[Paper Review] RetinaFace : Single-stage Dense Face Localisation in the Wild
RetinaFace : Single-stage Dense Face Localisation in the Wild
Deng, Jiankang, et al. “Retinaface: Single-stage dense face localisation in the wild.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.00641 (2019).
Abstract
-
Face detection은 엄청난 발전이 있었지만, 현실세계에서의 정확하고 효율적인 face localisation은 아직 풀리지 않은 문제로 남아있음
- 강력한 single-stage face detector(RetinaFace) 제시
extra-supervision과 self-supervision을 공동으로(multi-task learning) 학습시키면서 다양한 scale의 face에 대한 pixel-wise localisation을 수행
- Contributions
1) WIDER FACE dataset에서 5개의 landmark를 annotate(fig1의 Facial landmark regression 참고), hard face detection에서 상당한 정확도 향상을 보임
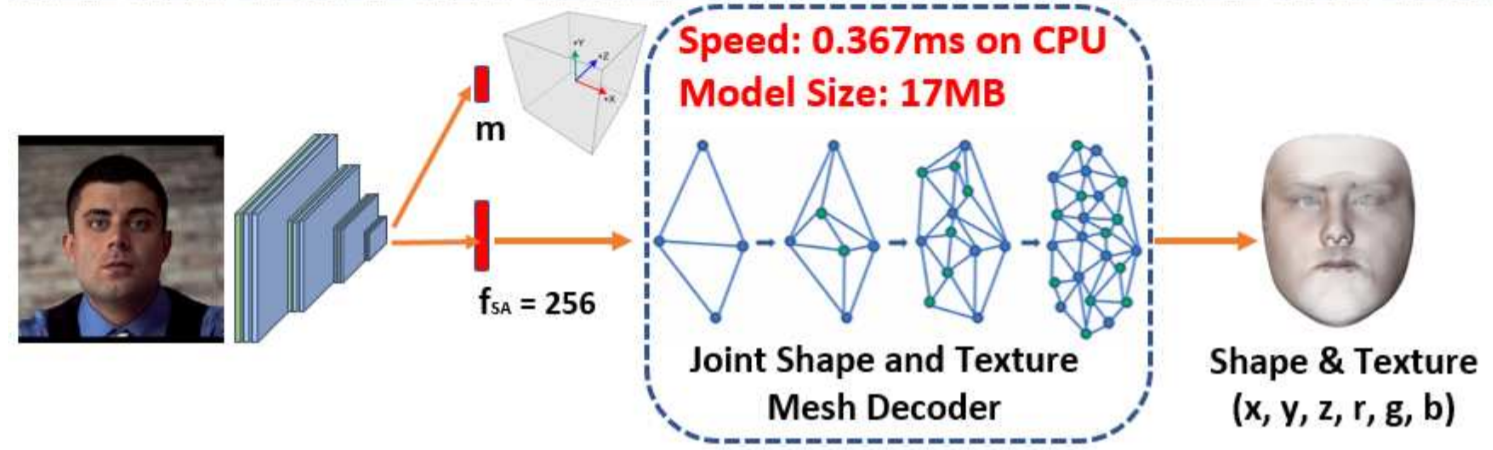
2) pixel-wise 3D shape face information을 예측하기 위해 self-supervised mesh decoder branch 추가 (존재하는 supervised branches와 동시에 학습)
Y. Zhou, J. Deng, I. Kotsia, and S. Zafeiriou. Dense 3d face decoding over 2500fps: Joint texture and shape convolutional mesh decoders. In arxiv, 2019.
3) WIDER FACE hard test set에서 SOTA 성능 능가 (1.1% AP)
4) IJB-C test set에서 SOTA 방식(ArcFace)이 face verification에서 성능을 향상시킬 수 있게 함
5) 가벼운 backbone network를 사용하면서 single GPU에서 real-time으로 동작 (VGA,640x480 resolution)
Introduction
- Automatic face localisation은 facial image analysis에 기본적으로 필요한 부분
facial image analysis : facial attribute(ex,감정표현,나이), facial identity recognition
-
좁은 범위의 face localisation : scale과 위치에 대한 사전정보 없이 bounding box를 예측하는 것 (traditional face detection)
- 넓은 범위의 face localisation : face detection, face alignment, pixel-wise face parsing, 3D dense correspondence regression
모든 다양한 scale에 대한 정확한 얼굴 위치 정보 제공
- Face detection
=> Object detection과 다르게 face detection은 비율 변화(width:height)는 작지만 훨씬 큰 크기 변화가 특징
- 최근 SOTA 방식은 single-stage 구조에 focus를 둠 : feature pyramids에서 얼굴의 위치과 크기를 dense하게 추출
=> two-stage 방식에 비해 좋은 성능과 빠른 속도를 보임
- RetinaFace
- single-stage face detection framework를 발전시킴
- supervised, self-supervised signal에서의 multi-task losses를 이용하는 SOTA dense face localisation 방식 제안
RetinaFace
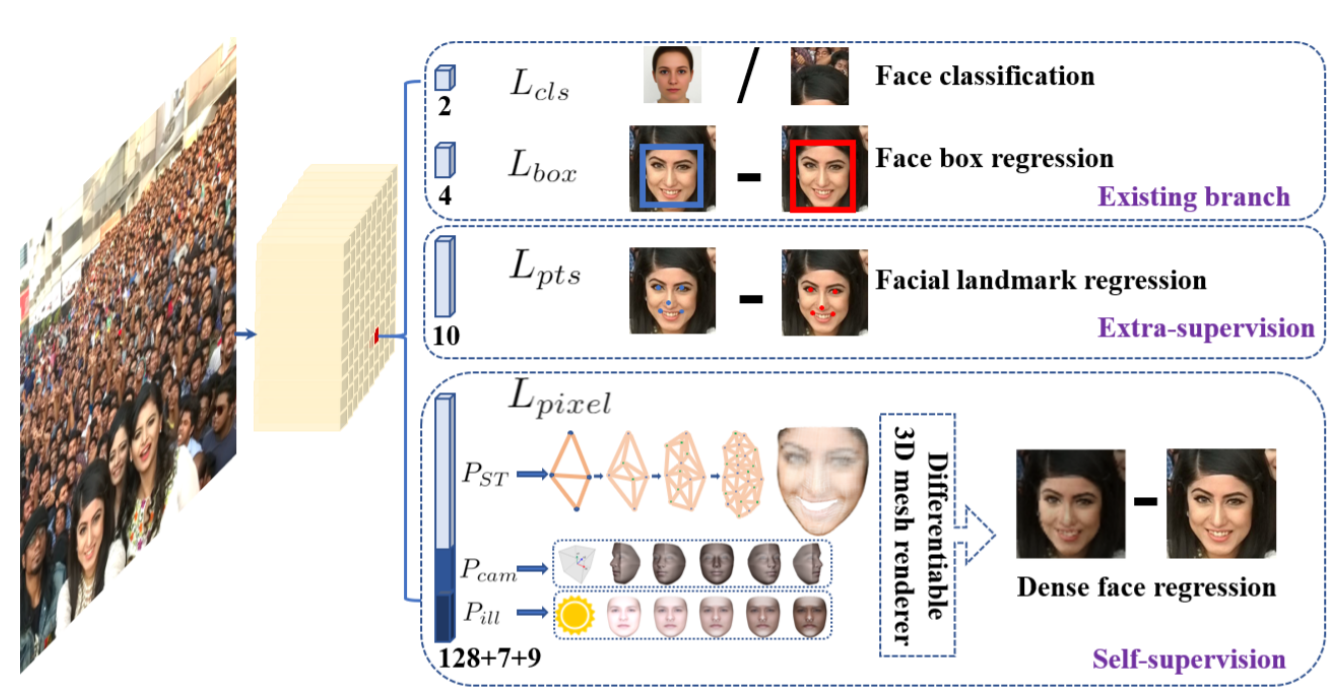
- 3.1 Multi-task Loss
1) Face classification loss
anchor i가 face인지 아닌지 classification (soft max for binary classes)
2) Face box regression loss
bounding box 조정 (the robust loss function, smooth-L1)
3) Facial landmark regression loss
positive anchor에 대해 5개의 facial landmark 예측 (the target normalisation based on the anchor center)
4) Dense regression loss
- 3.2 Dense Regression Branch
- Mesh Decoder
- Mesh decoder를 사용 (mesh convolution, mesh up-sampling)
- 학습과정을 가속화 시키기 위해 shape과 texture decoder를 공동으로 사용
- the concept of graph convolutions
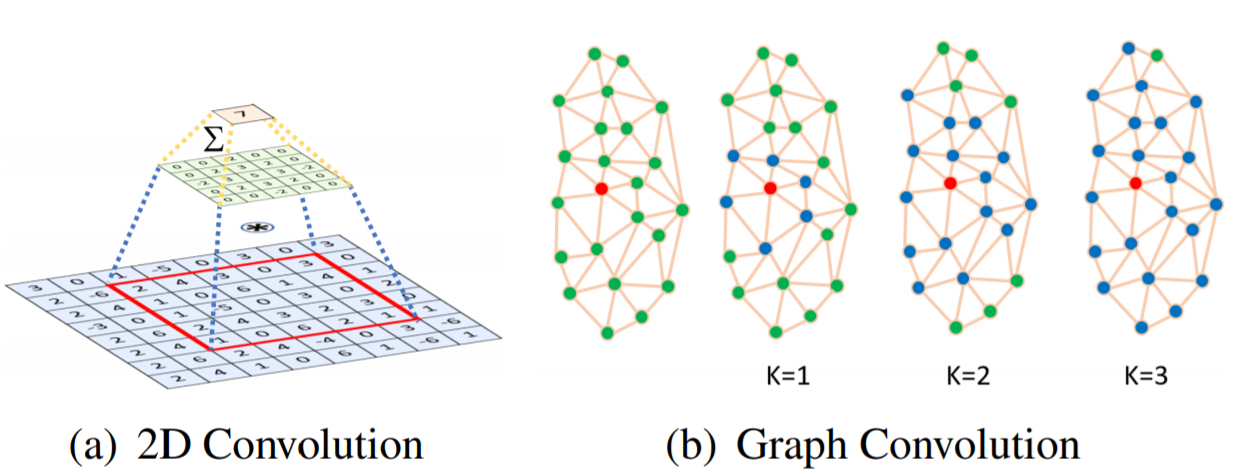
2D convolution operation(fig3(a)) : Euclidean grid receptive field 내에서의 kernel-weighted neighbor sum
graph convolution(fig3(b)) : graph에서 neighbor distance 계산 (교차점을 연결하는 최소의 edges로 이루어진 graph)
- Differentiable Renderer
shape과 texture를 예측한 뒤에 efficient differentiable 3D mesh renderer을 사용하여 coloured mesh D를 camera parameters와 illumination parameters를 가진 2D image plane에 projecting
- Dense Regression Loss
rendered 2D face R를 얻고 나서, R과 original 2D face를 비교
- Architecture
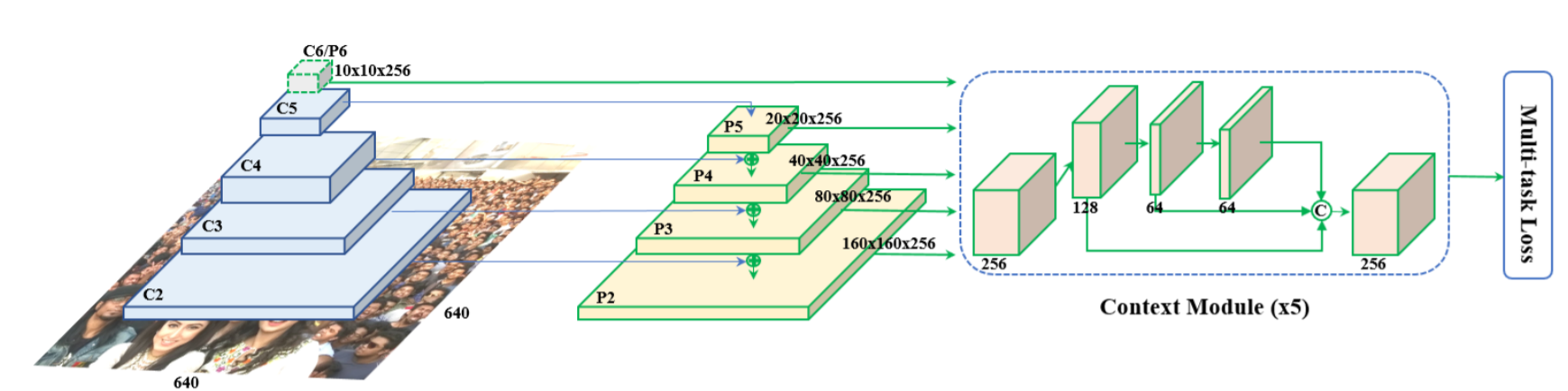
- Feature Pyramid
FPN 구조 : P2-P6까지 feature pyramid levels (P2-P5은 C2-C5과 residual connection)
P6 : C5에서 stride가 2인 3x3 convolution로 계산
C1-C5 : pre-trained ResNet-152 / P6 : Xavier method를 이용한 random initialization
- Context Module
SSH와 PyramidBox에서 영감을 얻어 5개의 pyramid level에 개별적으로 context module 적용
receptive field가 커지고 regid context modelling power가 향상(??)
모든 3x3 convolution layers를 deformable convolution network로 대체
non-rigid context modelling power가 강력해짐(??)
- Loss Head
negative anchors에 대해서는 classification loss만 적용
positive anchors에 대해 multi-task loss 적용
다른 feature maps에 대해 shared loss head 사용 (1x1 conv)
mesh decoder에 pre-trained model 적용 (계산 비용을 줄이기 위해)

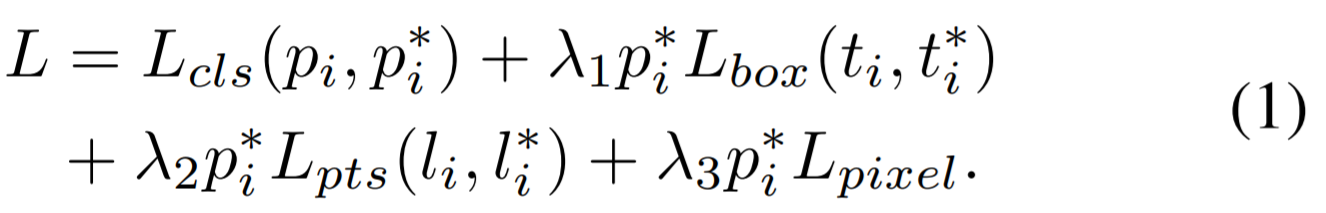
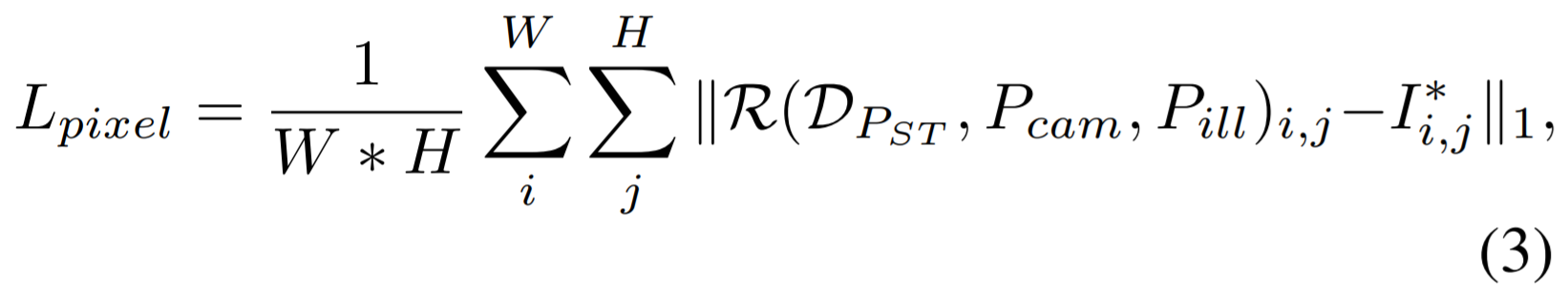
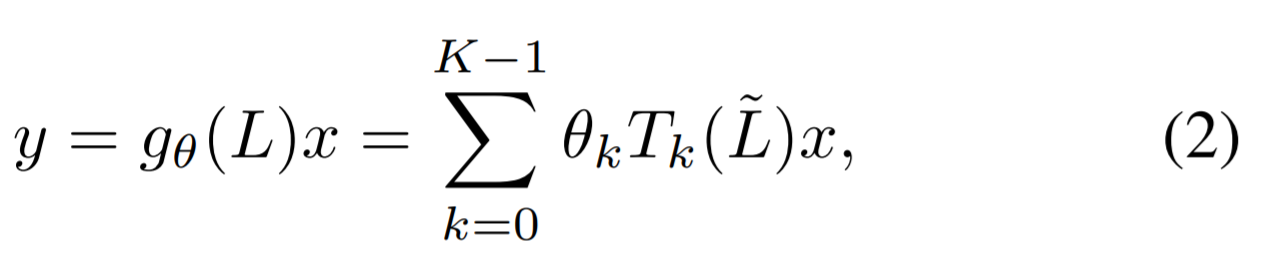
Leave a comment