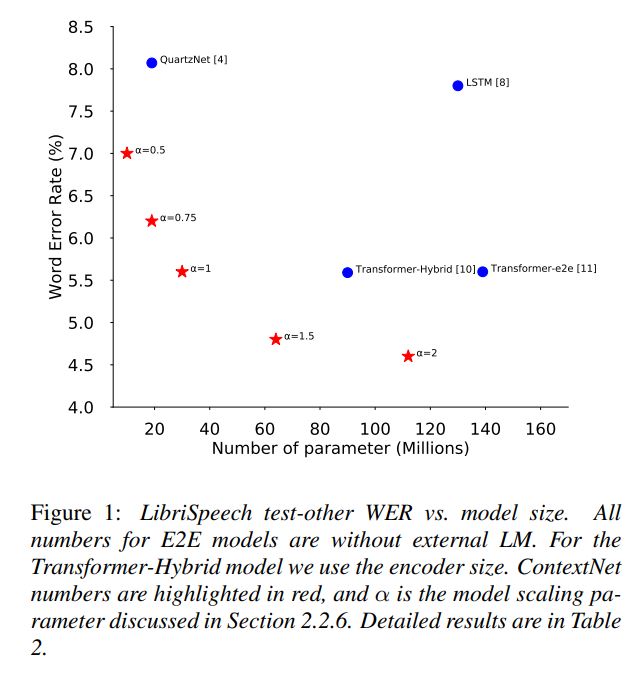
ContextNet의 너비를 조정하는 간단한 scaling method 제안
모델 사이즈(widths)는 연산량과 정확도 간 trade-off 관계가 있음
가장 널리 사용되는 Librispeech benchmark(clean/noisy)에서 좋은 성능을 보임
외부적인 language model(LM) 없이 2.1%/4.6% WER (word error rate)
LM 추가하여 1.9%/4.1% WER
10M parameters만으로 2.9%/7.0%
Introduction
end-to-end (E2E) speech recognition을 위한 CNN 기반 모델들에 대한 관심이 높아지고 있음
-
the Jasper model
외부적인 neural language model을 사용하여 LibriSpeech test-clean에서 2.95% WER로 SOTA와 근접
여러번 쌓은 1D convolutions과 skip connections으로 구성된 deep convolution 기반 encoder
CNN 모델의 정확도와 성능을 개선하기 위해 Depthwise separable convolutions 활용
-> 이러한 CNN 기반 모델의 장점은 parameter efficiency이지만, CNN 기반 모델 중 가장 성능이 좋은 QuartzNet은 여전히 RNN/Transformer 보다 성능이 떨어짐
RNN/transformer 기반 모델과 CNN 기반 모델의 가장 큰 차이점은 context length에 있음 (문맥을 어느정도 범위까지 고려할 수 있는지)
양방향 RNN 모델의 경우, 이론상으로 하나의 셀은 전체 시퀀스 정보에 접근할 수 있음
Transformer 모델의 경우, attention mechanism은 두개의 서로 다른 타임 스탬프에 존재하는 노드들이 서로의 연산에 참여함
하지만, 제한된 kernel 사이즈를 가진 convolution은 특정 시간에 작은 window 사이즈만을 고려할 수 있음
-> 이러한 문맥은 범위가 작고, global 정보를 담지 못함
본 논문에서 CNN 기반 ASR 모델과 RNN/transformer 기반 모델 간 성능 차이의 주된 원인은 global context의 부족이라고 주장
CNN 모델에서 global context를 향상시키기 위해, the squeeze-and-excitation (SE) layer로부터 영감을 얻어 새로운 CNN 기반 ASR 모델인 ContextNet 제안
-
SE layer가 local feature vectors의 시퀀스를 하나의 global context vector로 만듦
-
이러한 context를 다시 각각의 local feature vector로 broadcating 시킴 (global 정보 local로 보내기)
-
multiplication을 통해 두가지 정보를 합침
convolution layer 뒤에 SE layer를 위치시켰고, convolution 출력이 global 정보에 접근할 수 있도록 함 ??
실험을 통해, squeeze-and-excitation layers를 ContextNet에 추가시키는 것이 WER 값이 크게 감소시키는 것을 확인함
많은 layer를 쌓거나 개별적으로 학습된 global vector를 accustic model에 도입하는 하이브리드 ASR 방식의 기존 연구들이 성공적이었음
[17]에서 SE가 unsupervised adaptation을 위한 RNN에 적용되었음
본 논문에서는 SE가 RNN 뿐만 아니라 CNN encoders에도 효과적으로 적용될 수 있음을 보여줌
ContextNet의 구조는 encoder에서 depthwise separable 1D convolution 이용과 같은 QuarzNet의 선택에서 영감을 얻음
하지만, SE layer를 도입했다는 점이 다르고, 이외에도 다른 점이 있음
-
CTC decoder 대신 RNN-T decoder 사용
-
Swish activation function 사용
ContextNet은 LibriSpeech test clean/test-other에서 WER 기준 1.9%/1.4% 성능을 달성
QuartzNet과 같은 기존 CNN 기반 방식을 크게 뛰어넘었고, tansformer와 LSTM 기반 모델도 뛰어넘음
또한, 빠른 학습과 평가를 위해 ContextNet의 계산 비용을 감소시킬 수 있는 방식을 연구함
-
점진적인 downsampling scheme
점진적으로 인코딩된 시퀀스의 길이를 8번 감소시켜서 계산 비용을 크게 줄임
이런 scheme으로 모든 convolution layers의 kernel 사이즈를 감소시킬 수 있었음
-
convolutional filters에서 채널 수를 변경함으로써 ContextNet 사이즈를 조절할 수 있음
Contributions
-
ASR을 위해 global context를 적절히 다룰 수 있는 향상된 CNN 모델 제안
-
점진적 downsampling scheme, 정확도의 모델 사이즈의 trade-off 간 적절한 모델을 찾기 위한 model scling scheme
Model
End-to-end Network: CNN-RNN-Transducer
본 논문에서 제안한 네트워크는 RNN-Transducer framework 기반 모델임
네트워크는 input utterance에 대한 audio encoder, input label에 대한 label encoder, 둘을 결합하고 decoding하는 joint network로 구성
LSTM 기반 label encoder와 [20]에서 사용된 joint network를 사용하지만, 새로운 CNN 기반 audio encoder 제안
Encoder Design
encoder가 신호 x를 high level representation h로 변환
\[x = (x_{1},...,x_{T}), h = (h_{1},...,h_{T}), where T'<=T\] \[h = AudioEncoder(x) = C_{K}(C_{K-1}(...C_{1}(x)))\]C는 convolution block이고, 여러개의 convolution layers로 구성 (batch normalization과 activation function이 뒤에 붙음)
squeeze-and excitation component와 skip connections을 포함하고 있음

Leave a comment