[Paper Review] Pyramidbox: A context-assisted single shot face detector
Pyramidbox: A context-assisted single shot face detector
Tang, Xu, et al. “Pyramidbox: A context-assisted single shot face detector.” Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). 2018.
Abstract
-
Face detection challenges : small, blurred, partially occluded faces를 detection 하는 것
-
새로운 context assisted single shot face detector(PyramidBox) 제안 : hard face detection 문제를 잘 다루는 detector
-
Contextual information 활용을 위한 3가지 방안
1) 새로운 context anchor design
semi-supervised method에 의해 high-level contextual feature를 학습 (PyramidAnchors)
2) The Low-level Feature Pyramid Network 제안
high-level context semantic feature와 Low-level facial feature를 적절히 결합시키기 위한 network
PyramidBox가 single shot으로 모든 scale의 face를 예측할 수 있게 함
3) Context sensitive structure 도입
prediction network의 capacity를 증가시키기 위한 구조 (model의 accuracy 향상)
- Data-anchor-sampling 방식 사용
다른 scale에 대한 training samples을 augmentation (smaller faces에 대한 training data의 다양성을 증가시킴)
- Contextual 정보를 이용하면서 SOTA 달성 (FDDB, WIDER FACE)
Introduction
- Anchor-based detection framework의 목표 : 통제되지 않은 환경(ex,WIDER FACE)에서의 hard faces를 detection 하는 것
SSH, S3FD : single network에서 다른 layers로부터 다른 scales의 face를 detection하는 scale-variant network 개발
Face R-FCN : position-sensitive average pooling을 사용하여 각 facial part에 대한 non-uniformed contribution을 제거하고(??), discrimination을 향상시키기 위한 embedding features 생성
FAN : anchor-level attention(가려진 face를 detection하기 위해 face region의 features를 강조) 제안
- 기존 방식의 한계 : hard faces를 detection 하는 데 중요한 역할을 하는 contextual 정보를 제대로 활용하지 못함
contextual 정보가 중요한 이유 : low-resolution, blur, occlusion과 같이 facial texture를 잘 구별할 수 없을 때, 풍부한 contextual associations을 제공
- contextual signals의 완전한 사용을 위한 PyramidBox 제안
1) network가 단순히 faces만 학습하지 않고, 주변 contextual parts(heads,bodies)도 학습해야 함
3가지 part에 대한 extra labels과 anchors가 필요 -> semi-supervised solution을 사용하여 contextual parts에 대한 labels과 PyramidAnchors(face-head-body) 생성
2) high-level contextual features가 low-level features와 적절하게 결합되어야 함
문제 : hard face와 easy face의 appearances는 상당히 다르기 때문에, 모든 high-level semantic features가 smaller targets에 무조건적으로 도움이 된다고 가정할 수 없음
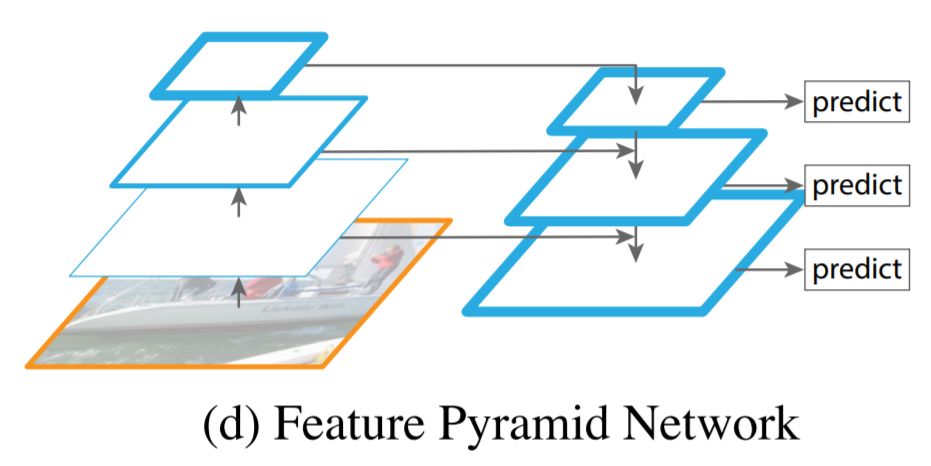
FPN(Feature Pyramid Network) -> LFPN(Low-level Feature Pyramid Network) 수정 : 상호간에 도움이 되는 features를 결합하기 위한 네트워크 (필요하지 않은 features는 결합 X)
FPN : top-down 구조로 high-level semantic feature map을 모든 scales에 사용하기 위해 low-level layers(with high resoloution)로 통합
3) The predict branch network가 결합된 features를 완전히 사용할 수 있어야 함
Context-sensitive-prediction module(CPM) 도입 : target face에 대한 context information을 통합시키기 위한 모듈
the prediction module에 max-in-out layer을 제안 : classification network의 capability를 향상시키기 위한 layer
- Data-anchor-sampling : training dataset의 distribution을 조정 (hard-set을 늘리기 위해)
-
Main contributions
-
1) anchor-based context assisted method인 PyramidAnchors 제안 : small, blurred, partially occluded faces를 위해 contextual features를 학습하도록 함
-
2) the Low-level Feature Pyramid Networks (LFPN) : contexual features와 facial features를 더 좋게 합치기 위해 design
single shot 방식으로 다른 scale의 face를 잘 다룸
-
3) context-sensitive prediction module : merged features로부터 정확한 location과 classification을 학습하기 위한 모듈로 mixed network structure와 max-in-out layer로 구성
-
4) the scale aware Data-anchor-sampling strategy : smaller faces(training data가 적은 faceset??)에 집중할 수 있도록 training samples의 distribution을 변화시킴
-
5) FDDB, WIDER FACE에서 SOTA 달성
PyramidBox
-
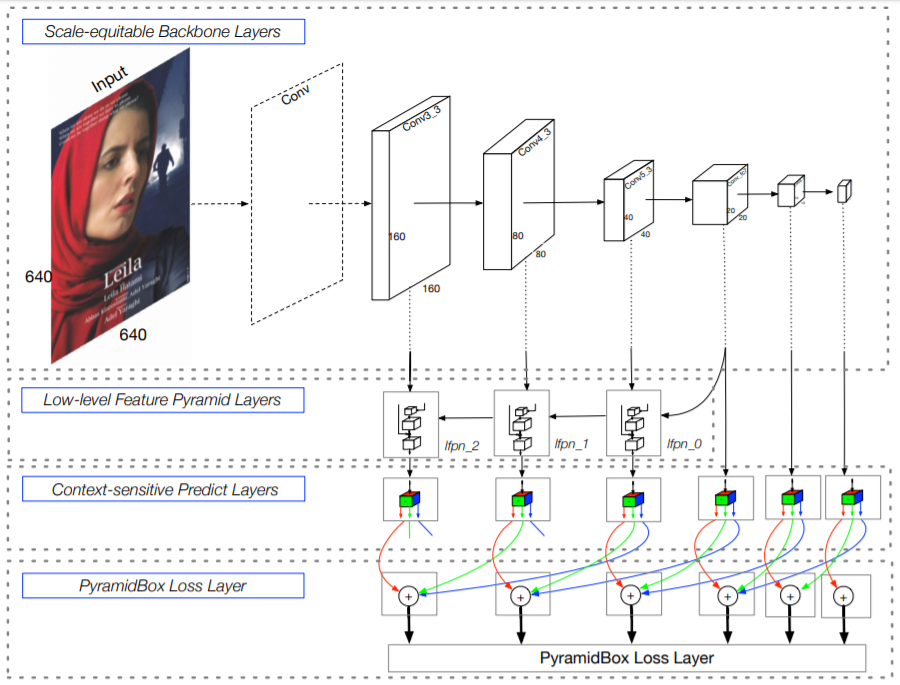
3.1 Network Architecture
S3FD와 동일한 extended VGG16 backbone, anchor scale design 사용 (다른 levels의 feature maps과 동일한 비율 간격을 갖는 anchors를 생성)
backbone에 Low-level FPN을 추가하고, final output을 얻기 위해 각 pyramid detectoin layer 별로 Context-sensitive Predict Module을 적용
- Scale-equitable Backbone Layers
the base convolution layers와 S3FD에서 사용한 extra convolutional layers를 사용
VGG16의 conv1_1~pool5를 유지하고, fc6과 fc7을 conv_fc layers로 변경하여 더 깊게 만들어 줌
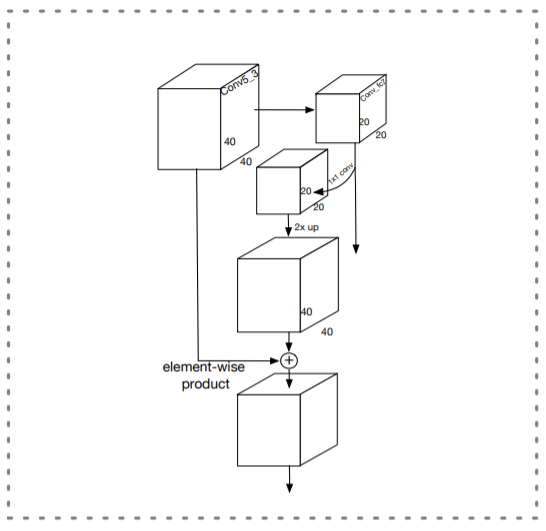
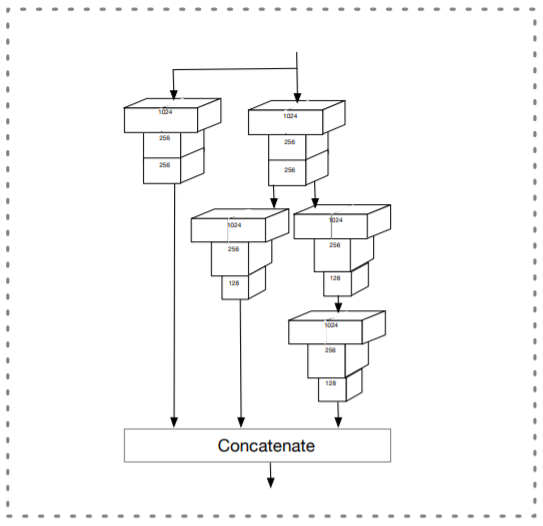
- Low-level Feature Pyramid Layers
다른 scales의 face를 다루는 face detector의 성능을 향상시키기 위해서는 high-resolution을 가진 low-level feature(for small face detection)가 중요한 역할을 함
high level semantic feature를 low-level layers로 통합하기 위한 FPN-style framework가 좋은 성능을 냄
기존 FPN은 top layer부터 integration을 수행하지만, 이 방식은 모든 high-level features가 small faces에 도움이 되는 것은 아니라는 문제점이 존재함
1) large, clear, complete faces의 feature와 small, blurred, occluded faces의 feature는 다른 texture feature를 가짐
2) face의 texture 정보를 적게 포함하는 high-level feature는 noise가 될 수도 있음
the top two layers(conv7_2, conv6_2)의 receptive field는 각각 724, 468로 너무 많은 noisy context features를 포함하여 medium, small faces에는 도움이 안됨
-> 이를 해결하기 위해 중간 layer에서 top-down을 시작하는 Low-level Feature Pyramid Network를 제안 (LFPN의 각 block 구조는 FPN과 동일)
- Pyramid Detection Layers
lfpn_2, lfpn_1, lfpn_0, conv_fc7, conv6_2, conv7_2가 detection layer임 (anchor size는 각각 16,32,64,128,256,512)
SSD-style methods와 비슷하게 LFPN layers의 norm을 rescale 하기 위해 L2 normalization 사용
- Predict Layers
각 detection layer는 Context-sensitive Predict Module(CPM)로 들어감
CPM의 outputs은 pyramid anchors를 학습하는데 사용됨 (face-head-body)
output의 각 channel들은 face/head/body의 classification와 regression에 사용됨 (classification:4/2/2, regression:4/4/4)
- PyramidBox loss layers
pyramid anchors에 대해 classification과 regression을 동시에 학습하기 위해 PyramidBox Loss 고안 (classification : softmax / regression : smooth L1)
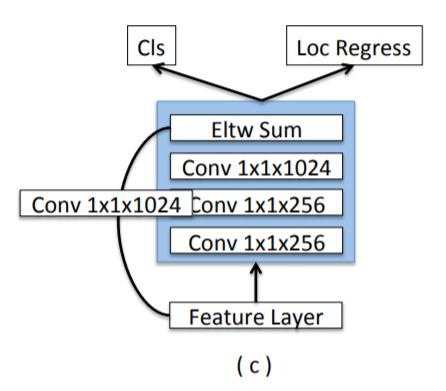
- 3.2 Context-sensitive Predict Module
- Predict Module
Inception-ResNet에서 영감을 얻어 wider 하고 deeper 한 network를 사용
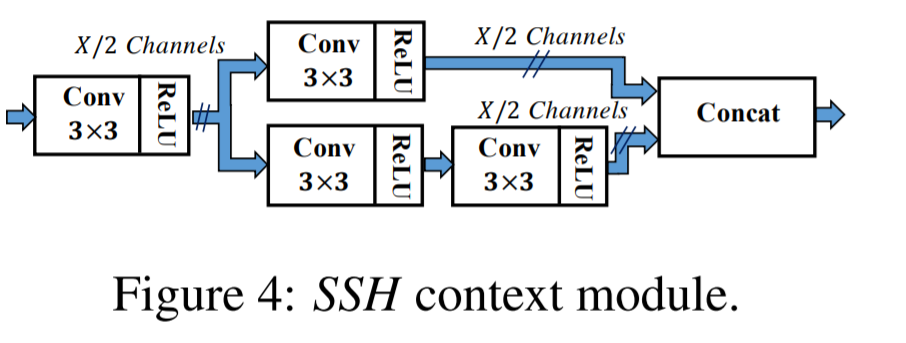
the Context-sensitive Prediction Module(CPM) 고안 : SSH의 context module의 convolution layers를 DSSD의 residual-free prediction module로 대체
SSH의 context module / DSSD의 prediction module
- Max-in-out
최근 S3FD에서 적용된 max-out background lebel : small negatives의 false positive(틀린 정답:배경인데 face라고 예측한 것) rate를 감소시키기 위해 사용
max-in-out : positive와 negative samples에 둘 다 적용
prediction module에서 prediction score Cp(positive score)과 Cn(negative score)에서 max 값을 취함
우리는 첫번째 prediction module에서 Cp=1, Cn=3으로 설정 (small anchor일수록 배경이 많기 때문에)
loss balancing 해결
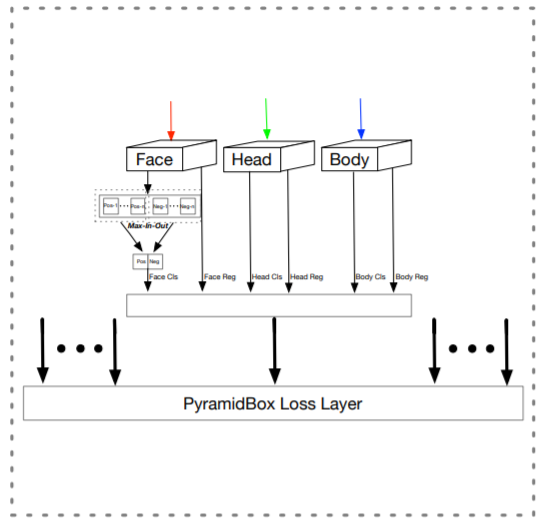
- 3.3 PyramidAnchors
기존 face detector는 small face를 detection하기 위해 anchor의 banlance를 맞추는데 노력을 하였으나, 여전히 context feature는 무시
모든 target face에 대해 PyramidAnchors는 face 주변 larger regions에 해당하는 일련의 anchors를 생성 (head, shoulder, body와 같이 더 많은 contextual 정보를 포함)
semi-supervised way
boxes의 특징들이 서로 다른 얼굴들 사이에서 유사하기만 하면, 머리, 어깨, 몸의 실제 영역을 대략 맞추기 위해 uniform boxes set을 사용할 수 있음
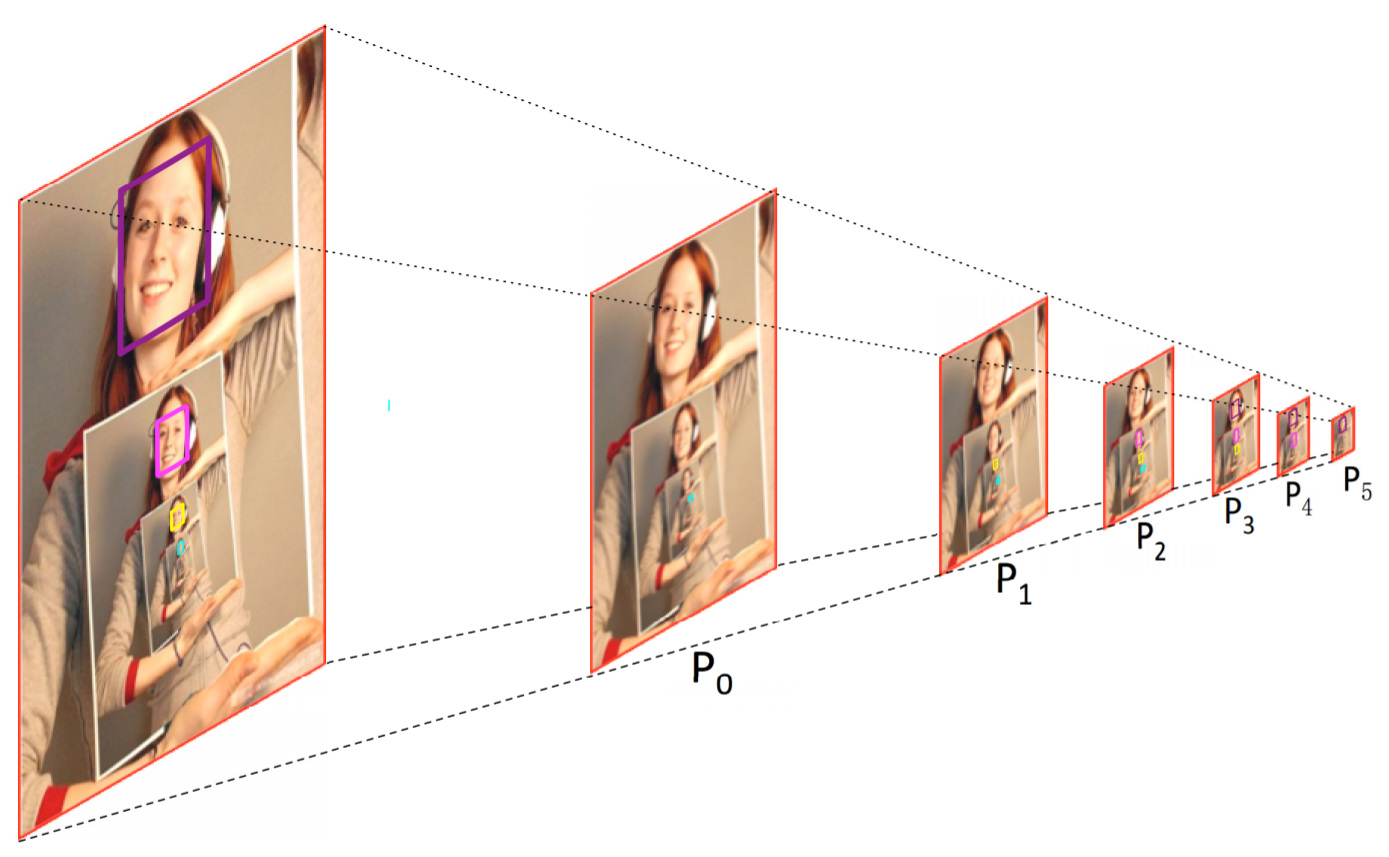
3개의 연속적인 prediction modules에서 하나의 facesms 3개의 targets 생성 (face(label0)-head(label1)-body(label2))
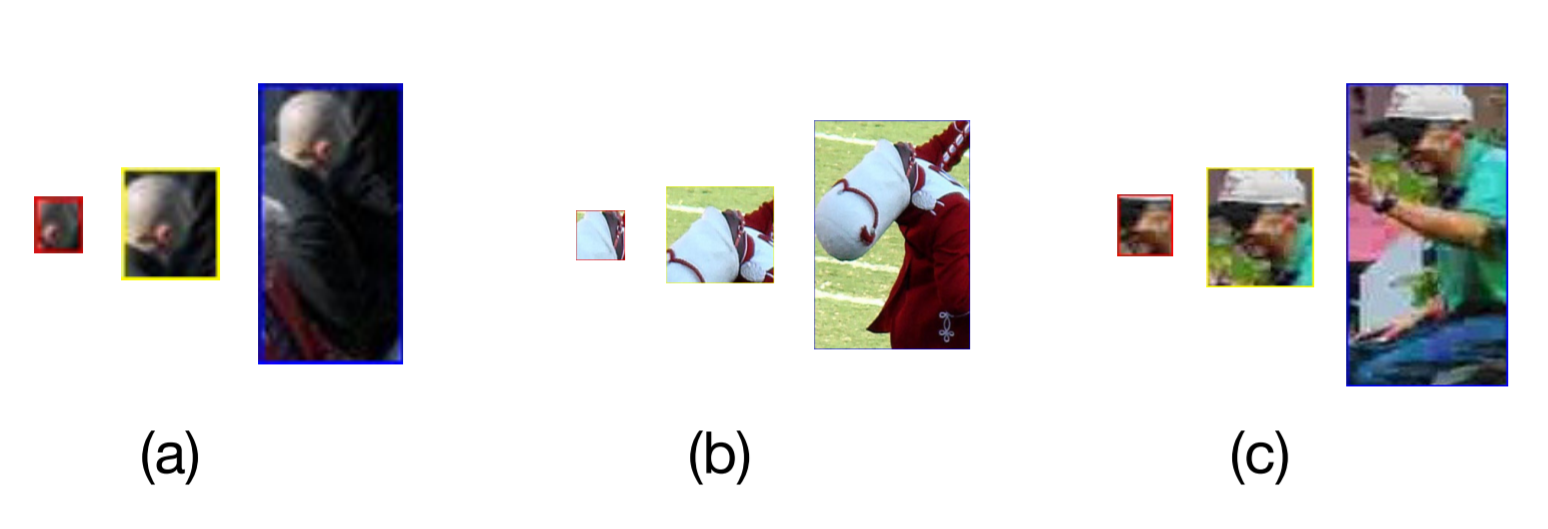
제일 size가 큰 purple face를 살펴보면, P3는 conv_Fc7에서 생성된 anchor로 face-self이고, P4는 conv6_2에서 생성된 anchor로 head이고, P5는 conv7_2에서 생성된 anchor로 body임
PyramidBox로 인해, small, blurred, partially occluded faces를 더 잘 다룰 수 있음
extra label 없이 자동적으로 pyramid anchors를 생성하고, semi-supervised learning이 PyramidAnchors는 대략적인 contextual features 추출
prediction 과정에서는 face branch만 사용하기 때문에 runtime 시에 추가 계산 비용은 없음
- 3.4 Training
Train dataset : 12,880 images의 WIDER FACE training set (color distort, random crop, horizontal flip 적용)
- Data-anchor-sampling
image에서 random face를 random smaller anchor size로 reshaping하면서 train images를 resize
1) image에서 random으로 face를 선택
2) 가장 비슷한 anchor size를 찾기
3) target size를 선택 (16,32,64,128,256)
4) image resize scale 결정 : S_target/S_face
5) original image(640x640)에서 resize로 size로 crop하여 train data을 얻음 (crop된 이미지에는 face가 포함되어 있어야 함)
Data-anchor-sampling effects
small faces의 비율이 large faces의 비율보다 높아짐
하나의 큰 image를 통해 작은 face samples을 생성 (smaller scales의 face samples을 다양하게 만들어주기 위해)
- PyramidBox loss
k-th pyramid-anchor loss
classification loss : log loss / regression loss : smooth L1 loss

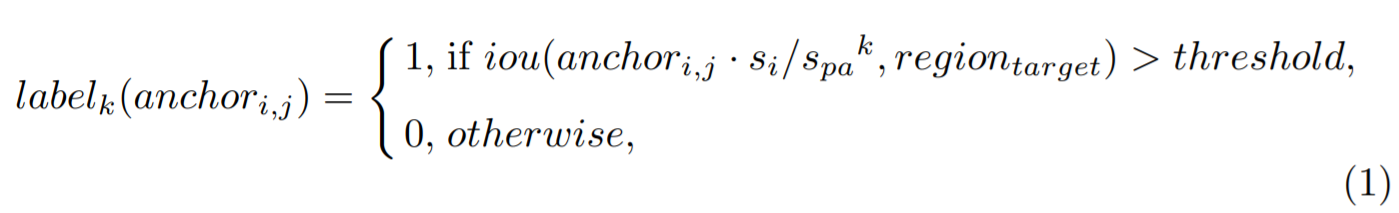
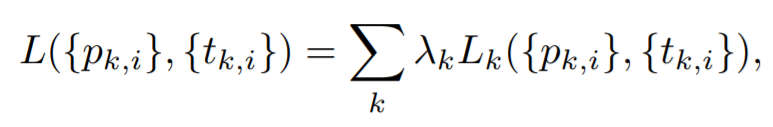
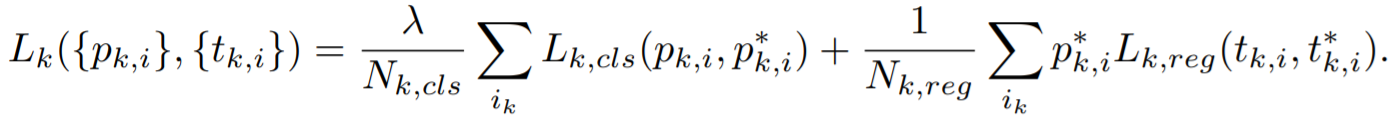
Leave a comment