[Paper Review] Deep video inpainting
Deep video inpainting
Kim, Dahun, et al. “Deep video inpainting.” proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019.
Abstract
- video inpainting : video에서 spatio-temporal holes을 그럴듯한 이미지로 채워주는 것
image inpainting 분야는 deep learning을 통한 큰 발전이 있었지만, 이를 time dimension이 추가된 video domain으로 확장 시키는 것은 challenging 함
- fast video inpainting을 위한 새로운 deep network 제안 (VINet)
image-based encoder-decoder model로, 인접 frames에서 정보를 모으고 정제하여 알 수 없었던 부분(still-unknown regions)을 생성
recurrent feedback과 temporal memory module을 이용하여 temporally consistent output을 얻을 수 있음
-
기존 image inpainting algorithm SOTA와 비교하였을 때, semantically correct, temporally smooth 한 video 생성
-
time-consuming optimization에 의존하던 이전의 video completion 방식과 다르게, 좋은 성능을 내면서 real-time에 가까운 speed
-
제안한 방식은 video retargeting task에도 적용될 수 있고, 시각적으로 좋은 결과를 얻음
Introduction
- video inpainting은 다양한 video editing이나 restoration tasks에 활용됨
object removal, scratch or damage restoration and retargeting
- 증강현실(AR)과도 결합하여 사용할 수 있음
Diminished Reality(DR) : 원하지 않는 object를 제거하는 기술
- image inpainting 기술을 video inpainting 기술로 확장시키는 것은 추가적인 time dimension을 처리해야 하기 때문에 challenging 함
원인 : complex motions and high requirement on temporal consistency
- video inpainting을 수행할 수 있는 가장 단순한 방법은 각 frame을 독립적인 image inpainting 방식을 통해 처리하는 것임
문제점 : motion 정보(video dynamics)를 무시하고, 시간에 따른 image-space에서의 변화에 대한 예측을 이용할 수 없음
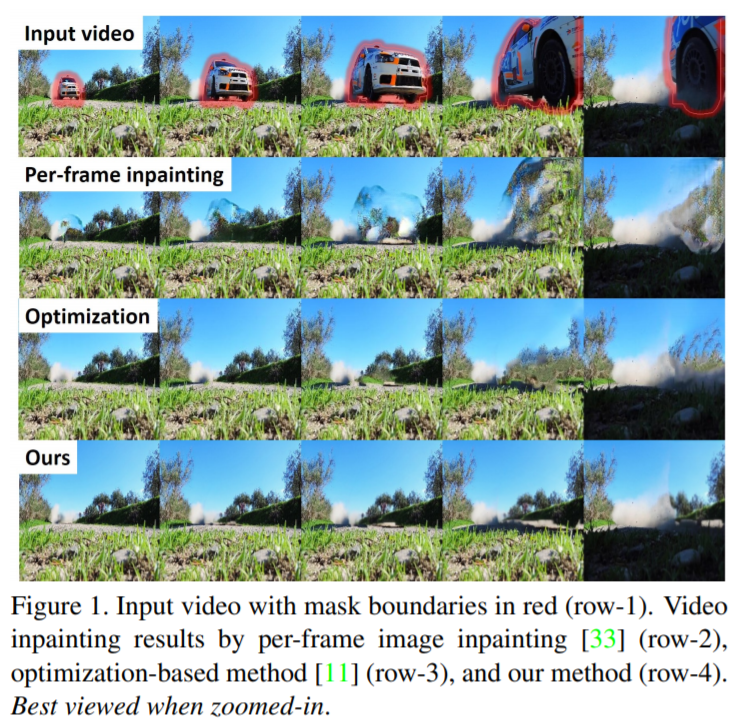
이런 방식은 temporal inconsistencies, severe flickering artifacts를 유발함 (fig1의 2번째 줄)
- temporal consistency 문제를 해결하기 위한 여러가지 방식들이 연구됨
greedy selection of local spatio-temporal patches[24], per-frame diffusion-based technique[16], iterative optimization[11]
단점 : [24],[16] 방법은 color estimation과 독립적으로 flow estimation을 처리해야 하고, [11] 방법은 time-consuming optimization에 의존적임
- Lai et al.[14]에서 original frame과 처리된 frame을 input으로 넣고, temporally consistent video를 생성함
두개의 input videos가 하나의 pixel-wise correspondences를 가질 때만 적용 가능함 (ex,colorization)
video inpainting에는 적용할 수 없음
- feed-forward deep network가 video inpainting task에 적용될 수 있는지 연구
1) temporal feature aggregation
sequential multi-to-single frame inpainting problem으로 다룸
2D-based encoder-decoder model 기반의 새로운 3D-2D feed-forward network 제안
network는 인접 frames에서 잠재적인 hints를 모으고 정제하여, 공간과 시간 상에서 video content를 만들어 냄
2) temporal consistency
recurrent feedback과 memory layer(convolutional LSTM)를 사용
flow loss(이전의 생성된 frame의 warping 학습)와 warping loss(short-term과 long-term consistency를 위한 loss) 사용
- 하나의 통합된 deep CNN model인 VINet 제안
- 광범위한 실험을 수행하였고, 생성된 video는 [33] 방식보다 더 정확하고 시각적으로 보기 좋음 (fig1 마지막 줄)
임의의 개수의 video frames을 처리할 수 있고, test time 시에 optical flow 계산이 필요하지 않기 때문에 real-time에 가까운 속도
- Contribution
1) sequential multi-to-single frame inpainting task로 video inpainting을 다루면서, 새로운 deep 3D-2D encoder-decoder network를 제안
효과적으로 인접 frames에서의 features를 모으고, 그에 기반하여 missing content를 만들어 냄
2) temporal stability를 위해 recurrent feedback과 memory layer를 사용
강한 temporal consistency를 위해 2개의 loss 사용 (flow loss, warping loss)
3) video inpainting task를 위한 하나의 통합된 deep network를 제공하는 최초의 연구
다른 task에도 적용이 가능함 (video retargeting, super-resolution)
Method
3.1 Problem Formulation
Video inpainting : video frames에서 임의의 missing regions을 채우는 것
network는 realistic하고 temporally-consistent output sequences를 생성해야 함
- 하지만 시각적으로 보기 좋은 video results를 얻기 위해서 필요한 3가지 조건이 있음
1) spatio-temporal neighbor frames (N:temporal radius)
2) 이전에 생성된 frame Y_t-1
3) 모든 이전의 정보가 encoding 되는 recurrent memory M_t
experiments setting : N=2 / temporal stride = 3
3.2 Network Design
- 3.2.1 Multi-to-single Frame Video Inpainting
videos의 frame에서 가려지거나 제거된 부분을 인접 frame(past/future)에서 종종 발견할 수 있음
인접 frame(temporal radius)에서 hint가 존재한다면 그것을 이용하여 현재 frame을 복원할 수 있고, 그렇지 않은 부분은 합성되어져야 함
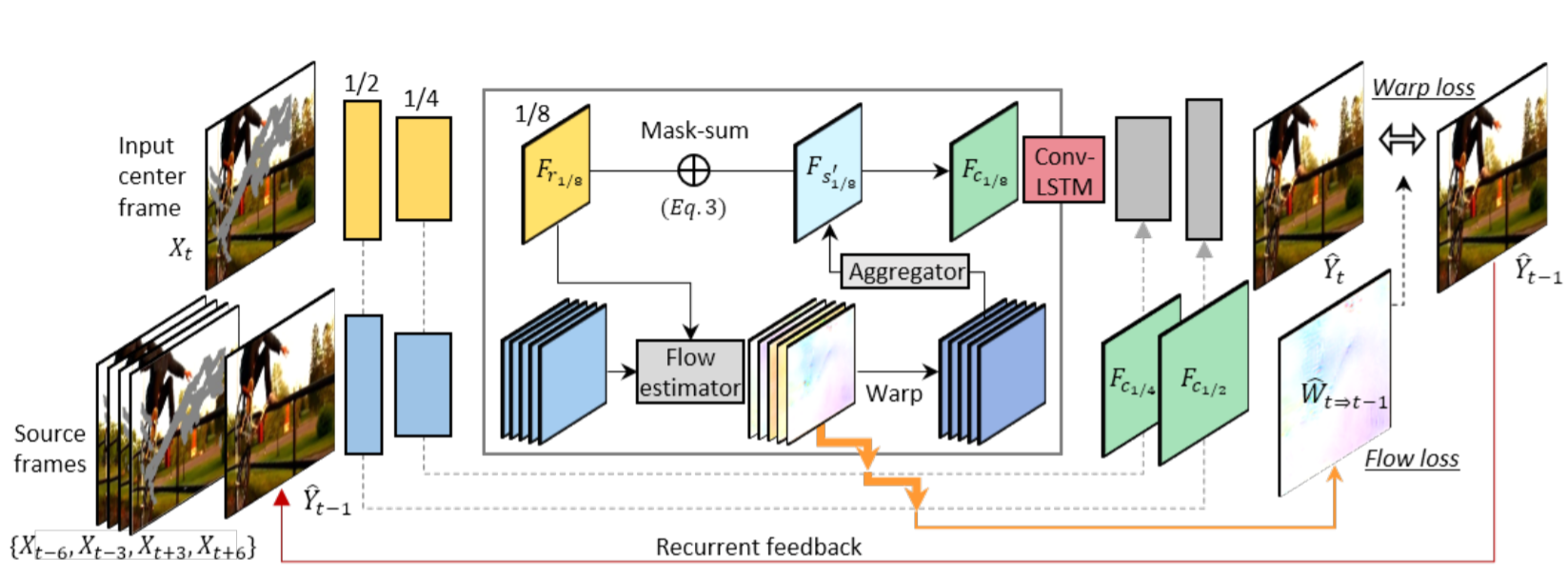
temporal feature aggregation과 single-frame inpainting를 동시에 학습하는 encoder-decoder network 제안
모든 input size를 다룰 수 있도록 fully convolutional 구조
- Source and reference encoders
encoder : source와 reference streams을 갖는 multiple-tower network
- source stream : inpainting masks를 갖는 past frames과 future frames을 input으로 취함
- reference stream : 현재 frame과 해당 frame의 inpainting mask를 제공 받음
channel 축으로 image frames과 masks를 concatenation 시킨 후, encoder의 입력으로 들어감
6-tower encoder 사용 (5 source streams + 1 reference stream)
- Feature flow learning
source features와 reference features를 직접 결합시키기 전에, feature points의 alignment(explicitly alignment)를 수행
flow sub-network를 사용하여 4개의 scale(1/8,1/4,1/2,1)에서 feature maps 사이(source-reference)의 flow 예측
PWCNet의 coarse-to-fine 구조를 채택하였고, 오직 연속적인 2개의 frames에서 flow 추출(FlowNet2 사용)
최종적으로 scale 1인 flow만을 이용하여 학습
- Learnable Feature Composition
5개의 source streams에서 aligned feature maps이 주어지면, time dimension으로 concatenation을 진행하고 5x3x3(THW) convolution layer의 input으로 넣어줌
5x3x3 convolution layer에서 time dimension이 1인 하나의 spatio-temporally aggregated feature map 생성
reference features에 보완되는 features를 강조하고, 그렇지 않은 경우에는 무시함으로써 시간 축에 걸쳐서 source features를 동적으로 선택하도록 설계됨
각 scale 별로 reference feature maps(F_r)과 융합된 feature map(F_s)을 결합시키는 mask sub-network 적용
- mask sub-network
input : 2개의 feature map 차이의 절댓값이 들어감
single channel composition mask m을 생성
3개의 convolution layers로 구성
- Decoder
image details을 decoder로 넘겨주기 위해, U-net에서의 skip connections을 고용
- 3.2.2 Recurrence and Memory
the recurrent feedback loop와 the temporal memory layer를 사용
이전 output의 정보가 찾고자하는 정보와 일치하는 경우 바꾸지 않고 사용하며, 이전 output에서 찾을 수 없는 경우 합성되어짐
output이 motion tragectories(경로)에 일관성이 있고, 가려지거나 motion이 연속적이지 않은 부분에서 ghosting artifacts를 피할 수 있음
recurrent feedback : 연속적인 frame을 연결 (short-term connection)
temporal memory layer(ConvLSTM) : large holes을 채우기 위한 knowledge 필요, 다른 time steps에서의 internal features connection (long-term connection)
warping loss 적용


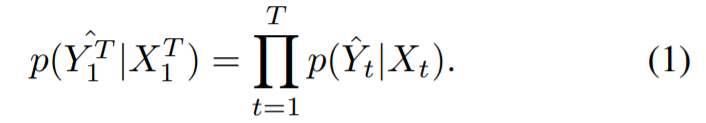
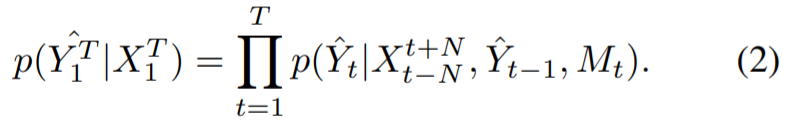
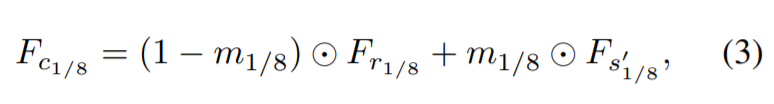
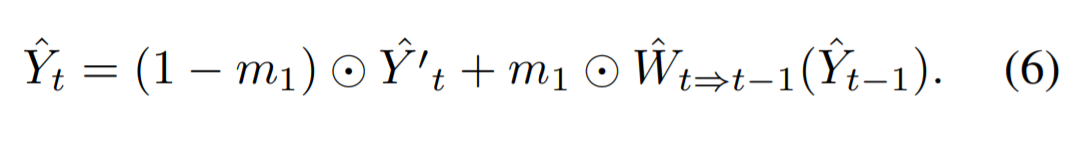
Leave a comment