[Paper Review] TDAN: Temporally-Deformable Alignment Network for Video Super-Resolution
TDAN: Temporally-Deformable Alignment Network for Video Super-Resolution
Tian, Yapeng, et al. “TDAN: Temporally-Deformable Alignment Network for Video Super-Resolution.” Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2020.
Abstract
- cameras와 objects의 다양한 motion으로 인해 reference frame과 supporting frames은 alginment가 맞춰져 있지 않음
VSR에서 temporal alignmnet를 맞추는 것은 중요한 문제이고, challenging 함
- 기존 VSR 방식들은 optical flow를 이용하여 alignmnet를 수행
문제점 : optical flow의 정확도에 매우 의존적이며, 부정확한 optical flow는 artifacts 생성
- temporal deformable alignmnet network(TDAN) 제안
optical flow 계산없이 feature level에서 frame 간 alignment를 적응적으로 수행
- TDAN은 동적으로 sampling convolution kernels의 offsets을 예측하며, 이를 이용하여 alignment를 수행
HR video frame을 예측하기 위해, reconstruction network는 aligned frames과 reference frame을 이용
- 실험을 통해 TDAN의 효과를 입증함
Introduction
-
VSR에서 필수적인 reference frame과 supporting frames 사이의 alignmnet
-
Optical flow
기존 방식들은 reference frame과 supporting frames 사이의 motion fields를 예측하기 위해 optical flow 사용
해당 motion field를 이용하여 supporting frames를 wrapping
문제점 : optical flow가 아주 중요한 역할을 하면서 optical flow에 의존적임
flow를 잘못 예측하면 artifacts를 생성
- temporally deformable alignment network(TDAN) 제안
optical flow를 사용하지 않는, one-stage temporal alignment
- TDAN은 feature level에서 frame 사이 alignment를 적응적으로 수행
without explicit motion estimation and image wrapping operations (optical flow)
- TDAN의 강점
1) aligned LR frames은 artifacts가 이전 방식들에 비해 적음
2) 복원된 HR frame의 image quality가 향상됨
3) deformable convolution을 사용하면서, temporal scenes에서 다양한 motion conditions을 다룰 수 있는 강한 capability와 flexibility를 가짐
- 흔하게 사용되는 VSR benchmark와 2개의 real-world LR video sequences에서 광범위한 실험 수행하고, SOTA 달성
- Contributions
1) 새로운 temporally deformable alignmnet network 제안
기존의 optical flow 기반 two-stage process를 피함 (속도가 느림)
2) end-to-end trainable VSR framework 제안
3) Vid4 benchmark dataset에서 SOTA 달성
Method
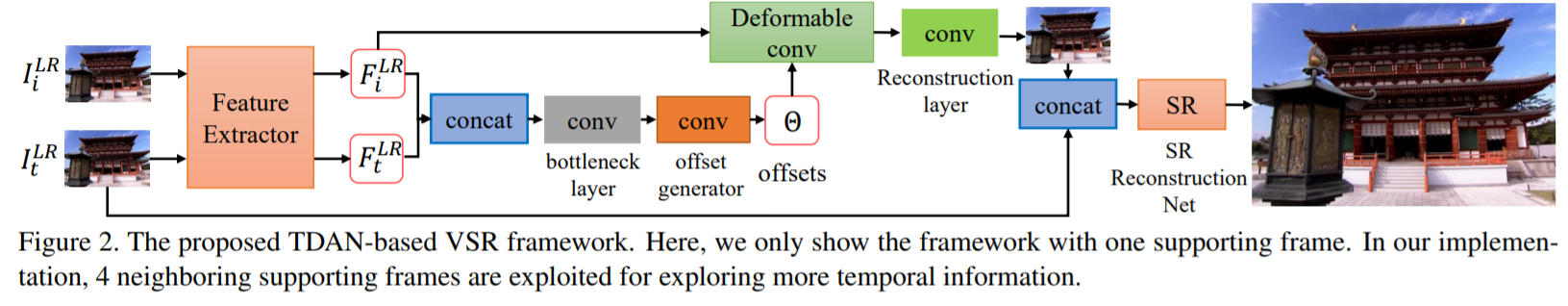
- 3.1 Overview
input : 연속적인 2N + 1 frames
1) temporally deformable alignment network (TDAN)
reference frame과 각각의 supporting frame의 alignment를 수행하는 network
2) SR reconstruction network
HR frame을 예측하는 network로 input으로 2N개의 aligned frames과 1개의 reference frame이 들어감
- 3.2 Temporally Deformable Alignment Network
1) Feature Extraction
하나의 공유된 feature extraction network를 통해, 각각의 LR frame으로 부터 visual features를 추출함
1개의 convolution layer와 k1 residual blocks로 구성되어 있음 (activation function : ReLU)
추출된 features는 feature-wise temporal alignment를 위해 사용됨
2) Deformable Alignment
인접 frame i의 feature에 대한 sampling parameters(offset)를 예측하기 위해 input으로 feature i와 feature t를 사용
convolution kernel의 offset
offset과 feature i를 통해 aligned feature를 얻음
deformable convolution
each position p0 on the aligned feature map F
deformable convolution function 이전, 이후에 transformation의 flexibility와 capability를 향상시키기 위한 3개의 추가적인 convolution layers를 사용함
deformable alignment module은 몇개의 regular convolution과 deformable convolution으로 구성
- offsets 예측 방식
1) sampling parameter generation function을 위해 feature i 와 feature t를 concatenation 시키고, 3x3 bottleneck layer를 사용하여 channel의 수를 감소시킴
2) sampling parameters는 kernel size R의 하나의 convolution layer로 예측됨
3) 최종적으로 offset과 feature i로부터 aligned feature i가 만들어짐
3) Aligned Frame Reconstruction
deformable convolution이 잠재적으로 motion cues을 포착하고, alignment를 수행할지라도, supervision 없이 학습을 진행하는 것은 어려움이 있음
align loss 적용
- 3.3 SR Reconstruction Network
1) Temporal Fusion
다른 frames에서의 temporal 정보를 융합시킴
서로 다른 프레임을 시간공간을 가로질러 융합하기 위해 2N + 1 frame을 직접 concatenation을 수행한 후, 하나의 3×3 convolution layer로 보내어 융합된 feature map을 얻음
2) Nonlinear Mapping
k2 residual blocks으로 구성되어 있고, deep features를 예측 (high-level visual features를 예측)
3) HR Frame Reconstruction
LR reference frame에 대한 HR frame을 복원시킴
하나의 sub-pixel convolution layer를 이용하여 upscaling을 수행하고, zoomed feature map으로 부터 하나의 convolution을 적용하여 최종 HR frame을 얻음
- 3.4 Loss function
align loss
sr loss
total loss


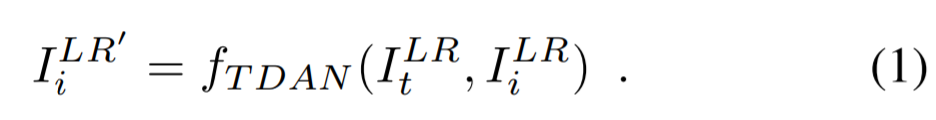
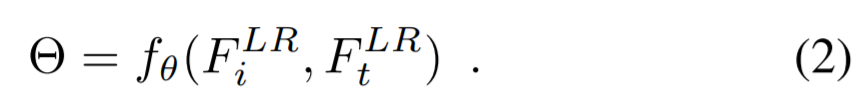
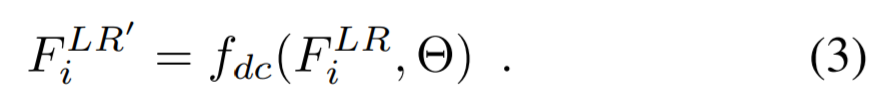
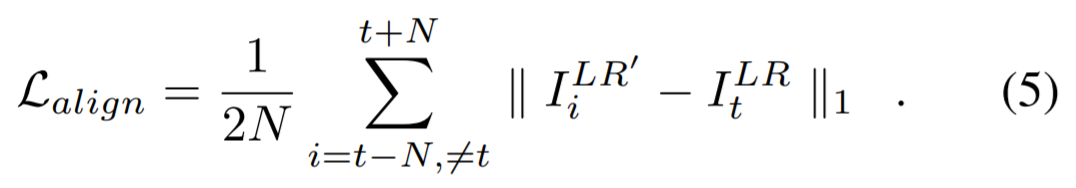
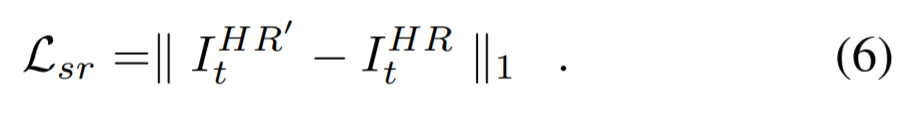
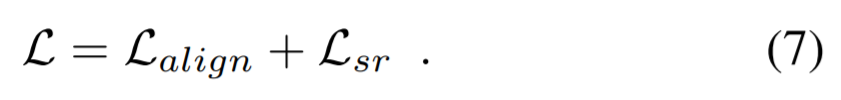
Leave a comment