[Paper Review] Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs
Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs
Chen, Liang-Chieh, et al. “Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs.” IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence 40.4 (2017): 834-848.
Abstract
- dense prediction에 강력한 atrous convolution을 사용함 (or convolution with upsampled filters)
resolution을 명시적으로 컨트롤 할 수 있음
추가적인 계산 비용 또는 파라미터 없이 receptive field를 확장시킬 수 있음
- 다양한 scale의 objects를 정확하게 segmentation하기 위해, atrous spatial pyramid pooling(ASPP) 제안
다양한 sampling rate와 receptive field에서 필터를 사용하면서 다양한 scale에서 이미지의 context와 objects를 포착함
- DCNNs과 probabilistic graphical models을 결합시켜 object boundaries의 정확도를 향상시킴
기존 문제점 : max-pooling과 downsampling의 결합은 localization 정확도를 낮춤
이를 해결하기 위해, 최종 DCNN layer에 fully connnected Conditional Random Field(CRF)를 결합시킴
- DeepLab은 PASCAL VOC-2012 semantic image segmentation task에서 SOTA 달성
Introduction
- DCNN으로 인해 computervision은 큰 발전을 이루었으나, 이를 그대로 segmentation에 적용하는 것은 한계가 존재
classification(abstract feature)와 segmentation은 task 간 차이가 존재하기 때문에, segmentation에 적용하였을 때 dense prediction result를 얻을 수 없음
- DCNN을 segmentation에 적용할 때, 3가지 challenge가 있음
- feature resolution이 감소함
반복적인 max-pooling과 downsampling(striding)으로 인해 발생
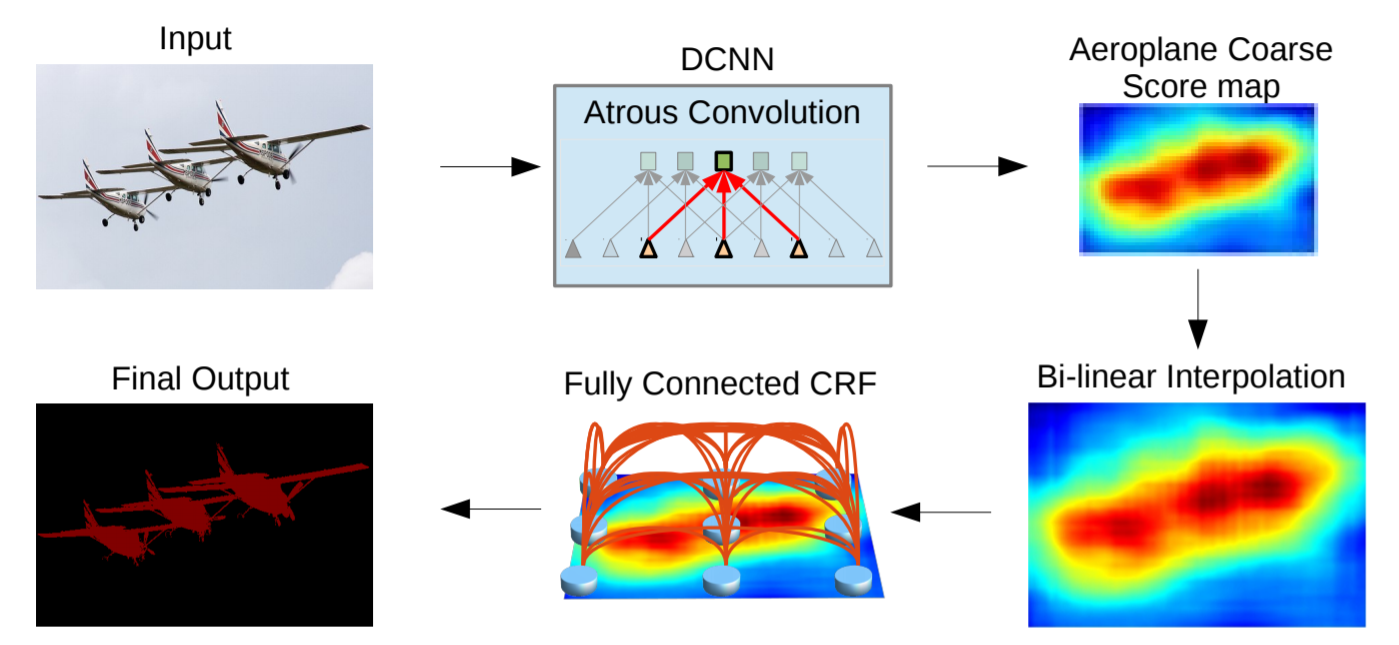
이를 해결하기 위해, 뒷 단의 max pooling layers를 제거하고 upsample the filters(higher sampling rate를 갖는 atrous convolution)를 붙임
Atrous convolution : filter 간격 사이를 0으로 채우기 때문에 계산 비용의 증가 없이 resolution을 키울 수 있고, 효과적으로 receptive field를 확장시킬 수 있음
Atrous convolution 뒤에 simple bilinear interpolation을 붙여 input image의 resolution을 유지함 (dense prediction result 생성)
- 다양한 scale의 objects가 존재함
기존 처리 방식 : 동일한 image에 대하여 rescale된 DCNN의 feature 또는 score maps을 융합시키는 방식을 사용하였으나, 계산 비용이 상당히 증가한다는 문제점이 존재
spatial pyramid pooling에서 영감을 얻어, 다양한 rate에서 feature layer를 resampling하는 계산적으로 효율적인 전략을 제안
이 방식은 receptive filed를 보완할 수 있는 다양한 filters로 input image를 학습할 수 있기 때문에 다양한 scales에서 image context와 objects를 포착할 수 있음
atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) : 서로 다른 sampling rates를 갖는 다양한 parallel atrous convolutional layers를 사용하여 효율적으로 구현됨
- DCNN invariance로 인한 localization 정확도 감소
classifier는 공간 변형에 대한 불변성을 필요로 하는데, 이는 spatial accuracy를 제한시킴
model의 성능을 높이기 위해, fully-connected Conditional Random Field(CRF)를 사용하여 정밀한 details 포착
- DCNN을 semantic segmentation task에 맞게 디자인
-
모든 fc layers를 convolutional layers로 변경 (fully convolutional network)
-
atrous convolutional layers를 통해 feature resolution 확장
기존 network에서는 32 pixel 별로 계산되던 feature를 8 pixel 별로 계산되도록 변경
그 뒤에 bi-linear interpolation(x8)을 적용시켜 input resolution으로 맞춰줌
- DeepLab의 3가지 main advantages
-
Speed : atrous convolution을 사용하면서 NVidia Titan X GPU에서 8 FPS로 동작
-
Accuracy : 다양한 datasets(PASCAL VOC 2012, PASCAL-Context, PASCAL-Person-Part, Cityscapes)에서 SOTA 달성
-
Simplicity : DCNNs, CRFs 두 가지 modules로 구성
Methods
Atrous convolution for dense feature extraction and field-of-view enlargement
-
기존 DCNN의 resolution 문제를 해결하기 위해, deconvolutional layers를 사용하기도 하였으나 이는 추가적인 memory와 시간이 들기 때문에 효율적이지 못함
-
효율적인 계산을 위해 atrous convolution을 사용
이 알고리즘은 원하는 resolution에서 모든 layer의 feature 계산을 가능함
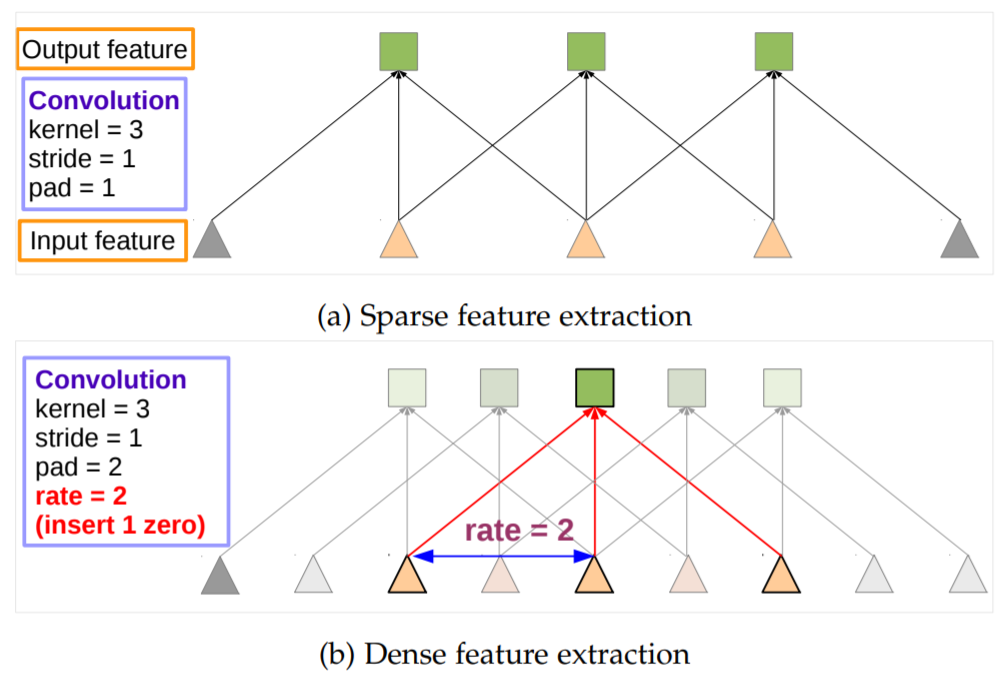
- 1-D : Sparse feature extraction(standard convolution) vs Dense feature extraction(atrous convolution)
(a) : 표준 convolution layer로 stride가 1이며, input feature map의 resolution이 작음
(b) : atrous convolution layer로 rate가 2이며, input feature map의 resolution이 큼
- 2-D : atrous convolution
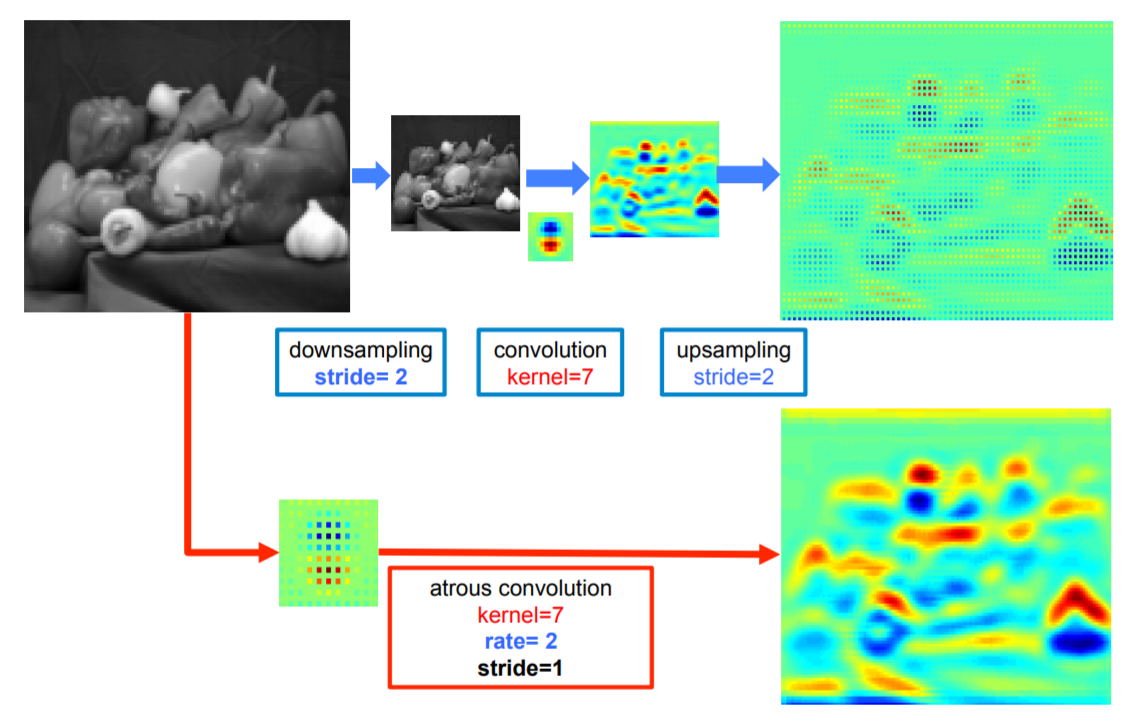
- 표준 convolutional layer 방식
image -> factor 2로 downsampling 수행 -> convolution 수행 -> stride=2로 upsampling 수행
input resolution의 4분의 1 크기의 responses만 얻을 수 있음 (sparse feature)
- atrous convolutional layer 방식
image -> atrous convolution
input resolution 전체에 대한 responses를 얻을 수 있음 (dense feature)
필터 값 사이를 0으로 채우면서 계산 비용과 파라미터의 증가없이 filter의 kernel size를 효과적으로 키움 (non-zero 값만 계산)
- 효율성과 정확도의 적절한 trade-off 관계를 고려하여, atrous convolution(factor 4)을 이용하여 density를 높이고, 이 후 빠른 bilinear interpolation(factor 8)을 이용하여 input resolution과 동일하도록 키움
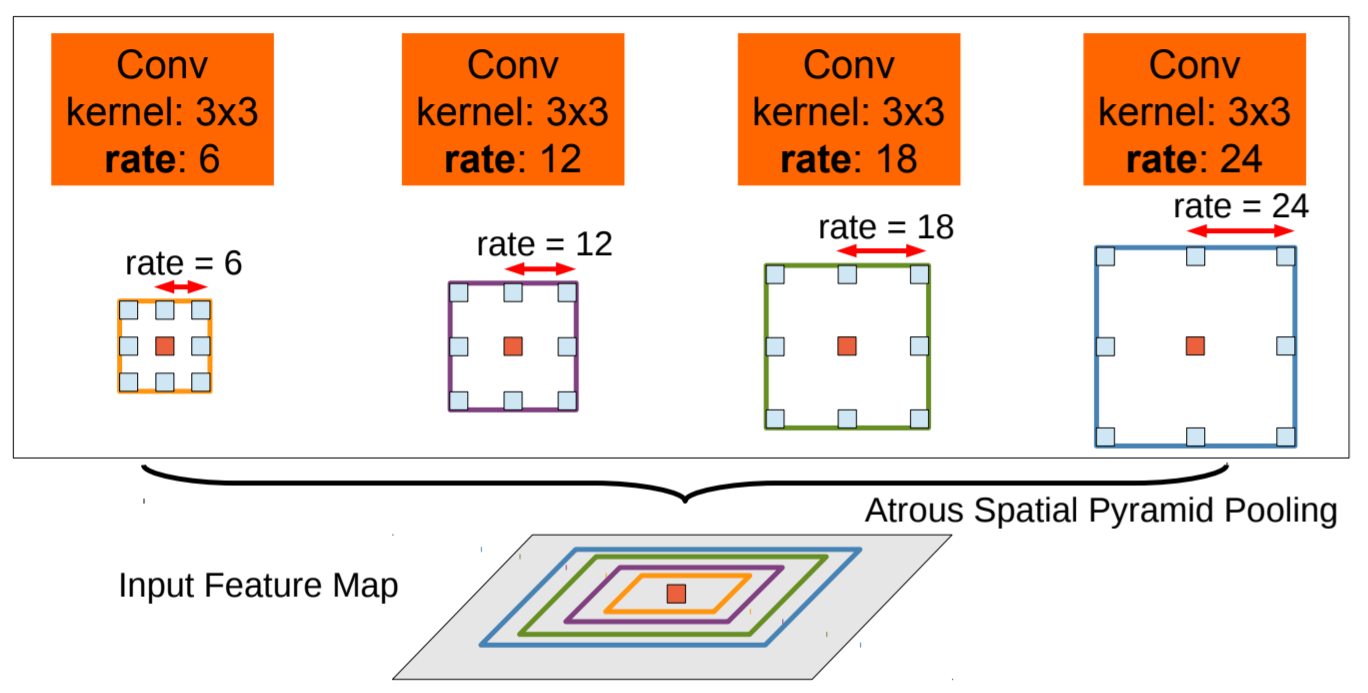
Multiscale image representations using atrous spatial pyramid pooling
-
DCNNs으로 다양한 사이즈의 objects를 예측하는 것은 어려움
-
기존 방식 : parallel DCNN branches를 통해 input image를 다양하게 rescale하여 score maps을 추출하고, 최종적으로 각 branches의 feature maps을 bilinear interpolation으로 input resolution과 맞춰주고 모두 융합
성능이 상당히 향상되지만, 다양한 scale의 input을 모두 처리해야 하기 때문에 계산 비용 문제가 있음
- ASPP : 다양한 sampling rates를 갖는 atrous convolutional layers를 parallel하게 사용
분리된 branches로 features가 추출되고, 모두 융합시켜 최종 output을 냄
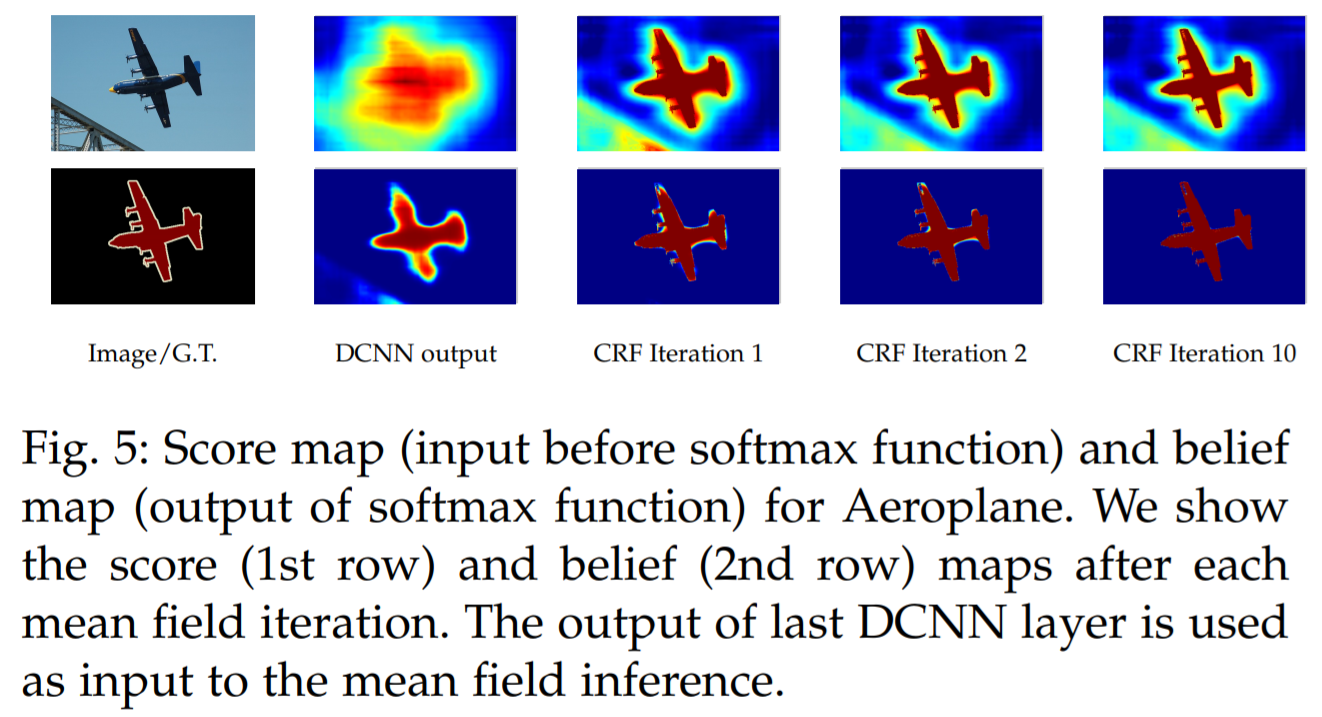
Structured prediction with fully-connected conditional random fields for accurate boundary recovery
- DCNNs의 recognition capacity와 fully connected CRFs의 localization accuracy를 결합하여 성능을 올림

Leave a comment