[Paper Review] Deformable convolutional networks
Deformable convolutional networks
Dai, Jifeng, et al. “Deformable convolutional networks.” Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2017.
Abstract
-
CNN의 한계 : module의 구조에서 고정된 geometric 구조(convolution filter)로 인하여 geometric transformations이 제한적임
-
CNN의 transformation modeling capability를 향상키시기 위한 새로운 2가지 module 제안
=> offsets을 추가하여 공간 샘플링 위치를 증가시키고, offsets을 추가적인 supervision 없이 task에 맞게 학습시킴
1) deformable convolution
2) deformable RoI pooling
-
새로운 module은 기존 CNN에서 쉽게 대체할 수 있고, end-to-end 학습이 가능함
-
광범위한 실험으로 module의 성능을 입증함
object detection, semanic segmentation과 같은 복잡한 visual tasks에 효과적
Introduction
- visual recognition에서의 주요 challenge : object의 scale, pose, viewpoint, part deformation에서의 geometric variations(또는 geometric transformations)을 수용하는 방법
1) training datasets에 변형을 수행하는 것 (data augmentation)
한계 : 학습과정에서 계산 비용을 증가시키고, model의 parameters를 복잡하게 만듦
2) transformation-invariant features and algorithms (ex, SIFT, sliding window based object detection paradigm)
위와 같은 방식들의 변형의 2가지 결점
1) geometric transformations은 고정적이고 알고 있다는 가정 하에 할 수 있음
data augmentation과 features and algoritms design과 같은 변형을 수행할 때, prior knowledge가 사용됨
unknown geometric transformations을 갖는 새로운 task에 일반적으로 적용할 수 없음
2) hand-crafted design of invariant features and algorithms은 매우 복잡한 변형을 하기에 힘듦
simple hand-crafted module : max-pooling
- 기존의 CNN은 large unknown transformations을 수행하기에는 제한이 있음
원인 : CNN modules의 고정된 geometric 구조 (convolution, pooling layer, RoI pooling layer)
geometric transformations를 처리하기 위한 internal mechanisms이 부족
1) CNN layer에서 고정된 receptive field sizes
다른 scale과 다른 변형을 다룰 수 있도록 field size를 적응적으로 결정하는 것이 바람직함
2) feature extraction에 기반한 초기 bounding box에 의존 (object detection) ??
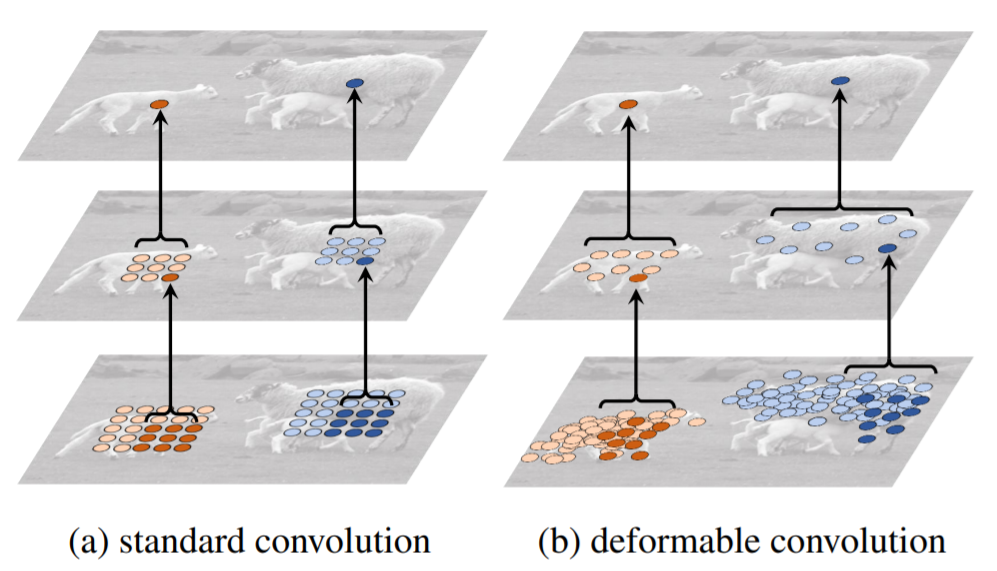
- geometric transformations을 만들어내는 능력을 향상시키기 위한 2가지 새로운 module 소개
1) deformable convolution
일반적인 convolution에 2D offsets을 추가 (추가적인 convolution layer를 통해 feature map으로부터 offsets 학습)
sampling grid의 자유로운 변형을 가능하게 함 (local, dense, and adaptive manner)
2) deformable RoI pooling
RoI pooling에서의 각 bin에 offset을 추가 (feature map과 RoI로부터 offsets이 학습됨)
다른 shapes을 갖는 objects에 대한 adaptive part localization을 가능하게 함
Deformable Convolutional Networks
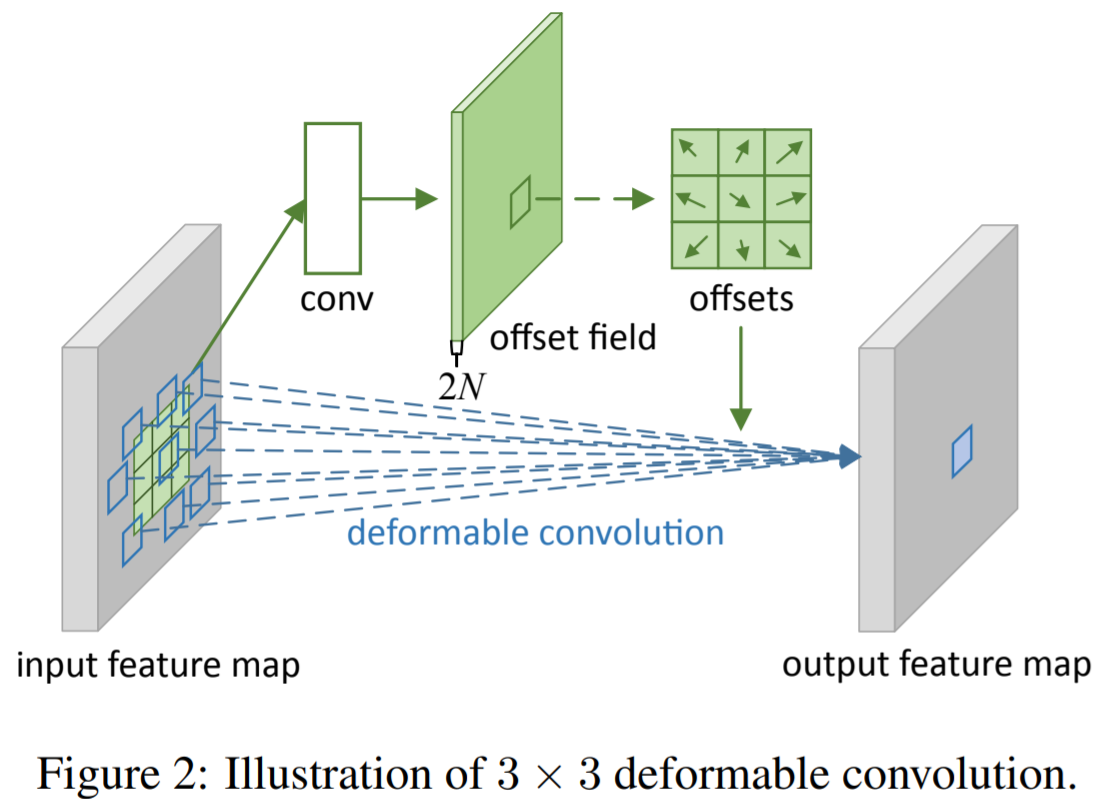
- 2.1 Deformable Convolution
input feature map에 대한 하나의 convolution으로 offsets을 얻음
The 2D convolution
P0 : output feature map y에 대한 위치 (좌표)
1) input feature map x에서 grid R을 이용하여 sampling
2) w로 가중치가 부여된 sampled values의 합
The deformable convolution
grid R이 offset을 통해 augmentation
x(p)는 bilinear interpolation(G:2-dimension)을 이용하여 구현됨 (gradients가 backpropagation하면서 offset이 학습됨)
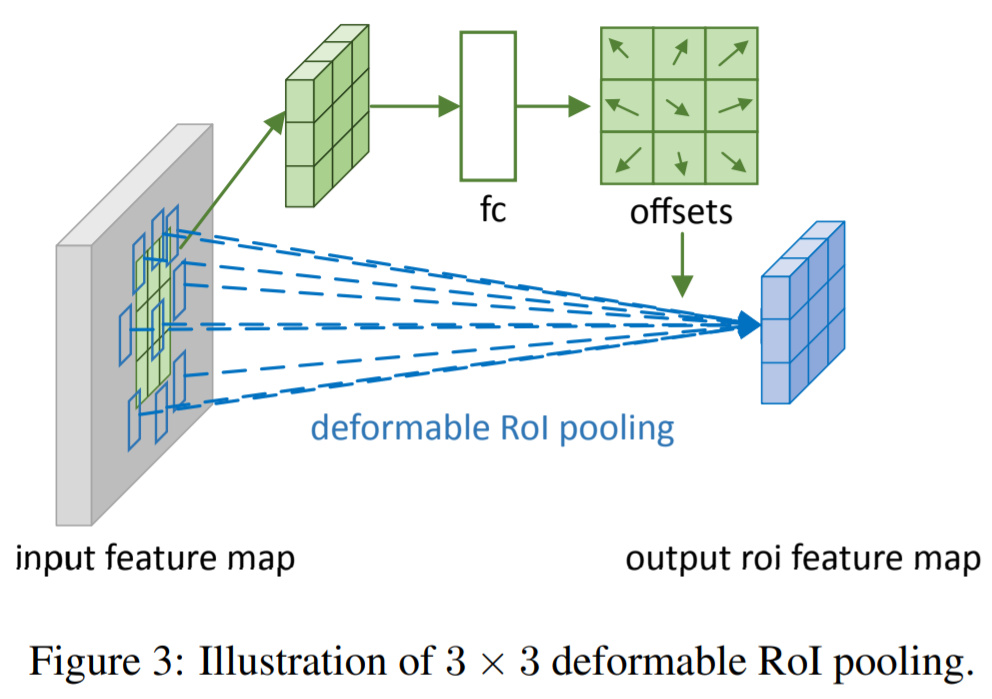
- 2.2 Deformable RoI Pooling
RoI Pooling : 임의의 size의 input rectangular region을 고정된 size의 feauture로 변환 (임의의 크기 -> 고정된 크기)
The RoI Pooling
input feature map x와 RoI size wxh, top-left corner P0이 주어지면, RoI pooling은 RoI를 kxk bins으로 나누고 kxk feature map y를 output으로 내보냄
(i,j)-th bin (n은 bin 내 pixel 개수)
The deformable RoI pooling
bin position에 offsets이 더해짐
1) RoI pooling이 pooled feature maps을 생성
2) 생성된 feature maps에서 하나의 fc layer를 통해 normalized offsets 생성
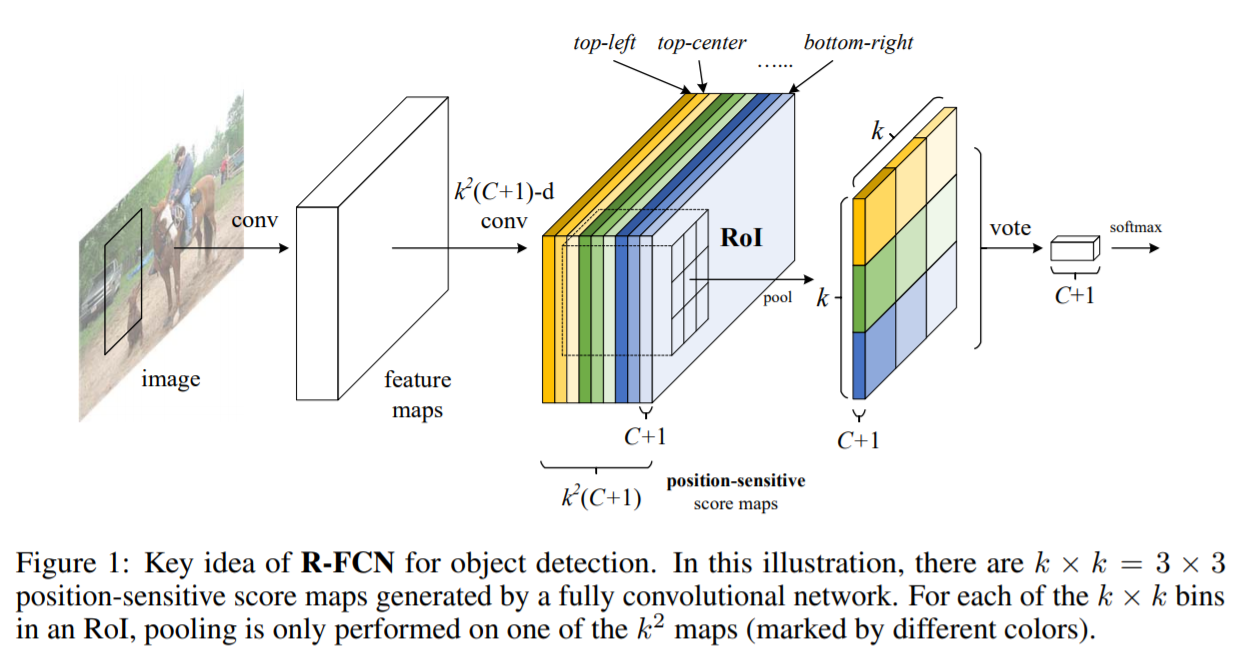
The Position-Sensitive (PS) RoI Pooling
RoI pooling과 다르게 fully convolutional 구조
하나의 convolution을 통해 모든 input feature maps을 각 object class(C+1)에 대한 kxk score maps으로 변환
(i,j)-th bin에 대한 output value는 bin에 해당하는 하나의 score map의 합계
RoI pooling과의 차이점 : general feature map x가 specific positive-sensitive score map x로 대체됨
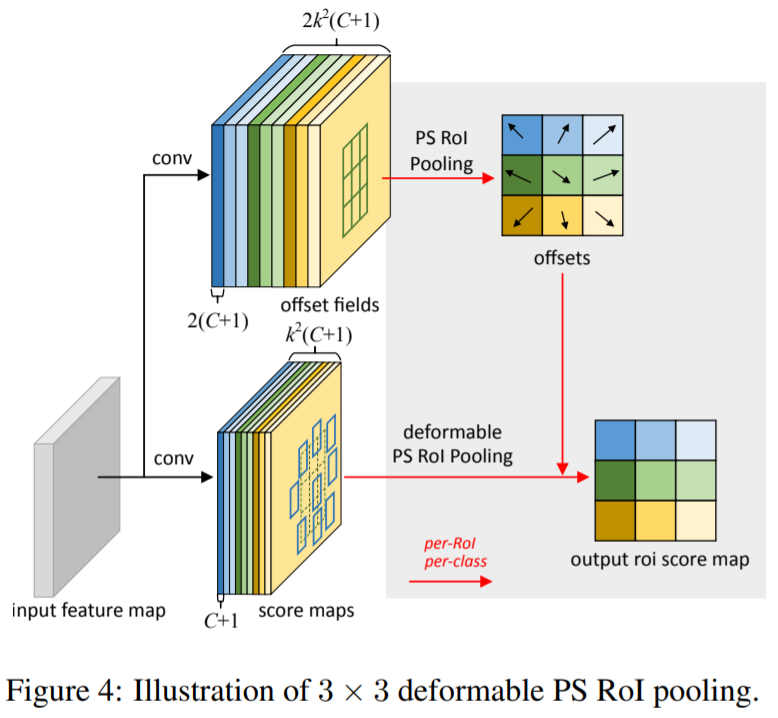
The deformable PS RoI pooling
top branch : 하나의 convolution을 통해 offset fields 생성


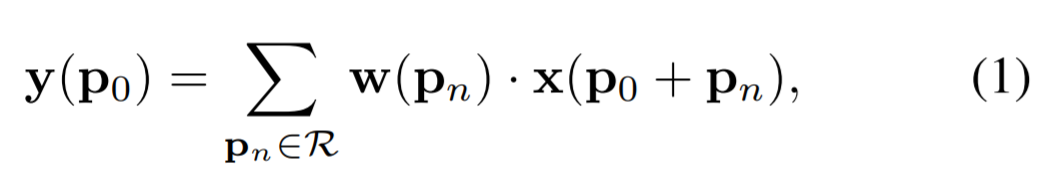
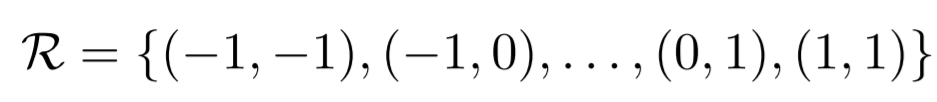
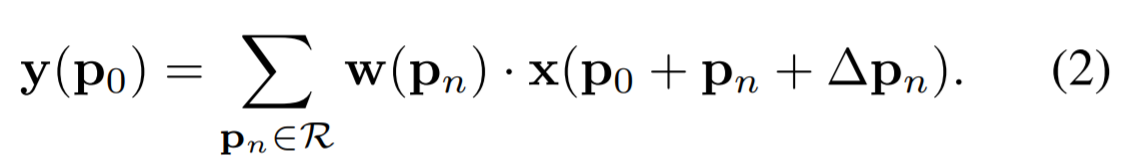
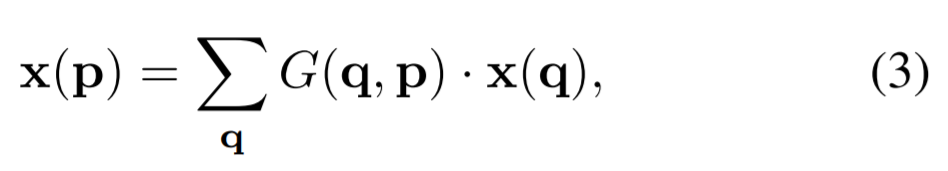
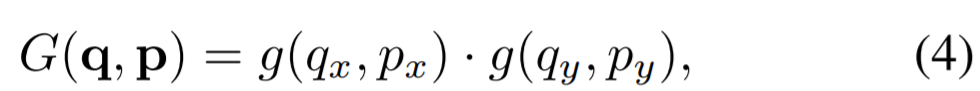
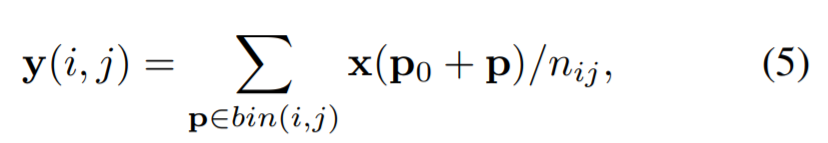
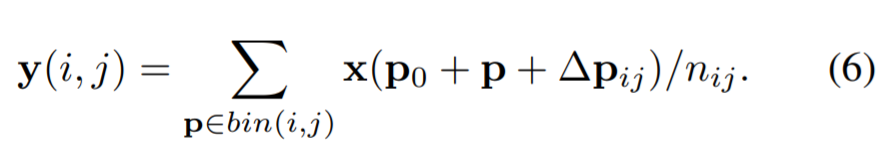
Leave a comment