[Paper Review] Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook
Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook.
Ye, Mang, et al. “Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook.” arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.04193 (2020).
Abstract
-
person re-identification(Re-ID) : 여러개의 겹치지 않는 cameras에서 찾고자 하는 사람을 찾는 것
-
Re-ID는 closed-world와 open-world 두가지 카테고리로 나누어질 수 있음
- closed-world : deep feature representation learning, deep metric learning, ranking optimization
성능에 한계점이 생기면서, open-world 방식들이 등장
- open-world : 5가지로 나눠질 수 있음
- 기존 방식들의 장점을 분석함으로써, 강력한 AGW baseline을 디자인
SOTA를 달성하거나, single/cross-modality Re-ID taske에서 비교할만한 성능을 냄
- person Re-ID를 위한 새로운 evaluation metric mINP 도입
올바른 매칭을 찾는 것에 대한 cost를 나타냄
- 마지막으로, 중요하지만 조사되지 않았던 이슈들에 대해 토론함
Introduction
- person Re-ID : 중복되지 않는 카메라들 사이에서 특정 인물을 찾는 문제
query(찾고자하는 사람)가 주어지면, 해당 인물이 특정 시간 다른 장소의 카메라에 의해 발견되었는지 알아내는 것이 목적
query person은 image, video sequence, text description으로 표현됨
- 대학교 캠퍼스, 공원, 도로 등등에서 감시카메라가 증가하고 공공 안전이 중요시되면서, Re-ID의 필요성이 증가하고 많은 발전을 이룸
-
person Re-ID의 challenging 원인 : different view points, low-resolution, illumination changes, unconstrained poses, occlusions, heterogeneous modalities 등등
-
deep learning을 통해 많은 발전이 있었지만, 여전히 현실에 적용하기에는 어려움이 있음
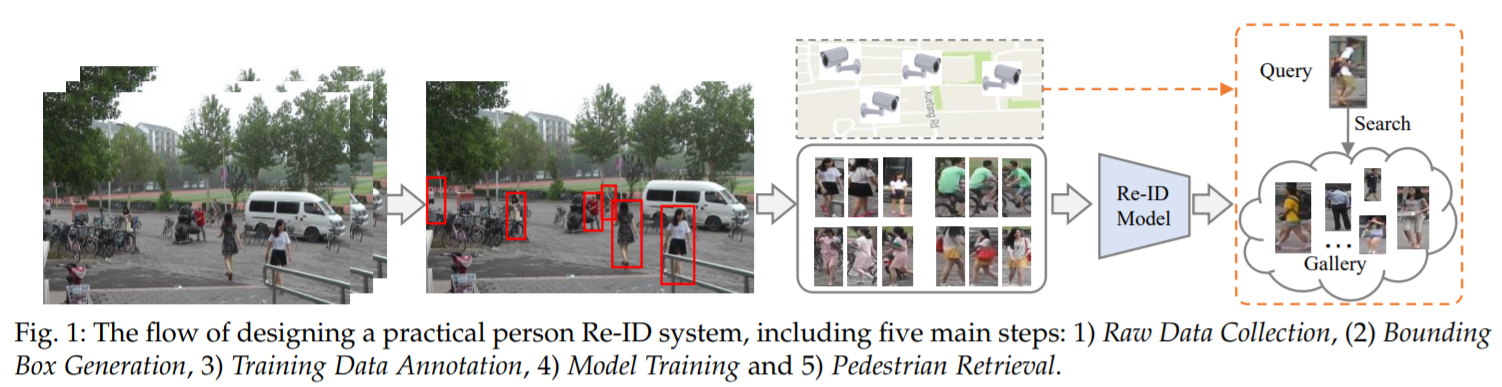
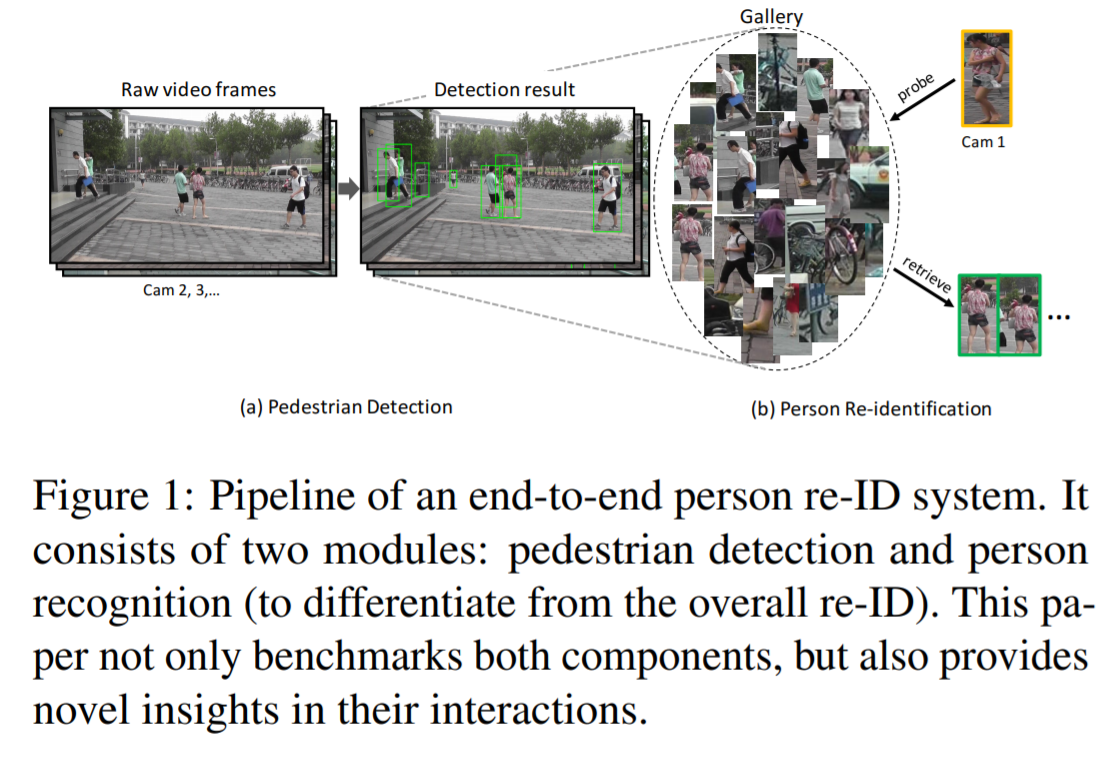
person Re-ID system
1) step 1 : raw data collection
감시카메라로부터 raw video data를 얻는 것으로, 이 data는 복잡하고 노이즈가 있는 background clutter를 포함
2) step 2 : bounding box generation
얻은 데이터에서 사람이 포함되어 있도록 bounding boxes를 추출
일반적으로, person detection이나 tracking 알고리즘에 의해 수행됨
3) step 3: training data annotation
cross-camera labels을 annotation
cross-camera 큰 차이 때문에, Re-ID model 학습을 위해서 필수적인 단계
4) step 4 : model training
구별적이고 강력한 Re-ID model을 학습시키기 위한 제일 중요한 단계
feature representation learning, distance metric learning, 두 방식의 결합 등등
5) step 5 : pedestrian retrieval
query와 gallery set이 주어지면, 학습된 Re-ID model을 사용하여 feature representations을 추출하고 query-to-gallery similarity를 계산하여 retrieved ranking list가 얻어짐
Closed-world person re-identification
- 5-assumptions
1) 사람은 single-modality visible cameras로 촬영됨
2) bounding box로 사람을 나타냄
3) annotation된 데이터세트가 충분하게 구성되어있음
4) annotation은 거의 정확함
5) query person은 gallery set에 반드시 존재함
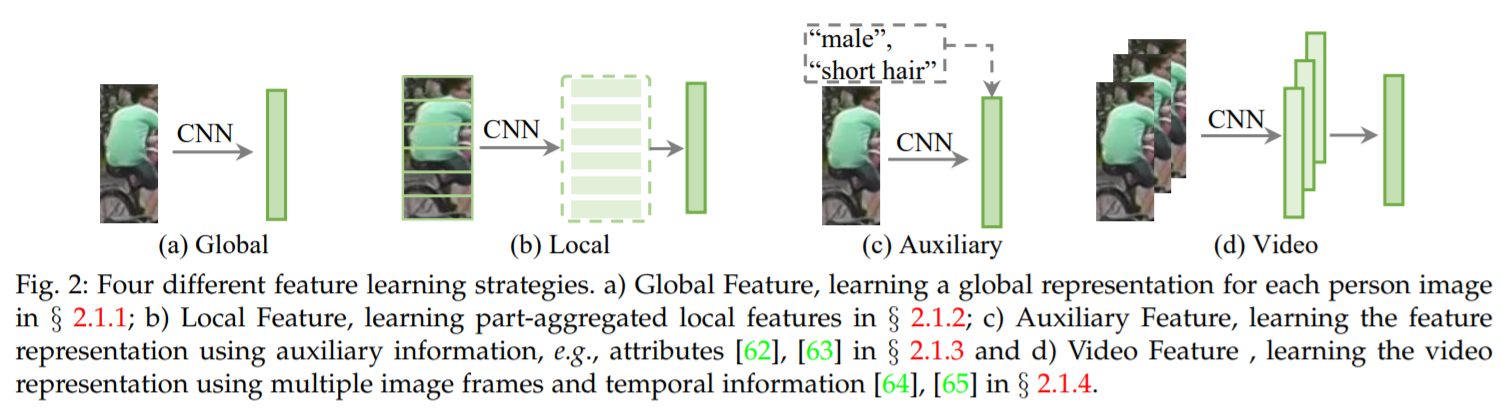
Feature representation learning
Global feature representation learning
-
각 사람의 이미지에서 global feature vector를 추출하여 Re-ID 수행
-
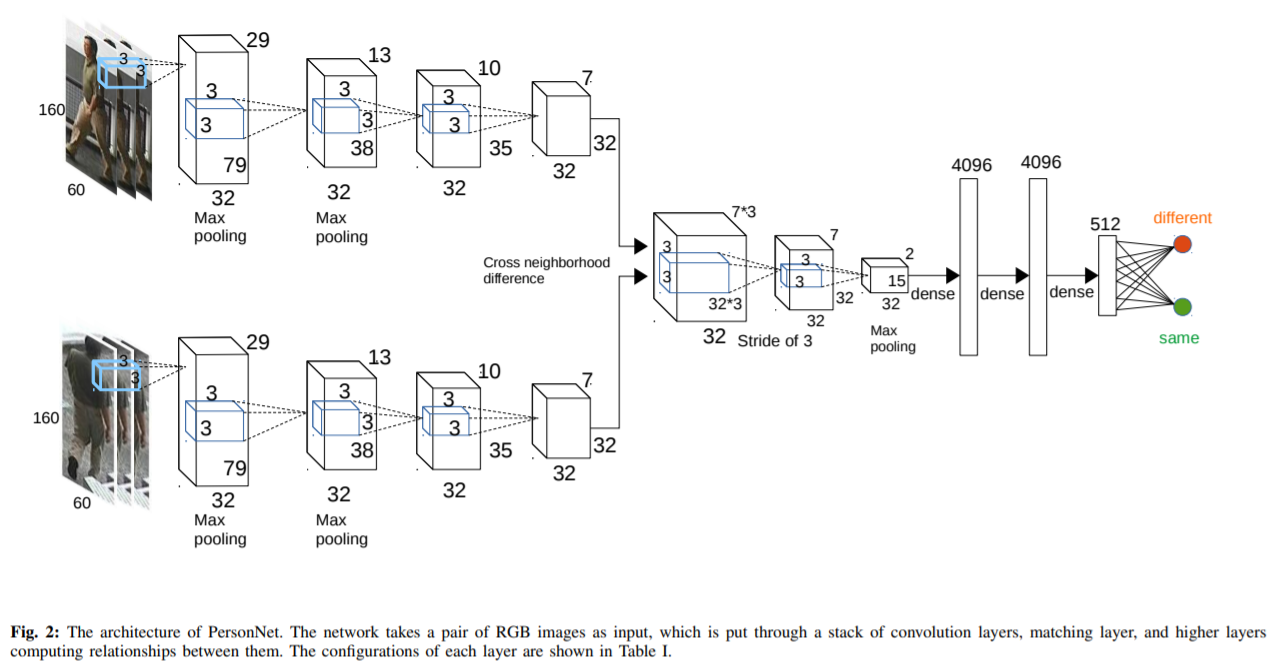
[73] : fine-grained features를 위해 작은 사이즈의 convolutional filters를 사용하는 PersonNet 디자인
high-level features와 그에 해당하는 similarity metric을 동시에 학습하는 deep end-to-end neural network 제안
input : pair of raw RGB images / output : 두 사람이 동일 인물인지를 나타내는 similarity value
depth를 10 weight layers로 증가시키고 매우 작은 convolution filters(3x3)를 사용하면서, 상당한 성능 향상을 보임
adaptive Root-Mean-Square(RMSProp) gradient decent 알고리즘 사용
- [74] : single-image representation(SIR)와 cross-image representation(CIR)로 구성되어 있는 joint learning framework 제안
triplet loss를 사용하여 학습을 진행
- [46] : ID-discriminative Embedding(IDE) model 제안
각 identity를 다른 class로 보면서, person Re-ID를 multi-class classification 문제로 해결
- [77] : 다른 scales에서 구별적인 features를 얻기 위해, multi-scale deep representation learning model 제안
person retrieval을 위한 적절한 scale을 적응적으로 찾음
- [78] : 픽셀 단위 discriminative features를 얻고, 다양한 자세 변화에 강력해지기 위해 Human semantic parsing 기술을 적용
- Attention information
representation learning을 향상시키기 위해 사용
1) For attention within the person image
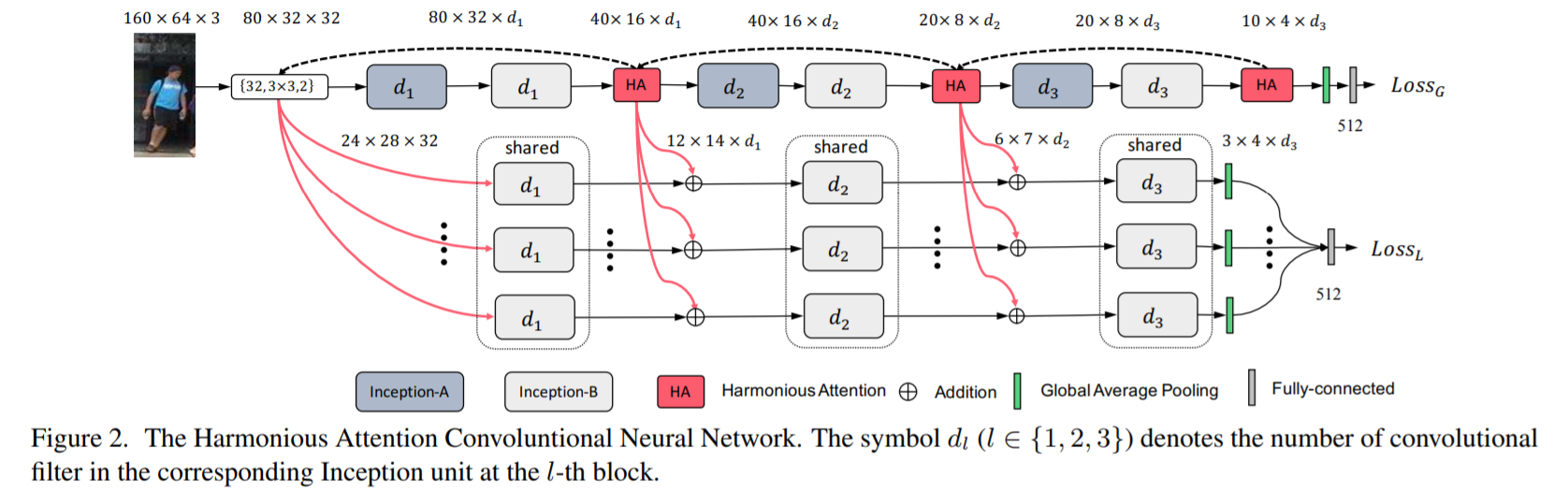
- [79] : Harmonious Attention CNN(HA-CNN) model 제안
기존의 방식들은 person bounding box images를 well-aligned images라고 가정하지만, 이는 임의의 aligned person images에 대해서 취약할 수 있음
misalignment에 강력해지기 위해 soft pixel attention과 hard regional attention을 공동으로 학습
하나의 CNN에서 attention selection과 feature representation을 공동으로 학습하는 것의 이점을 보여줌
새로운 Harmonious Attention CNN(HA-CNN) model 구현 : feature representations의 최적화와 함께, soft pixel attention과 hard regional attention을 공동으로 학습
- [80] : 채널 단위 feature response를 조정하기 위한 Fully Attentional Block(FAB) 제안
FAB는 다른 CNN 구조에도 적용될 수 있음
- [81] : Kronecker Product Matching(KPM) module 제안
soft warping 기법을 통해 feature maps의 alignment 수행
-
[82] : convolutional 구조로 feature maps의 alignment를 수행하는 BraidNet 제안
-
[83] : spatial, channel 단위 attention을 수행하는 self-critical reinforcement learning
-
[84] : Mask-Guided Contrastive Attention Model(MGCAM) 제안
region-level triplet loss로 학습을 하며, background clutter의 영향을 제거함
2) For attention across multiple person images
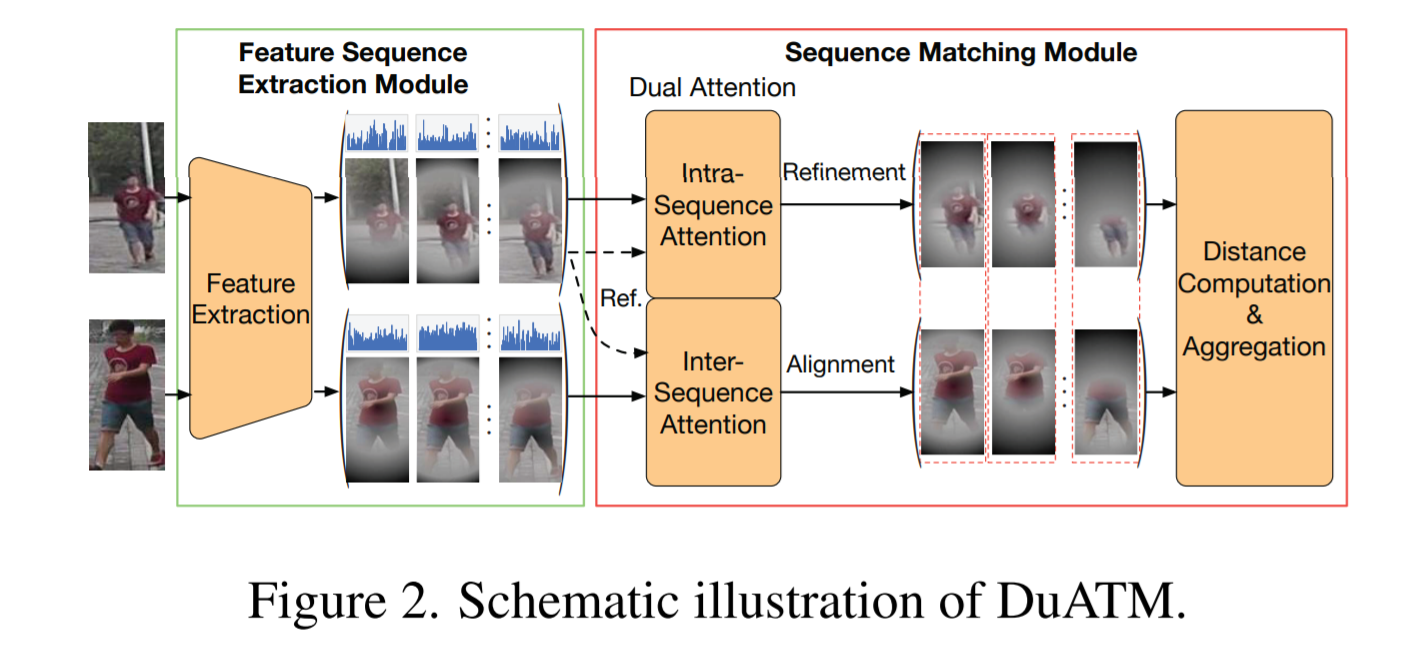
- [85] : context-aware attentive feature learning 방식 제안
기존의 Re-ID 방식들은 pedestrian을 하나의 feature vector로 나타내고, metric space에서 그들을 매칭함
하지만, 하나의 feature vector는 현실세계에서 자주 발생하는 시각적 애매모호함을 해결하기 어려움
pair-wise feature alignment와 refinement를 위해, intra-sequence와 inter-sequence 통합
temporal 정보에 의존적이지 않기 때문에, 이미지 기반 Re-ID에서 multiple images를 하나의 sequence로 만들어 냄
Dual ATtention Matching network(DuATM) : context-aware feature sequences 학습과 attentive sequence 비교를 동시에 수행하는 새로운 end-to-end framework 제안
DuATM framework의 핵심요소는 dual attention mechanism
-
intra-sequence attention이 feature refinement에 사용
-
inter-sequence attention이 feature-pair alignment에 사용
DuATM network를 decorrelation loss와 cross-entropy loss를 돕는 triplet loss를 사용하여 siamese network로 학습
-
[86] : attention consistency를 갖는 siamese network를 제안
-
[87] : multiple images 간 attention consistency가 고려됨
-
[88] : group similarity가 cross-image attention을 하는 또 다른 방법
통합된 conditionalrandom field framework에서 image 기반 local, global similarities 모델링
- [89] : spectral feature transformation에도 group similarity 적용
Local feature representation learning
- part/region aggregated features 학습
misalignment variations에 강력해짐
-
main trend : 전체 body representation과 local part features를 결합
-
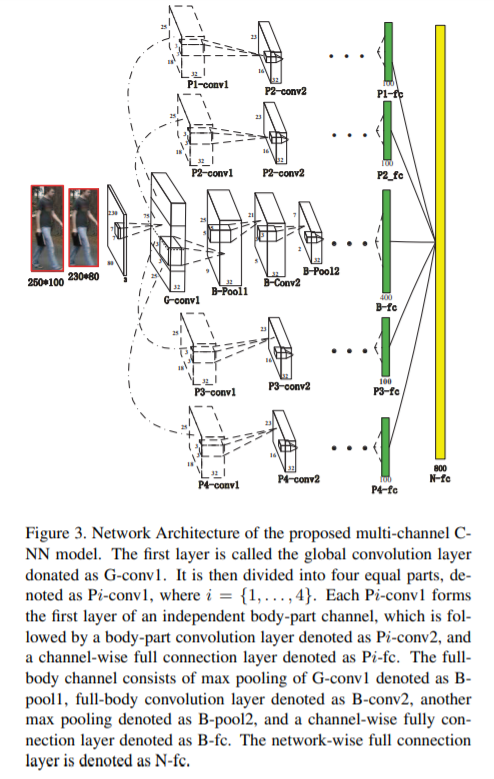
[92] : triplet 학습 framework에서 local body part features와 global full body features를 통합시키는 multi-channel parts-aggregated deep convolutional network 제안
기존의 challenge : 서로 다른 카메라들 사이에서 person Re-ID를 수행하는 것은 어려움
새로운 multi-channel parts-based convolutional neural network(CNN) model 제안
input persons의 global full-body features와 local body-parts features를 공동으로 학습하는 다양한 채널들로 이루어져 있음
같은 instance끼리는 가깝게 만들어주고, 다른 instance끼리는 멀게 만들어주는 향상된 triplet loss에 의해 학습됨
-
[93] : multi-scale convolutions을 쌓아 body parts 사이 local context 정보를 캡처
-
[16] : multi-stage feature decomposition, selective tree-structured fusion framework
-
[94] : body를 local regions(parts)로 분해, part-level matching 수행
-
[95] : global appearance와 local body part feature maps를 각각 추출하는 two-stream network 제안
bilinear-pooling layer를 통해 two streams을 결합시킴
-
background clutter에 대항할 수 있는 part level feature learning이 연구됨
-
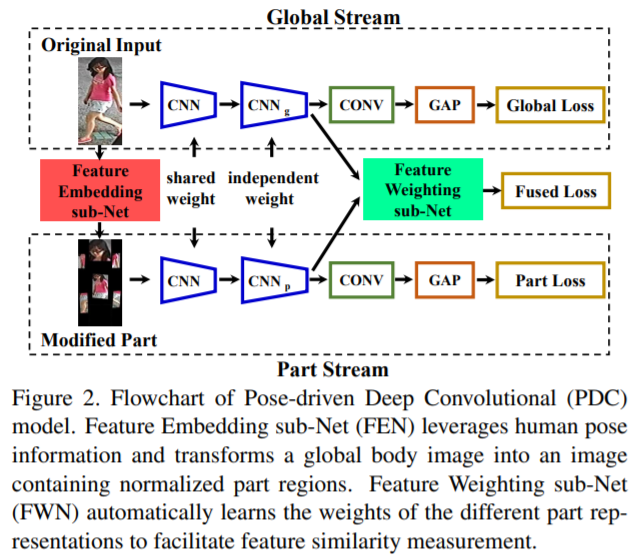
[96] : Pose driven Deep Convolutional(PCD) model 제안
challenge : pose, view point의 변형이 심하면, features의 매칭과 학습의 난이도가 상당히 높아짐
Pose-driven Deep Convolutional(PCD) model 제안 : 향상된 feature extraction, matching model을 end-to-end로 학습
pose 변형을 완화시키기 위해 human part 정보를 명시적으로 활용하고, global image와 다양한 local parts로부터 강력한 feature representations을 학습함
global human body와 local body parts의 features를 매칭시키기 위해, 적응적으로 feature fusion을 수행하는 pose driven feature weighting sub-network 디자인
- [97] : attention-aware compositional network로 원하지 않는 배경 feature를 가리기 위한 pose-guided part attention module 개발
또한, part-level features를 모아줌
-
[98] : person-region guided pooling deep neural network로 background bias를 해결하기 위해, human parsing 활용
-
[99] : two-stream network, full image representation learning + densely semantically-aligned part feature learning
-
[100] : human parts(사람의 신체)와 non-human parts(가방,소지품)가 alignment 됨
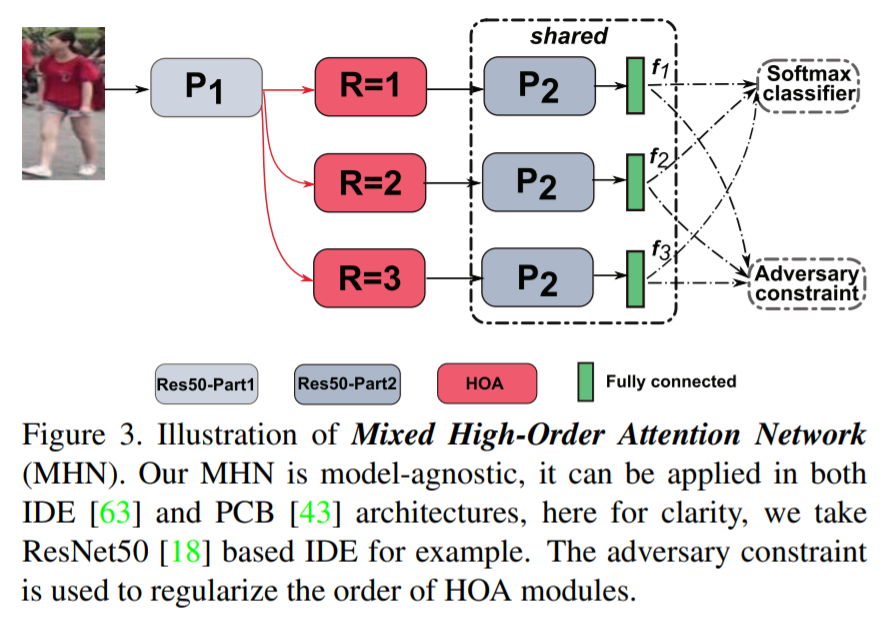
- [101] : 특정 part attention을 위해, high-order polynomial predictor가 scale maps 생성
기존의 방식들은 higher-order attention 메커니즘에 대해 연구가 거의 없음
attention 메커니즘에서 최초로 복잡한 high-order statics 정보를 활용하고 모델링하는 High-Order Attention(HOA) module 제안
pedestrians 사이 미묘한 차이를 포착하고 구별적인 attention proposals을 생성
Re-ID를 zero-shot learning 문제로 풀어내면서, Mixed High-Order Attention Network(MHN) 제안
명시적인 방식으로 attention 정보의 구별성과 풍부성을 향상시킴
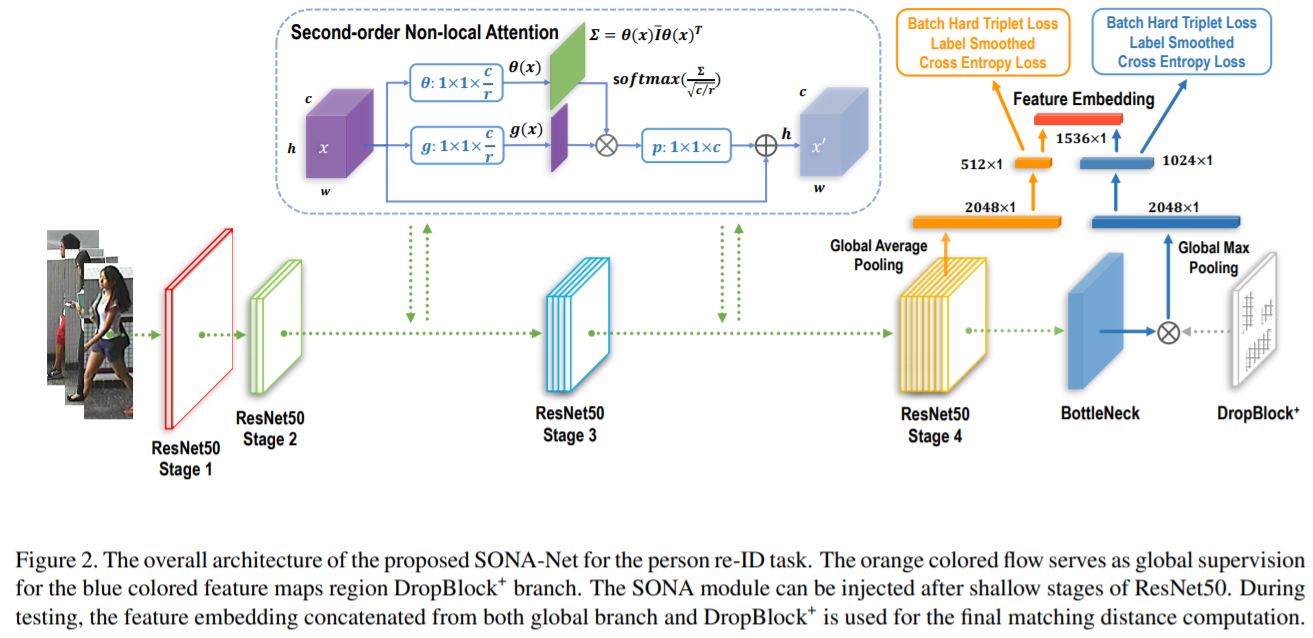
- [102] : long-range relationships을 직접 모델링하기 위해 second-order non-local attention 도입
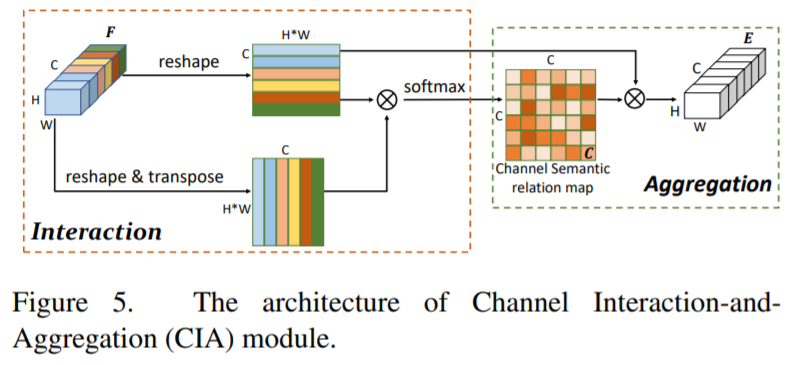
- [103] : Interaction-and Aggregation(IA)을 통해, spatial features 사이 inter-dependencies를 모델링하고 연관된 body part features를 융합
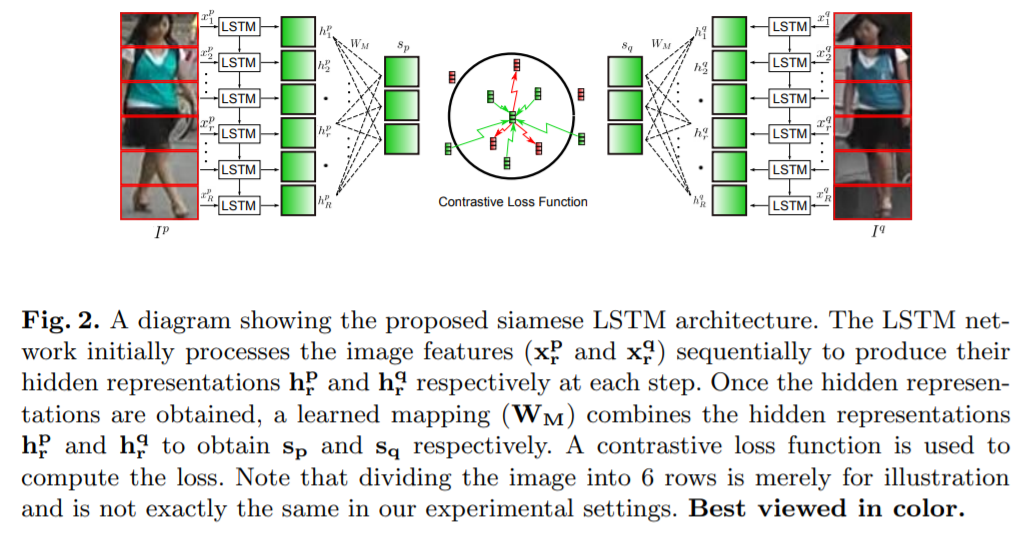
- [91] : pose estimation 없이 horizontal region features를 위해, Siamese Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) 구조를 도입
적응적으로, horizontal region features를 융합시킴
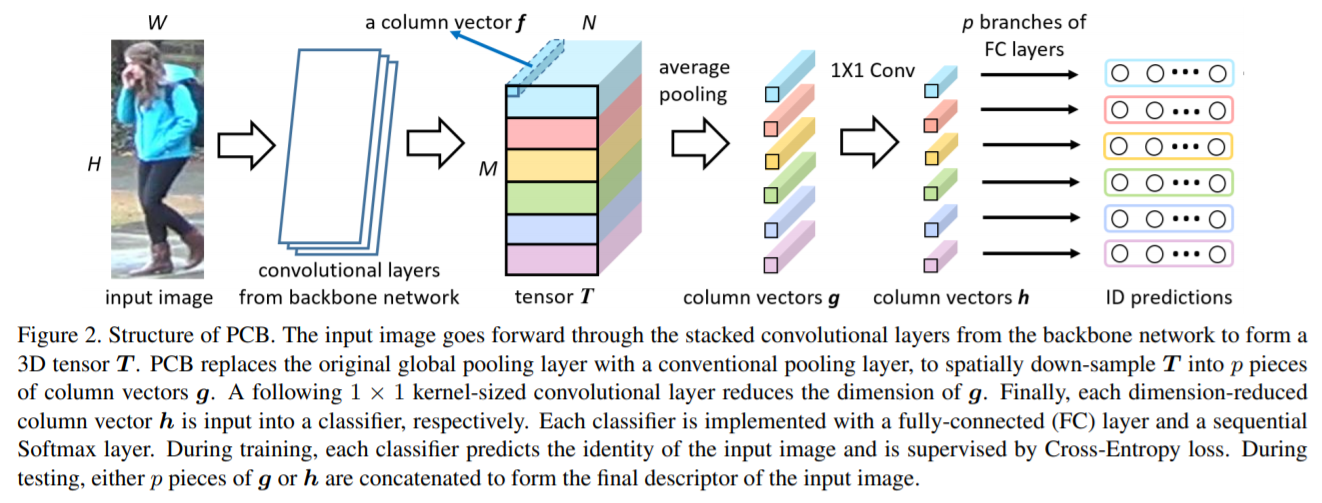
- [68] : strong Part-based Convolutional Baseline(PCB)가 다양한 classifiers로 part features를 학습하기 위한 uniform partition 전략으로 디자인 됨
또한, part 내부 일관성을 향상시키기 위한 refined part pooling 전략으로 성능 향상
- discussion
1) human parsing techniques
의미론적인 body parts를 얻을 수 있지만, 추가적인 pose detector가 필요하고 person Re-ID와 human pose estimation datasets 사이 큰 차이로 인한 잘못된 pose detection 결과가 영향을 끼칠 수 있음
2) uniform partition
horizontal stripe parts를 얻기 위해 사용하며 더 유연성이 있으나, heavy occlusion과 large background clutter에 민감함
Auxiliary feature representation learning
- feature representation을 강화하기 위해, 추가적인 annotated 정보나 generated/augmented 학습 샘플들을 필요로 함
-
Semantic Attributes
-
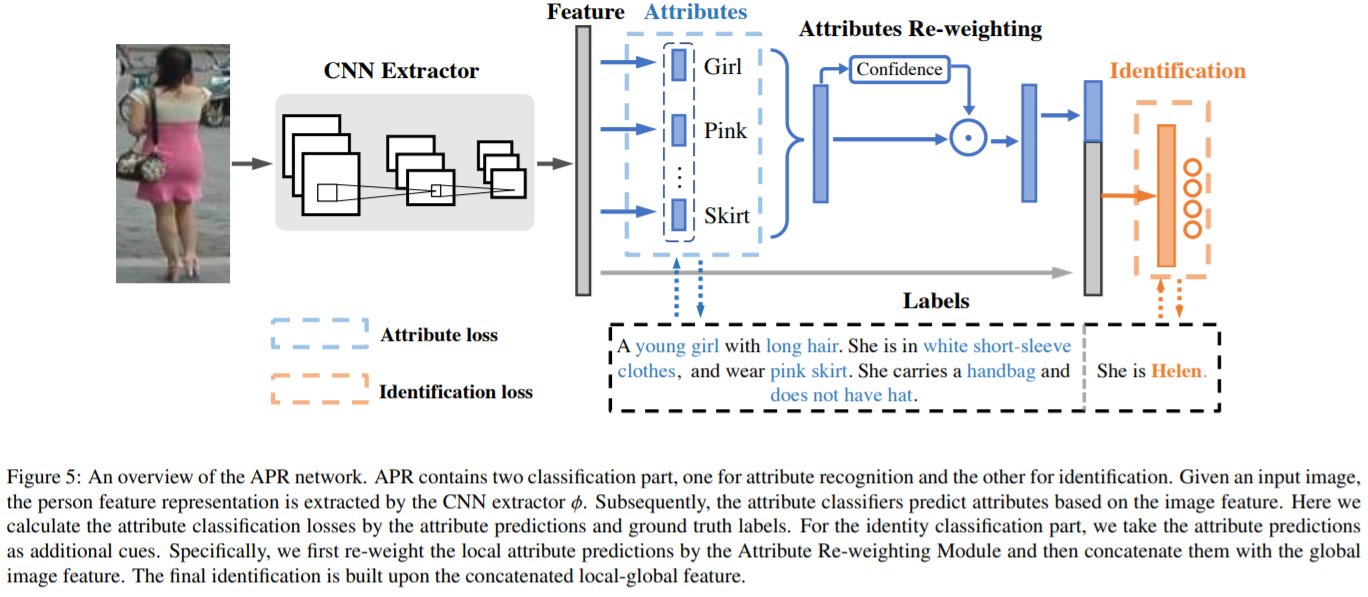
[63] : identity와 attribute(속성)를 공동으로 학습하는 baseline을 도입
상세한 부분 설명들을 포함하는 attributes는 re-ID model이 더 차별적인 feature representations을 학습할 수 있도록 도움을 줌
attribute labels과 ID labels 정보를 기반으로 하는 attribute person recognition(APR) network 제안
pedestrian attributes를 예측하는 동시에 re-ID embedding 학습하는 multi-task network
2개의 대규모 re-ID datasets를 위해 직접 sttribute labels을 annotation하였고, 두가지 task가 서로 얼마나 도움을 주는지 확인함
추가적으로, attributes 사이의 의존성과 연관성을 고려하여 attribute predictions을 re-weighting
- [62] : 예측된 semantic attribute 정보를 통합함으로써 deep attribute learning framework를 제안
semi-supervised learning 방식으로 feature representation의 generalizability와 robustness 향상시킴
-
[107] : part feature learning을 향상시키기 위해 semantic attributes와 attention scheme을 통합시킴
-
[108] : video Re-ID feature representation learning을 위해 semantic attributes를 적용
-
[109] : unsupervised learning 방식으로 auxiliary supervision을 학습
-
[110] : 각 person image에 대한 language descriptions으로 global, local image-language associations를 수집하여 representation learning 수행
-
Viewpoint information
-
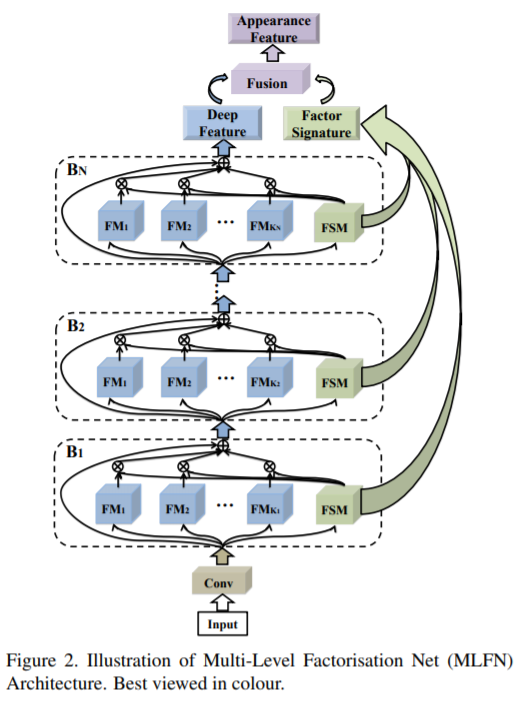
[111] : Multi-Level Factorisation Net(MLFN)은 identity-discriminative와 다양한 semantic levels에서의 view-invariant feature representations을 학습
Re-ID는 high, low semantic levels 모두에서 person apprearance의 차별적이고 다양한 view를 갖는 factors를 모델링하는 것이 아주 중요함
Multi-Level Factorisation Net(MLFN) 제안
수동적인 annotation 없이, 다양한 semantic levels에서 사람의 시각적 외향을 차별적인 factors로 분해하는 새로운 네트워크 구조
여러개의 블럭이 쌓여 있는 구조이고, 각 블럭은 다양한 factor modules과 factor selection modules을 포함
factor module : 특정한 레벨에서 잠재적인 factors를 만들어주는 역할
factor selection module : 각 input 이미지의 내용을 해석하기 위해, 동적으로 factor modules을 선택해주는 역할
- [112] : view confusion feature learning과 함께, view-invariant identity 단위 representation을 추출
-
Domain information
-
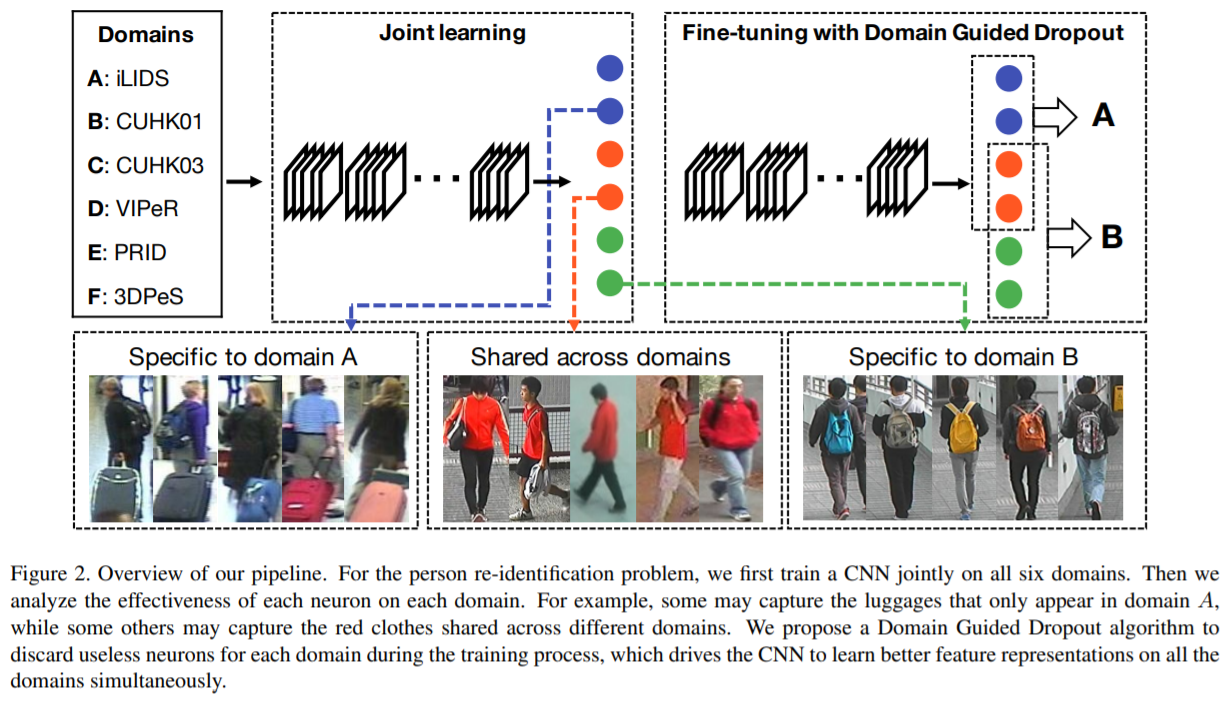
[45] : multi-domain deep feature representation learning을 위해, 적응적으로 domain-sharable, domain-specific neurons을 수집하기 위한 Domain Guided Dropout(DGD) 알고리즘을 디자인
다양한 도메인으로부터 deep feature representations을 학습하기 위한 CNN pipeline 제시
모든 도메인들에서의 데이터로 CNN을 학습시킬 때, 몇몇 신경세포들은 다른 도메인 간 공유된 representations을 학습함 (나머지 세포들은 특정 도메인 representations 학습)
이를 활용한 Domian Guided Dropout 알고리즘 제안
-
[113] : 각각의 카메라를 다른 domain으로 간주하는, multi-camera consistent matching constraint 제안
-
[17] : 특정 카메라 정보를 모델링하는 feature representation을 향상시키기 위해, 카메라 view point 정보나 탐지된 카메라 위치 정보를 적용
- Generation/Augmentation
auxiliary 정보로 augmented/GAN의 사용으로 생성된 images에 대한 내용
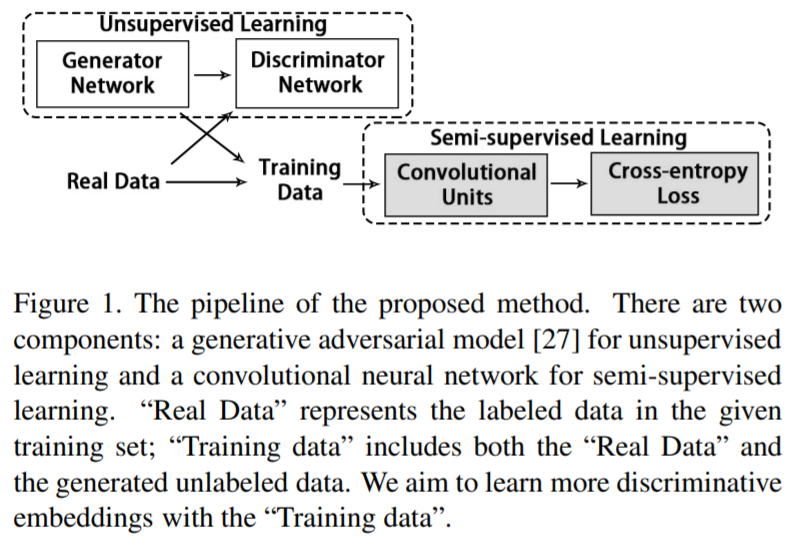
- [33] : person Re-ID에 GAN을 적용한 최초의 시도, 생성된 person images로 supervised feature representation learning을 향상시킴
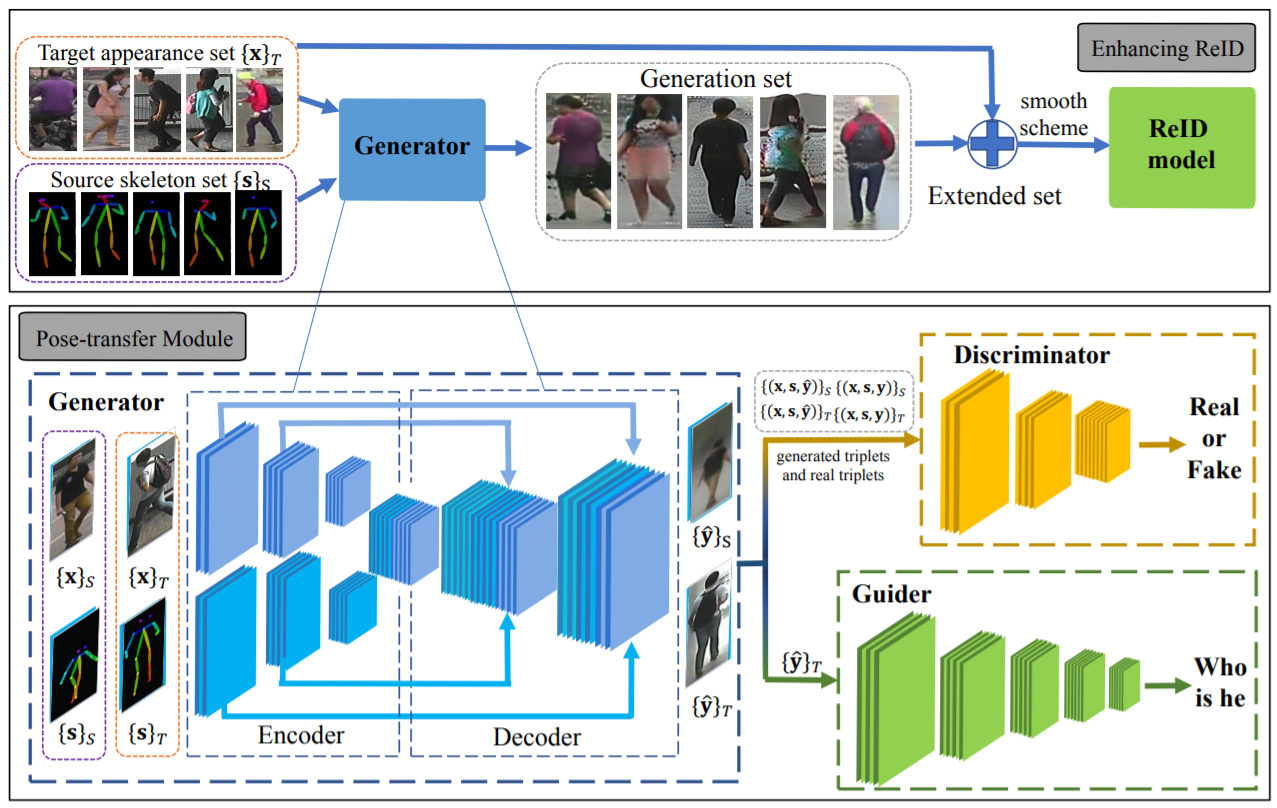
- [114] : GAN을 통해 새로운 포즈를 취한 사람의 이미지를 생성
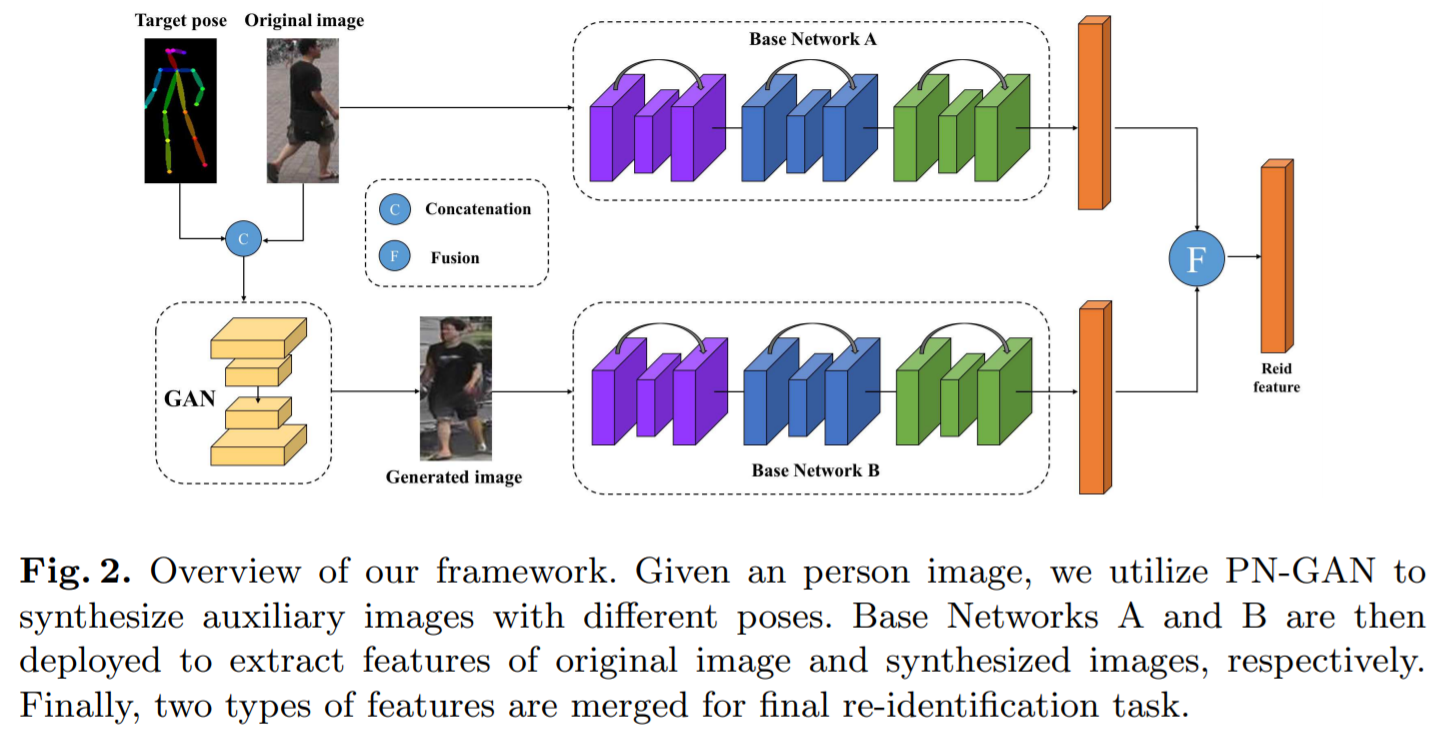
- [115] : 다양한 포즈에 대항하기 위한 pose-normalized image 생성
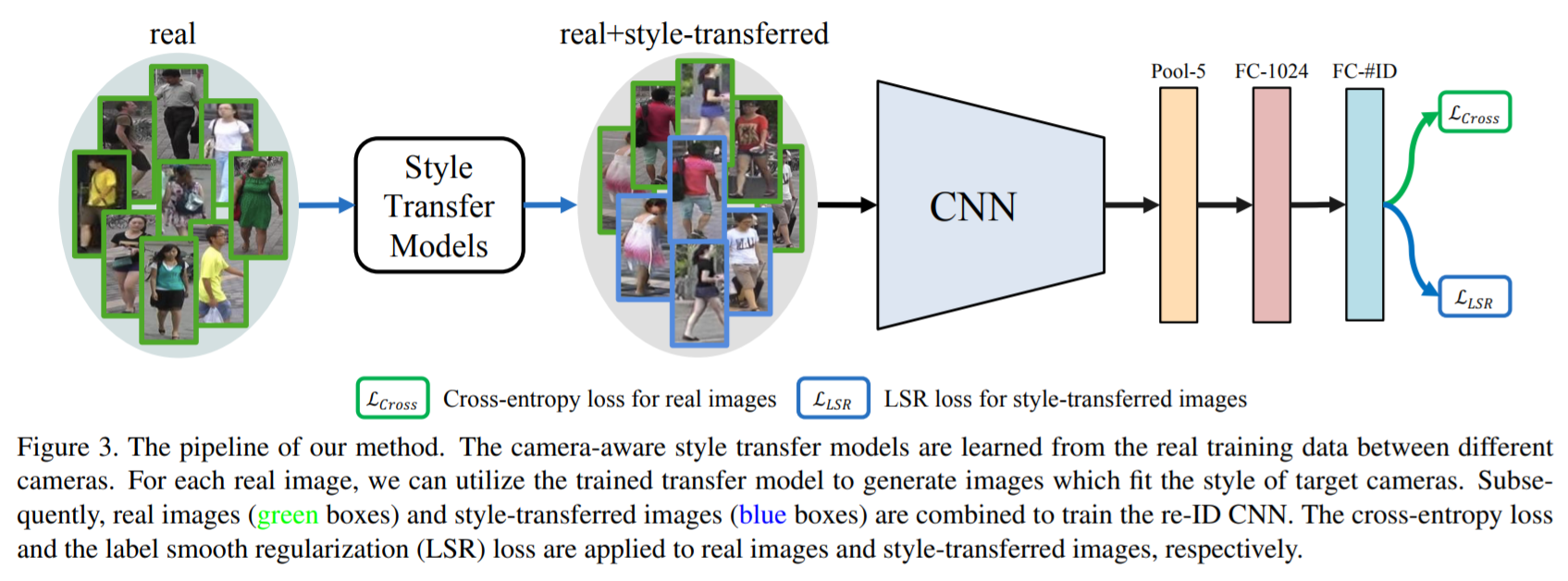
- [116] : 카메라간 큰 차이를 해결하기 위해, 이미지 생성과정에 camera style information을 도입
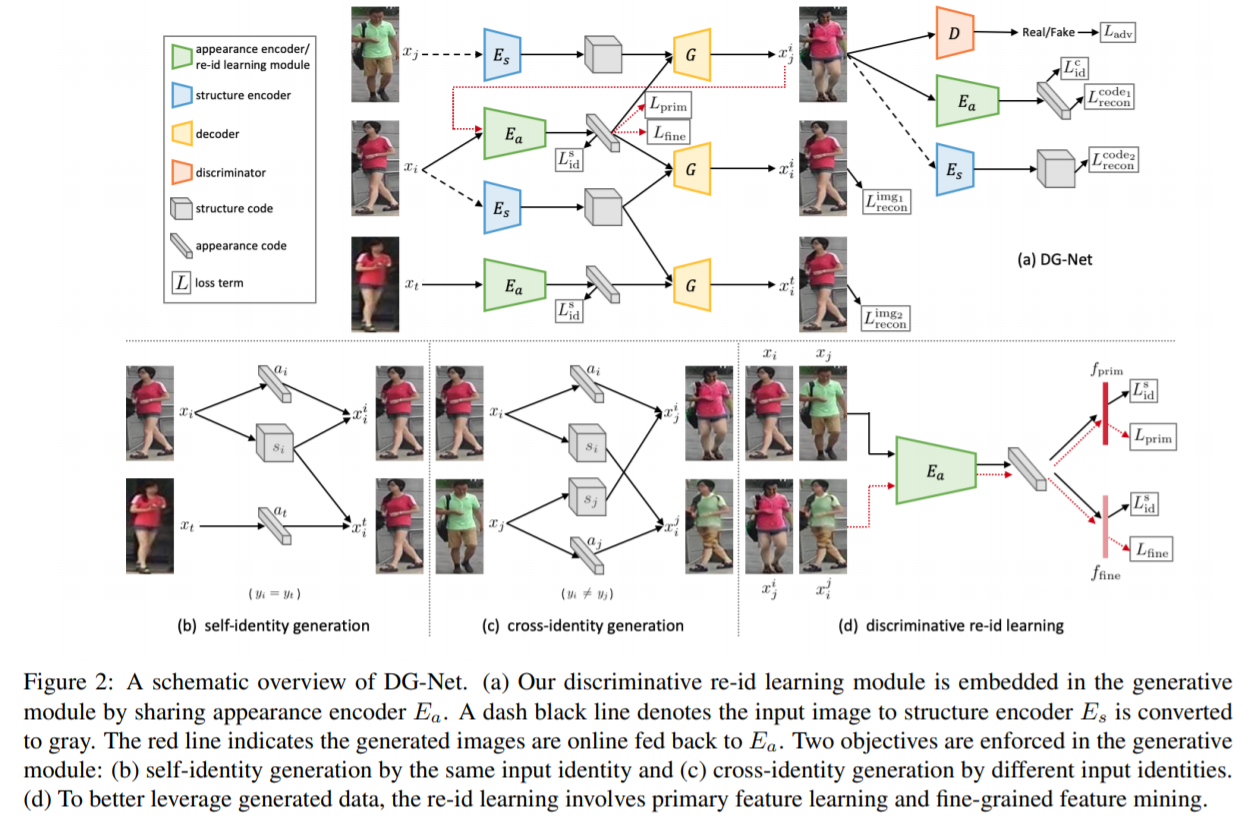
- [117] : 구별적인 feature와 일반적인 feature를 공동으로 학습하는 모델로 appearance와 structure code를 각각 학습하여 생성되는 이미지의 질을 높임
- [118], [119] : GAN으로 생성된 이미지를 사용하는 것은 unsupervised domain adaptation Re-ID에도 적용됨
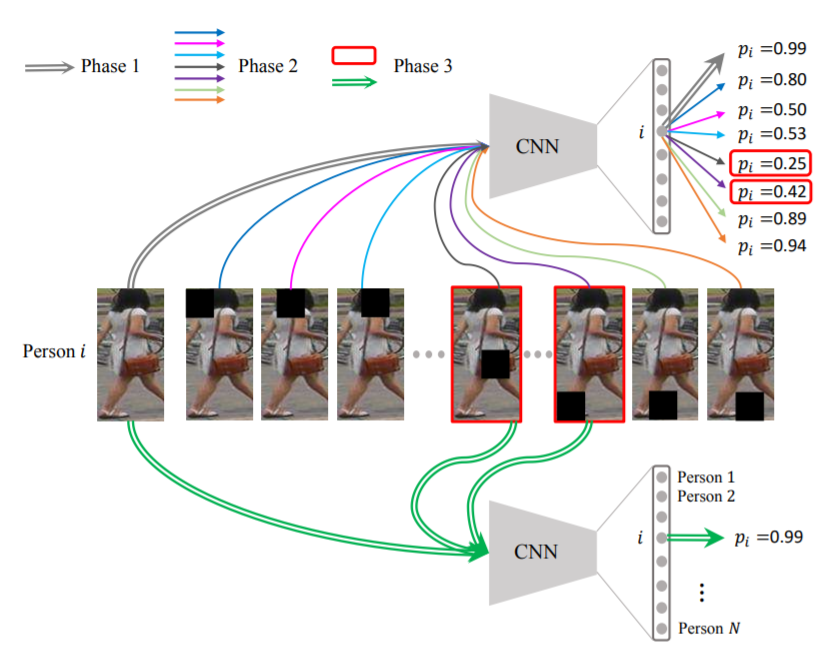
- [18] : augmented auxiliary information을 위해, 학습 데이터를 다양하게 하기 위해 가려진 샘플들이 생성됨
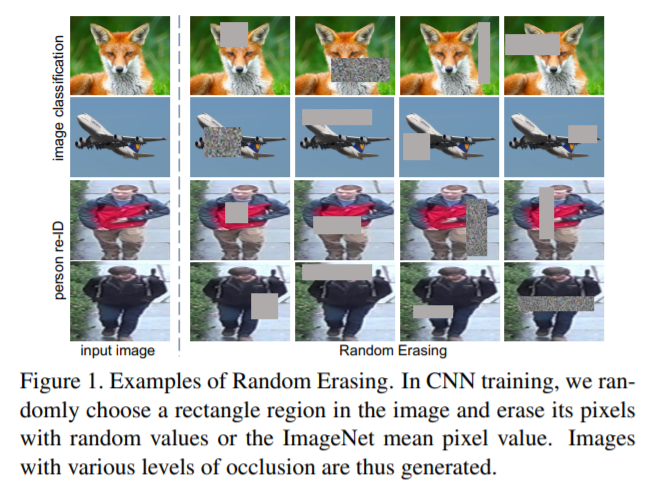
- [120] : random erasing 전략 사용 (input 이미지에 랜덤 노이즈를 추가)
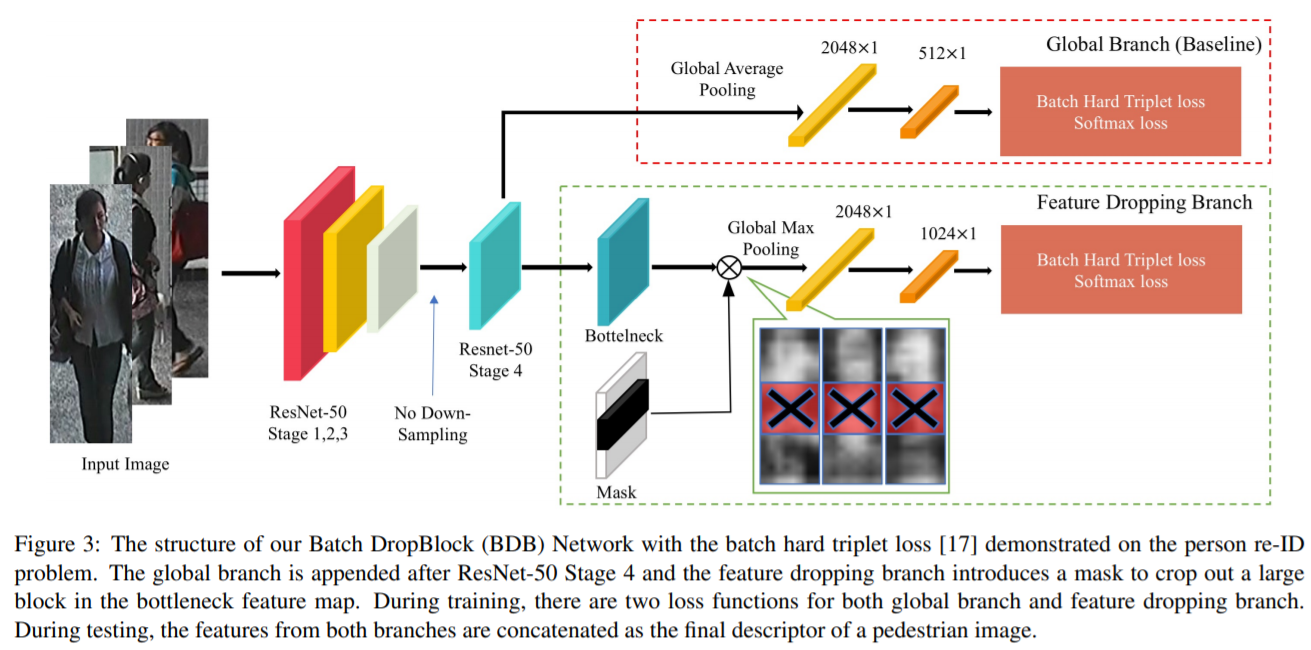
- [121] : batch DropBlock, attentive feature learning을 강화하기 위해 feature map에서 랜덤으로 region block을 drop
- [122] : 풍부한 supervision을 위해, 다양한 조명 환경에 놓여진 가상의 인물들을 생성
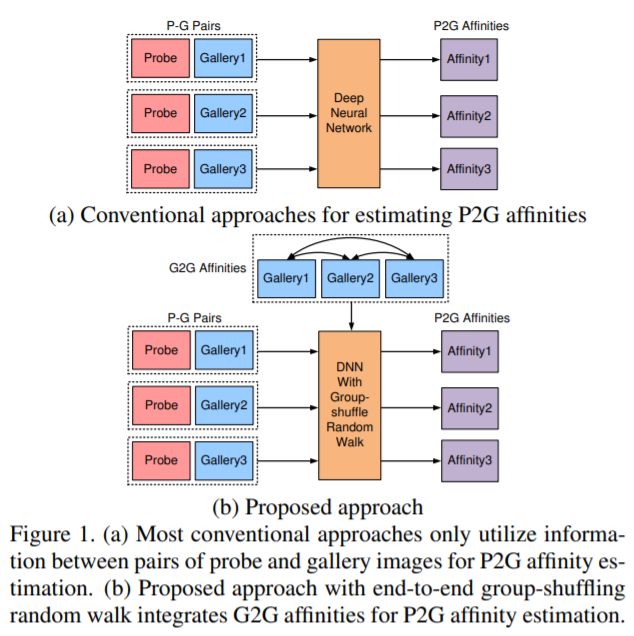
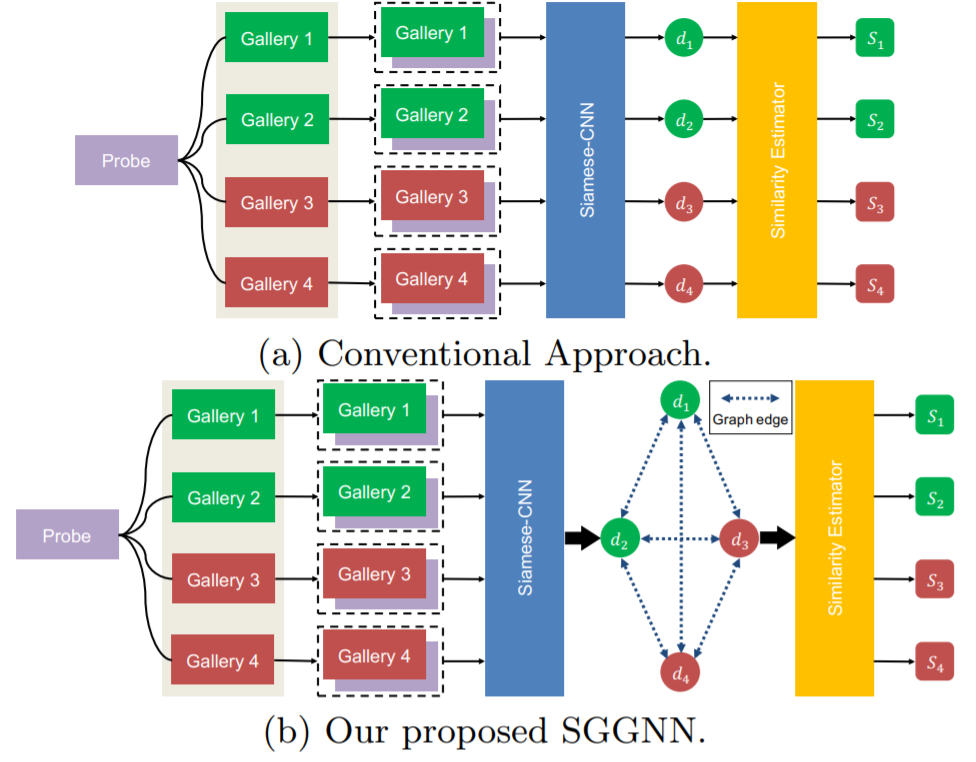
- [123] : deep group shuffling random walk framework 제안
end-to-end 방식으로 모든 갤러리 이미지들 사이의 관계를 활용하여 학습
- [124] : 서로 다른 probe-gallery 사이 유사도를 활용
- [125] : probe-gallery 측정을 향상시키기 위해, domain set을 도입하는 제한된 clustering 전략
Video feature representation learning
- video 기반 Re-ID는 사람이 video sequence(multiple frames)로 나타내어짐
풍부한 appearance와 temporal 정보를 활용할 수 있음
- 다양한 이미지를 활용하는 video feature representation learning이라는 challenge가 존재
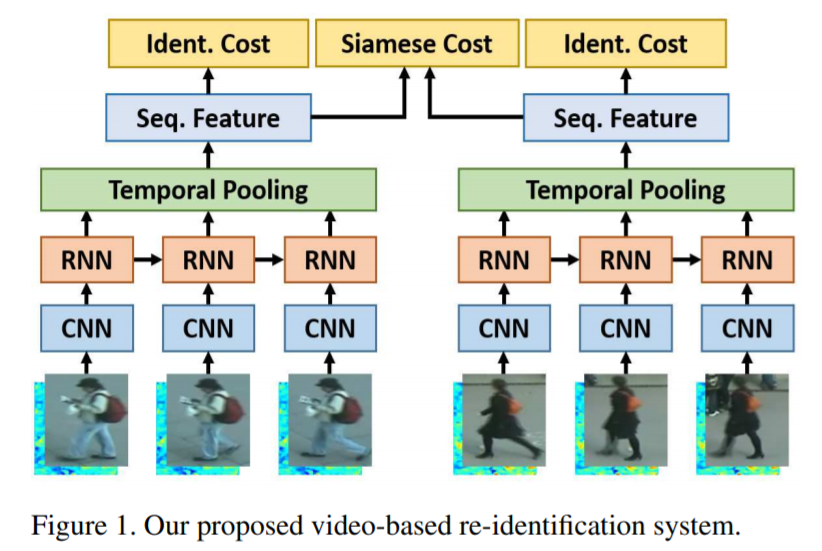
- [129] : 정확하고 자동적으로 temporal 정보를 포착하기 위해, recurrent neural network 사용
비디오 기반 Re-ID를 위한 새로운 recurrent neural network 구조 제안
video sequence가 주어지면, flow 정보를 이용하기 위해 recurrent final layer로 통합한 CNN을 사용하여 각 프레임으로부터 features를 추출
모든 시간 프레임에서의 features는 완성된 sequence를 위한 전체적인 appearance features를 제공하는 temporal pooling을 통해 결합
Siamese network : recurrent layer와 temporal pooling layer로 구성된 covnolutional network는 feature를 추출을 위해 공동으로 학습됨
apprearance 정보와 모션 정보를 포착하기 위해, colour 정보와 optical flow 정보를 사용
siamese network 구조로, temporal 정보 propagation과 temporal pooling layer를 공동으로 최적화시킴
-
[130] : spatial, temporal streams을 위한 weighted scheme 개발 (two stream)
-
[131] : LSTM 사용, frame-level human region representations을 융합시키기 위한 progressive/sequential fusion framework 제안
frame-level feature와 spatio-temporal appearance 정보를 공동으로 융합시킴
- [132] : cross-view person identification을 위한 triplet network 도입
view-specific optical flow learning과 underlying skeleton feature learning을 포함
- [108] : feature disentangling과 frame re-weighting과 함께 semantic attributes를 적용
-
video sequences에서 outlier가 포함되는 것을 피할 수 없기 때문에, attention scheme을 적용하는 방식들이 많이 존재
-
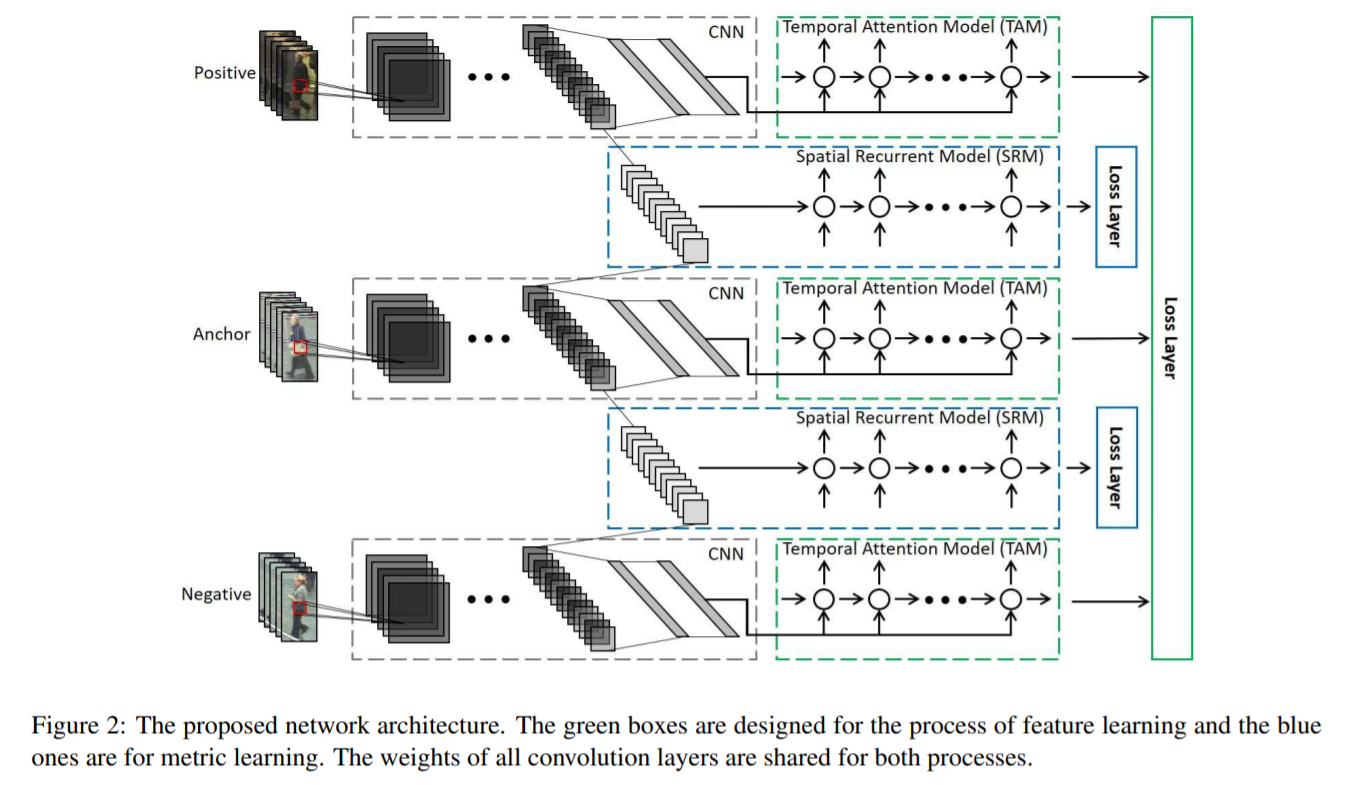
[133] : 비디오에서 자동적으로 가장 구별적인 frames을 선택하기 위한 temporal attention model 제안
person Re-ID에 대한 연구는 늘어났지만 비디오 기반 방식들은 별로 없음 (대부분 이미지 기반)
기존의 이미지 기반 방식들은 2-step으로 feature learning과 metric learning을 수행하는데, 이는 temporal 정보와 spatial 정보를 완전히 사용하지 못함
비디오 기반 Re-ID를 연구하고 end-to-end 방식으로 features와 metric을 공동으로 학습하는 deep neural network 구조 제안
제안된 방식은 temporal attention model에 의해, 자동적으로 가장 차별적인 frames을 고를 수 있음
게다가, 다른 pedestrian과의 유사도를 측정할때 spatial recurrent model로 각 위치의 주변 정보를 통합시킴
-
[134] : video sequence에서 중요한 frames을 선택하기 위한 joint Spatial and Temporal Attention Pooling Network(ASTPN) 제안
-
[135] : co-segmentation에서 영감을 얻은 attention model, 여러개의 video frames 간 salient features 탐지
-
[136] : video sequence에서 body parts를 구별하기 위해 다양한 regularization 사용
-
[138] : 다양한 길이의 video sequences를 다룰 수 있도록, 긴 video seqences를 여러개의 짧은 snippets으로 나눔
-
[19] : 자동으로 가려진 부분을 채우기 위해 여러개의 video frames을 활용함
Architecture design
- ResNet50을 backbone으로 사용하는 경우가 많았고, 마지막 convolutional stripe/size를 1으로 수정하여 사용
마지막 pooling layer에서 adaptive average pooling을 사용하고, 뒤에 batch normalization을 갖는 bottleneck layer 추가
- filter pairing neural network(FPNN) : Re-ID를 위한 네트워크가 처음으로 제안
misalignment와 occlusion을 공동으로 다룸
-
[141] : patch feature의 차이를 포착하기 위해 improved neighbor difference layer를 제안
-
[82] : WConv layer와 Channel Scaling layer로 이루어진 BraidNet 제안
WConv layer : misalignments를 해결하기 위해 두 이미지 사이 다른 정보를 추출
Channel Scaling layer : 각 input channel의 scaling factor를 최적화
- [111] : Multi-Level Factorisation Net(MLFN) 제안
다양한 semantic level에서 identity-discriminative feature와 view-invariant feature의 representations을 학습
- [142] : convolution similarity module을 갖는 efficient fully convolutional siamese network 제안
multi-level similarity measurement를 최적화
- [143] : 효율적이고 작은 네트워크인 Omni Scale Network(OSNet) 제안
multi-scale feature learning을 하기 위해, 다양한 convolutional streams으로 구성된 residual block 도입
계산 효율을 보장하기 위해 point-wise, depth-wise convolutions이 통합되어 있음
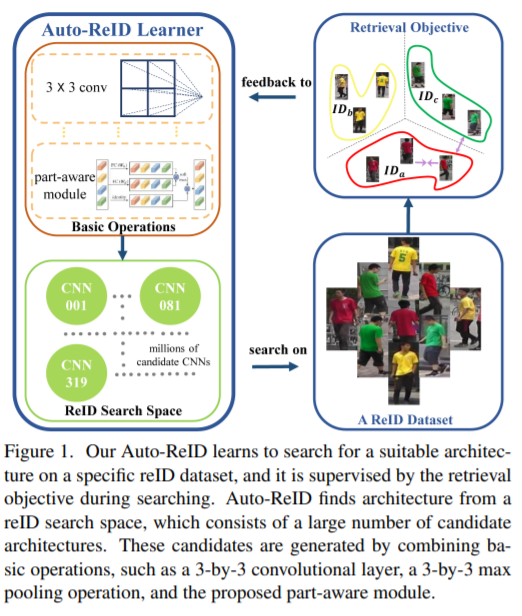
- [144] : Auto-Re-ID model 제안
효율적이고 효과적인 자동 신경망 구조
Deep metric learning
Loss function design
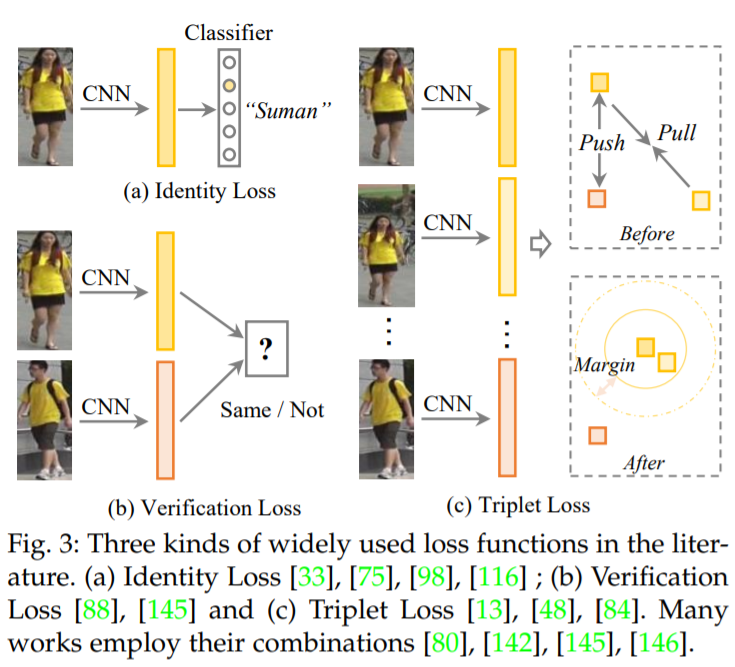
- Identity Loss
Re-ID를 image classification 문제로 해결(각 identity가 다른 class)
pooling layer나 embedding layer의 output이 feature extractor 역할을 수행
the cross-entropy
label y를 갖는 input image x가 주어지면, x의 class가 y일 확률이 softmax 함수로 encoding 됨
training 중 hard samples을 자동적으로 수집하며, training이 쉬움
- Verification loss
contrastive loss나 binary verification loss를 통해, pairwise relationship을 최적화함
[Contrastive loss]
상대적인 pairwise distance 비교의 향상을 위한 손실 함수
2개의 input samples 사이 거리는 Euclidean distance로 계산
[Binary verification loss]
input image pair의 positive(정답)와 negative(오답)를 구별하기 위한 손실 함수
the verification loss with cross-entropy
verification network는 서로 다른 feature를 정답 또는 오답으로 분류함
성능 향상을 위해, identity loss와 결합하여 사용되기도 함
- Triplet loss
Re-ID를 retrieval ranking 문제로 해결
idea : 정답 pair 사이 거리는 좁아야하고, 오답 pair 사이 거리는 넓어야 함
the triplet loss with a margin parameter
anchor sample x_i, positive sample x_j, negative sample x_k
2개의 samples 사이 거리 d는 Euclidean distance로 계산
- OIM loss : Online Instance Matching loss
instance features가 저장되어 있는 memory bank scheme
memory scheme은 unsupervised domain adaptive Re-ID에도 적용됨
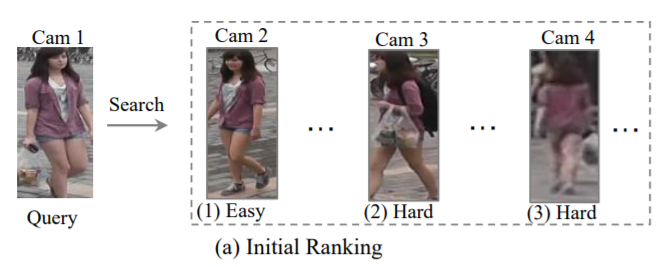
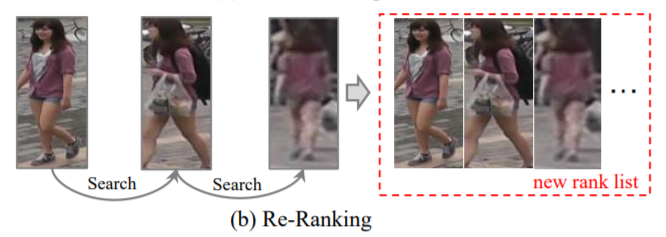
Ranking Optimization
초기 ranking list가 주어지면, 자동적인 gallery-to-gallery similarity mining 또는 human interaction에 의해 ranking 순서가 최적화됨
- Re-ranking
초기 ranking list를 최적화히기 위해, gallery-to-gallery similarity를 활용
top-ranked similarity pulling, bottom-ranked dissimilarity pushing
[Query adaptive]
query difference를 고려하면서, 균일한 searching engine을 대체하기 위해 query adaptive retrieval 전략 사용
[Human interaction]
ranking list를 최적화시키기 위해 human feedback을 사용
- Rank Fusion
retrieval 성능 향상을 위해, 다른 모델에서 얻어진 다양한 ranking lists를 활용
Datasets and Evaluation
Open-world person re-identification
Heterogeneous Re-ID
-
Depth-based Re-ID
-
depth images는 body shape과 skeleton 정보를 포착하고, 이는 다양한 illumination/clothes 환경에서 Re-ID를 가능하게 함
-
[183] : depth-based persion identification을 해결하기 위한 recurrent attention-based model 제안
reinforcement learning task로, human body의 작고 구별적인 local region을 식별하기 위해 convolutional network와 recurrent network 결합
RGB 정보가 없는 이미지에서 identity를 구별할 수 있도록 body shape와 motion dynamic 정보 사용
4D spatio-temporal 신호를 사용하여 해결
depth image만 주어진 dataset에서 SOTA 성능
view point, appearance, volumetric changes에도 강함
interpolation 처리를 통해, 2D, 3D, 4D 정보를 공유함
-
Text-to-image Re-ID
-
text description과 RGB images 사이 매칭을 통해 문제를 해결
-
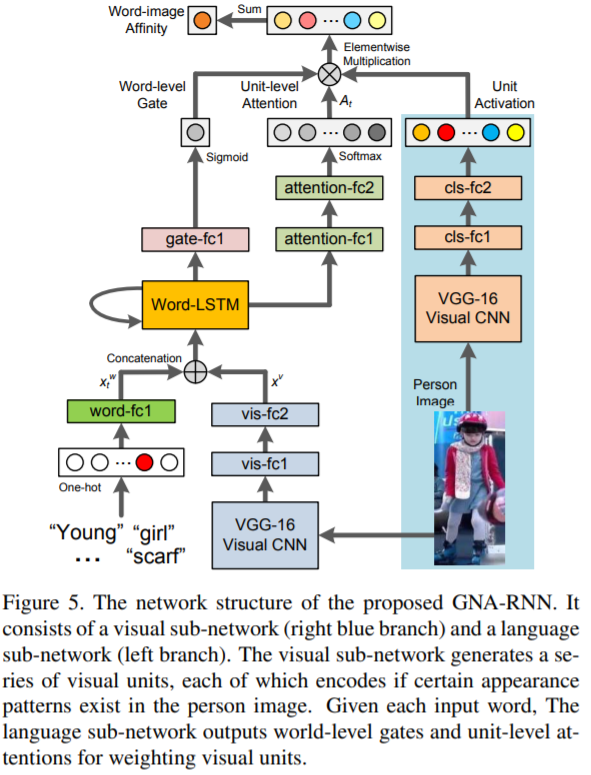
[54] : gated neural attention model
text description과 person images 사이 공유된 features를 학습하기 위한 recurrent neural network로 구성
자연어 description으로 사람을 식별하는 것을 연구
사람에 대한 설명이 주어지면, 알고리즘은 database의 샘플들의 ranking 수행하고 가장 연관된 샘플을 찾음
CUHK-PEDES : 대규모의 person description dataset을 수집
GNA-RNN : gated neural attention mechanism을 갖는 recurrent neural network 제안 (end-to-end로 학습이 가능)
-
Visible-infrared Re-ID
-
daytime visible image(RGB img)과 night-time infrared images 사이 cross-modality 매칭을 다루는 것
-
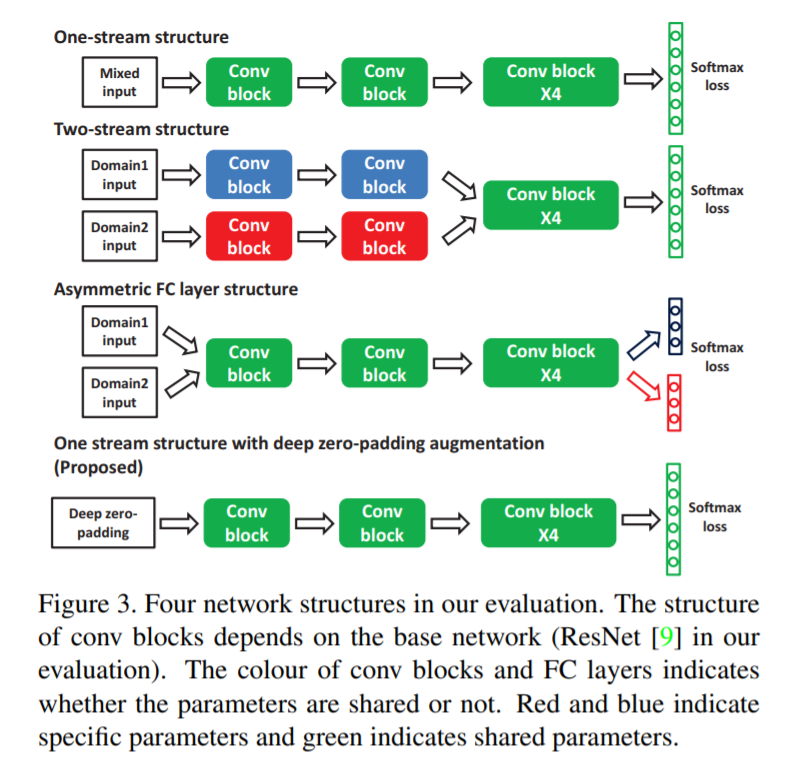
[20] : 적응적으로 공유할 수 있는 features를 학습하기 위한 deep zero-padding framework 제안
몇몇 응용분야에서는 RGB images가 적합하지 않을 수 있기 때문에, 적외선 이미지와 RGB 이미지 사이 매칭이 필요함
RCB-IR cross-modality Re-ID 문제를 해결하고 새로운 multiple modality Re-ID dataset(SYSU-MM01)을 제공
RGB-IR Re-ID 문제를 연구하기 위해, 기존의 유명한 cross-domain models(one-strean, two-stream, asymmetric FC layer)을 평가하고 분석
one-stream network를 학습하기 위한 deep zero-padding 제안
-
Cross-resolution Re-ID
-
low-resolution과 high-resolution images 사이 매칭을 수행
-
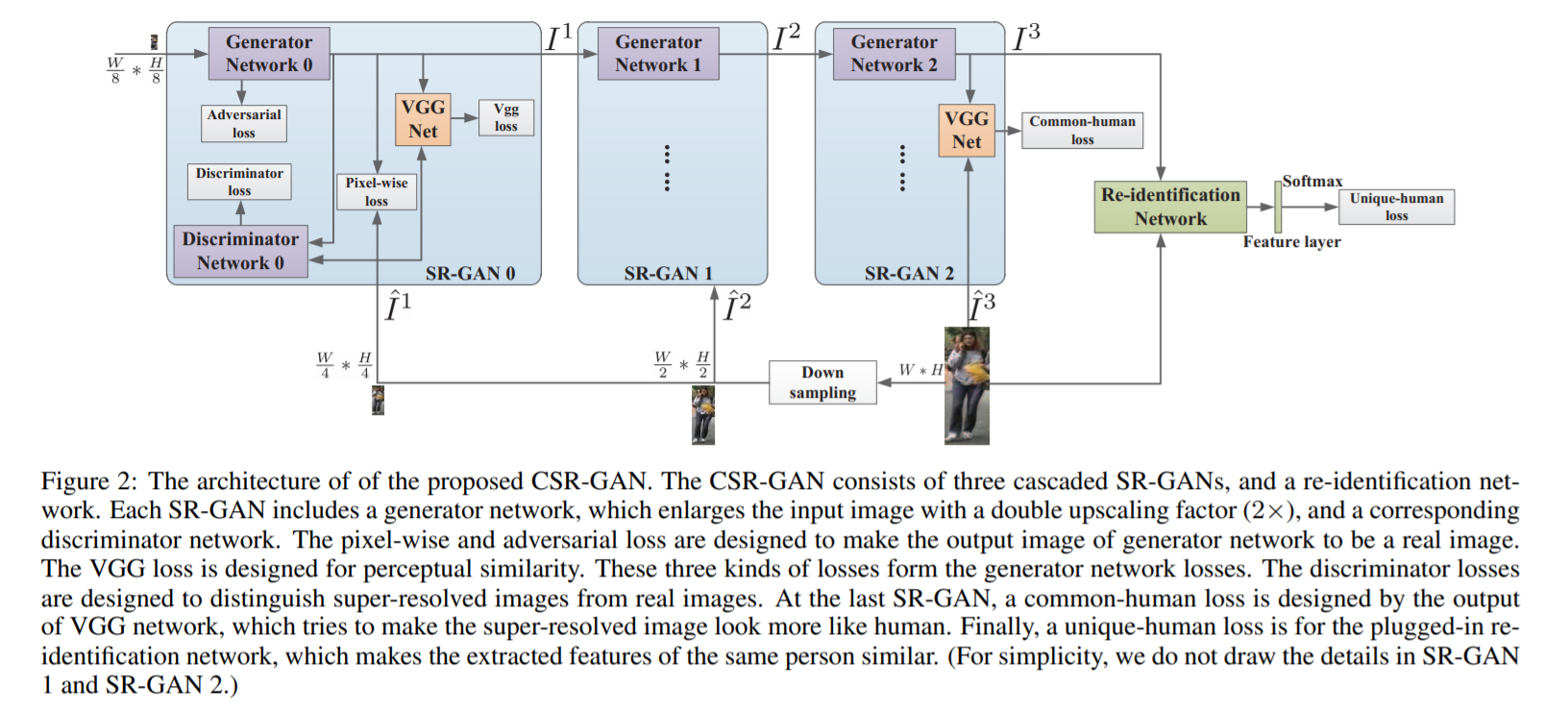
[196] : Cascaded Super-Resolution GAN 제안
실제로는 다양한 low-resolutions과 scale이 존재하기 때문에, 이를 해결할 수 있어야 함 (SALR-REID)
단순하게 다양한 low-resolutions을 균일한 high-resolution으로 증가시키는 것은 Re-ID task에 맞지 않음
-
scale-adaptive upscaling이 가능해야 하기 때문에, cascade multiple SR-GANs 사용
-
image feature representation 능력이 필요하기 때문에, re-identification network를 붙임
End-to-end Re-ID
-
Re-ID in raw images/videos
-
모델이 하나의 framework에서 person detection와 re-identification을 공동으로 수행
-
[46] : two-stage framework 제안
새로운 대규모 데이터세트를 제안하고, raw video frames에서 end-to-end 방식으로 pedestrian detection과 person recognition을 수행하는 종합적인 baselines 제안
3-contributions
-
PRW : 새로운 데이터 세트 제공
-
2가지 간단하지만 효과적인 방법을 통해 pedestrian detection이 Re-ID에 도움을 준다는 것을 보여줌
cascaded fine-tuning 전략, Confidence Weighted Simlilarity(CWS) metric
- 정확한 person Re-ID의 특정 상황에 대한 detector의 성능을 평가하는 것에서 통찰력을 얻음
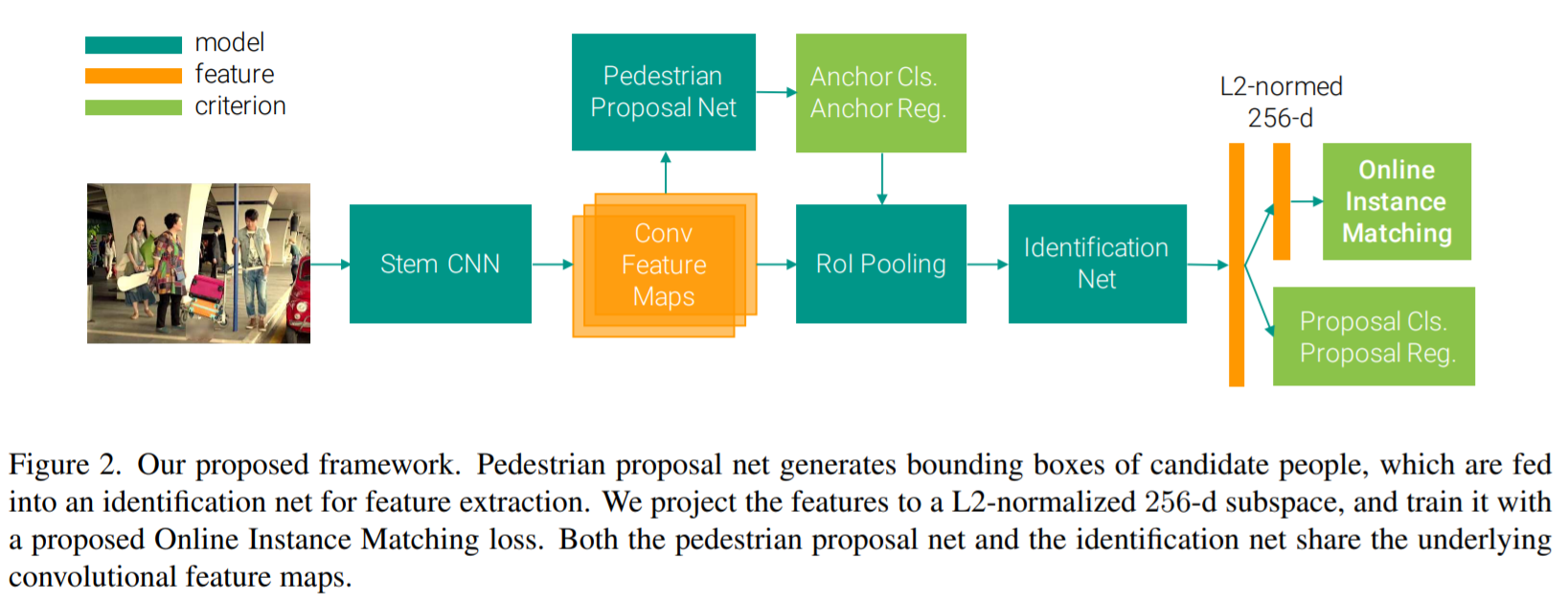
- [55] : single convolutional neural network를 이용한 end-to-end person search system 제안
현실세계에 적용을 할 때, pedestrian의 bounding boxes annotations을 이용할 수 없음
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해, 새로운 person search deep learning framework 제안
하나의 convolutional neural network로 pedestrian detection과 person re-identification을 공동으로 다룸
Online Instance Mathcing(OIM) loss 제안 : 많은 indentities를 갖는 datasets를 효과적으로 학습
person search를 위한 대규모 데이터세트를 수집하고 annotation 함
-
Multi-camera tracking
-
end-to-end person Re-ID는 multi-person tracking와 연관이 있음
-
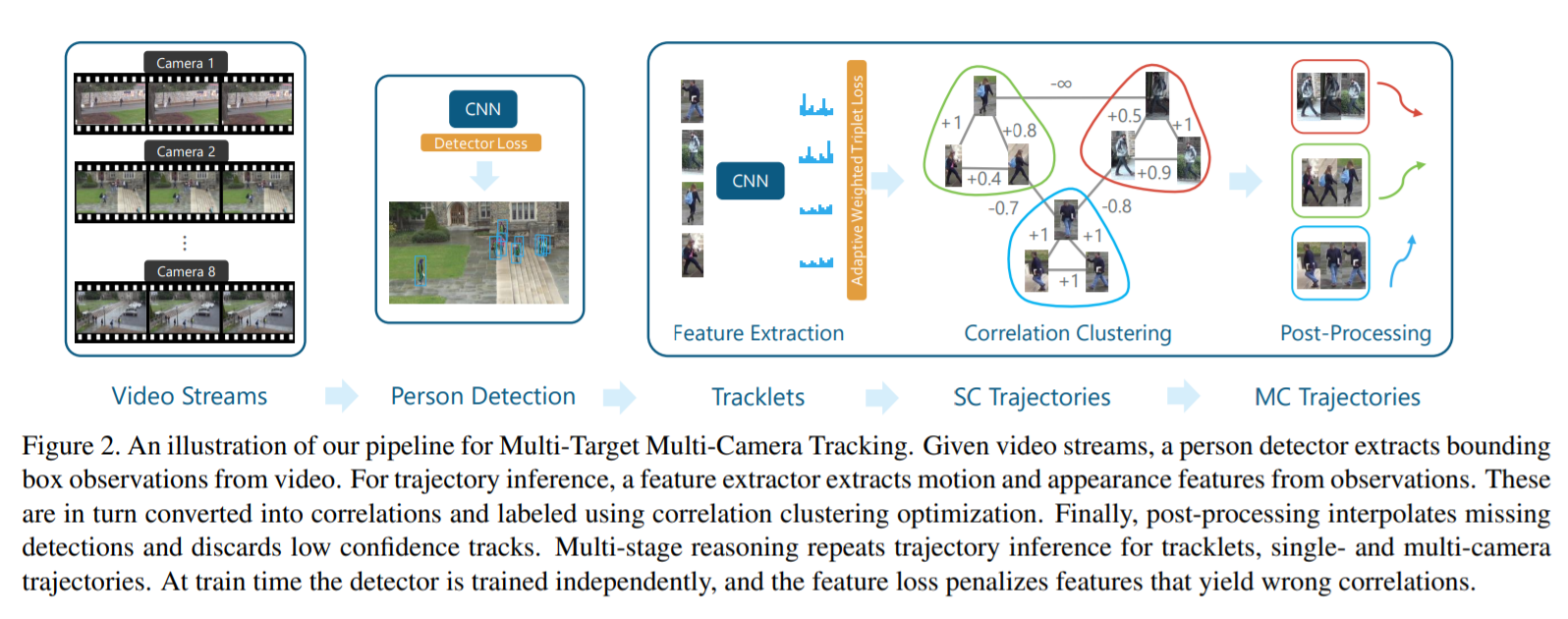
[43] : multi-target multi-camera tracking과 Re-ID 사이 연관성을 학습
Multi-Target Multi-Camera Tracking(MTMCT) : 여러개의 카메라로 촬영된 video에서 많은 사람들을 추적하는 것
하나의 convolutional neural network를 통해, MTMCT와 Re-ID로부터 좋은 features를 학습할 수 있었음
contributions
-
학습을 위해 adaptive weighted triplet loss를 사용
-
hard-identify mining을 위해 새로운 기술을 사용
제안된 방식은 두 task 모두에서 SOTA를 달성
Semi-supervised and unsupervised Re-ID
Unsupervised Re-ID
[deeply unsupervised methods]
cross-camera lavel estimation이 가장 많이 사용되는 방식
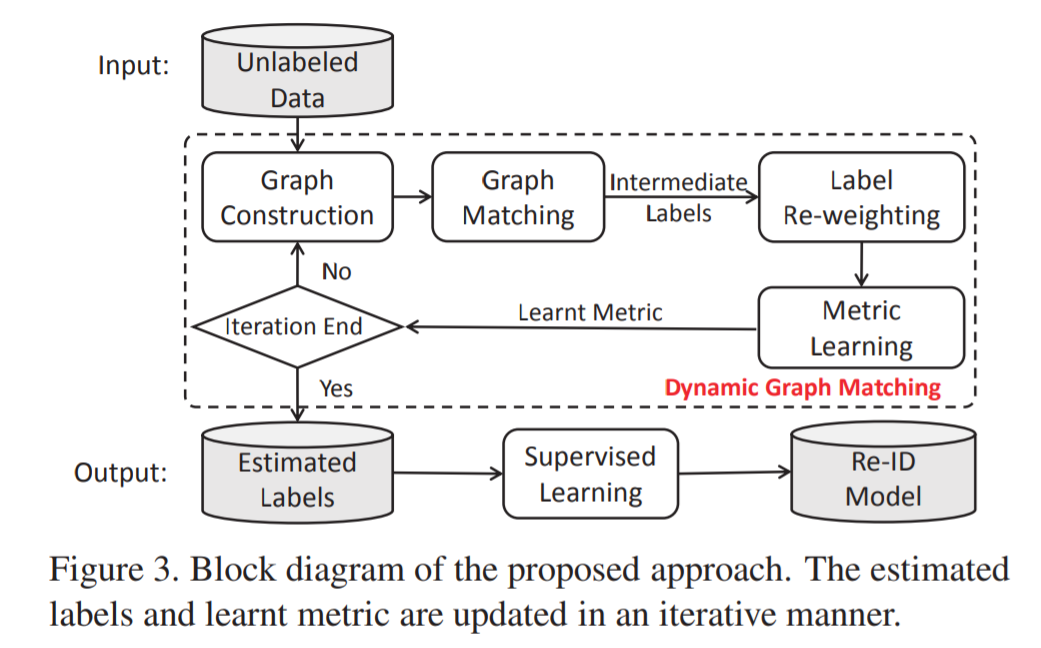
- [127] : Dynamic label graph matching for unsupervised video re-identification
unsupervised person Re-ID에서 label 예측은 아주 중요한 요소
강력한 Re-ID models을 학습시키기 위해 feature learning에 사용되는 cross-camera label estimation에 중점을 둔 연구
각 카메라에서의 samples에 대한 graph를 생성하고, cross-camera labeling association을 위해 graph matching scheme 도입
dynamic graph matching(DGM) 방식 제안 : 중간 예측 labels을 갖는 feature space를 더 잘 학습시키면서, 반복적으로 image graph와 label estimation 과정 업데이트
-
반복을 통해 예측된 labels의 정확도가 상당히 향상됨
-
noisy initial training data에 강력함
[end-to-end unsupervised Re-ID]
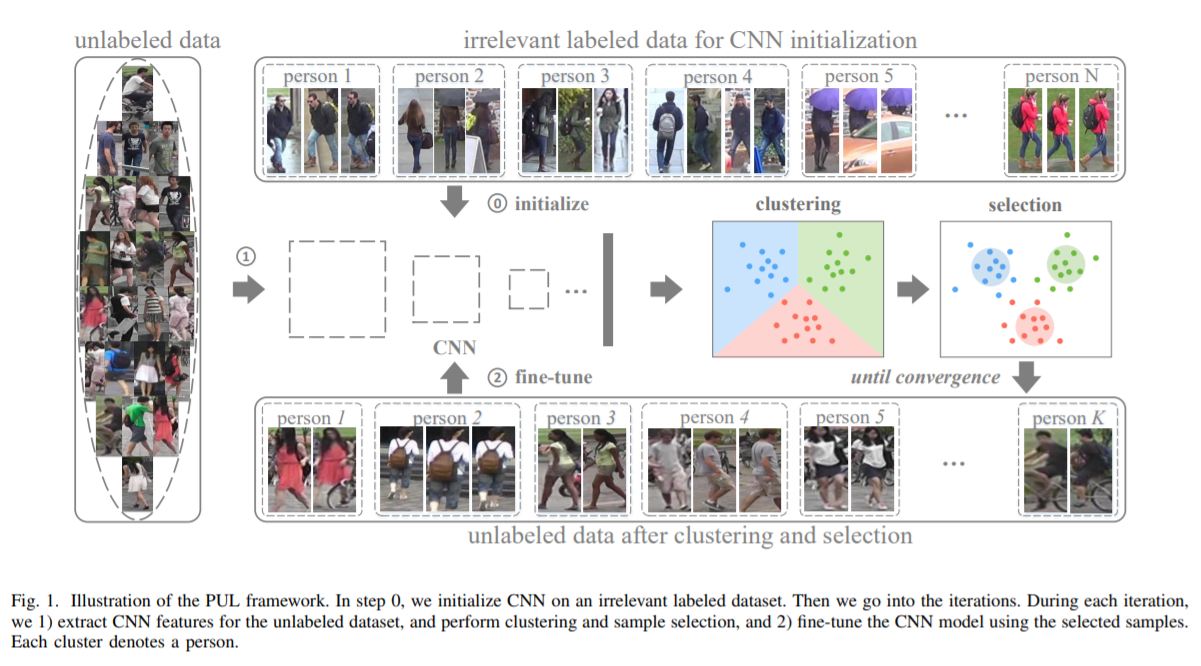
- [208] : 반복적인 clustering, Re-ID model learning 제안
label이 존재하지 않거나, 일부만 존재하는 상황에서 Re-ID 학습을 연구
progressive unsupervised learning(PUL) 방식 : pretrained deep representations을 보이지 않는 domain(처음 접하는 도메인)으로 transfer
PUL은 pedestrian clustering과 CNN의 fine-tuning을 반복적으로 수행
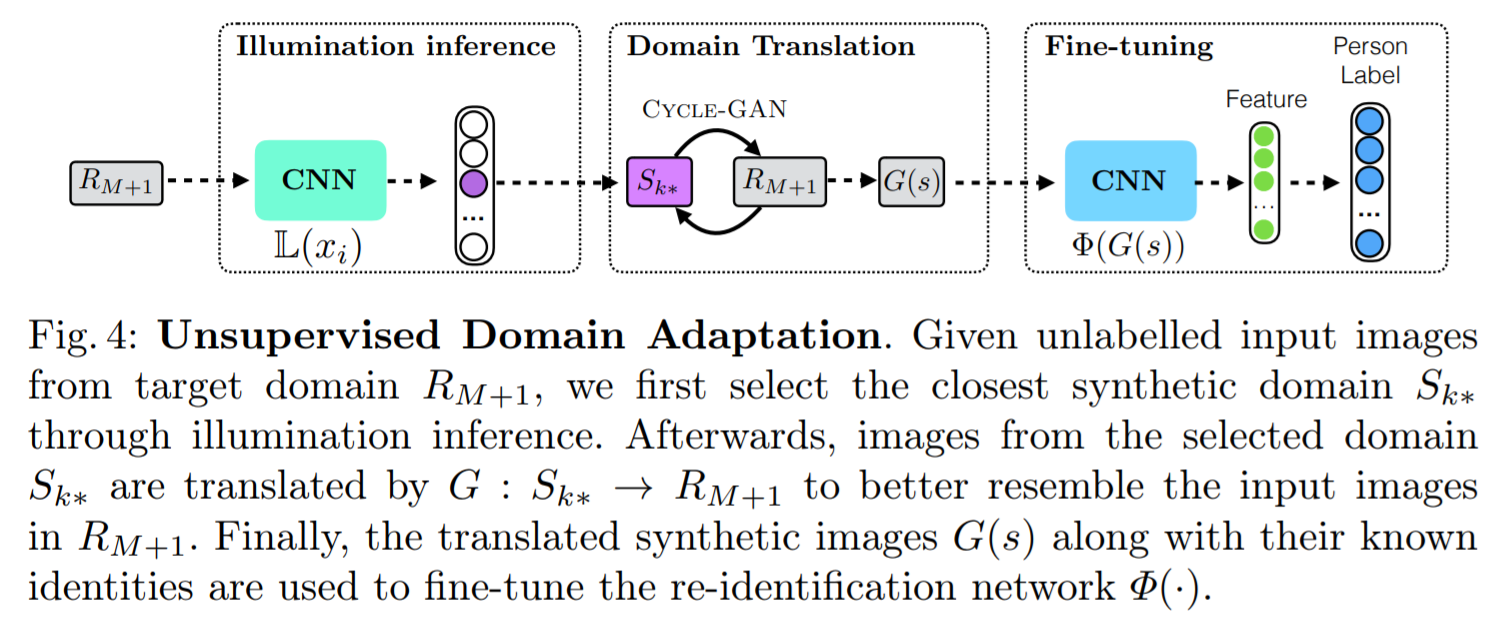
- Unsupervised domain adaptation


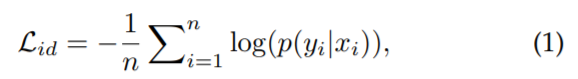
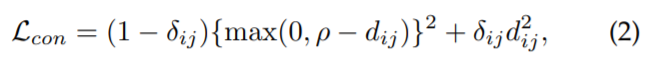
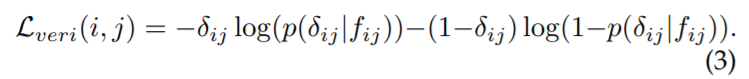
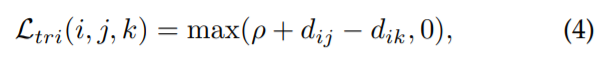
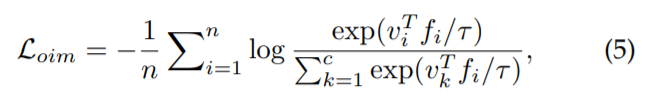
Leave a comment