[Paper Review] Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks
Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks
Tran, Du, et al. “Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks.” Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2015.
Abstract
- 간단하지만 효율적인 3d covolutional networks를 통한 spatiotemporal feature learning 방식 제안
large scale video dataset으로 학습 가능
1) 3D ConvNets은 2D ConvNet 보다 spatiotemporal feature learning에 더 적합함
2) 작은 3x3x3 convolution kernels을 갖는 homogeneous 구조가 제일 좋은 3D ConvNet 구조
homogeneous 구조 : 모든 layer가 동일한 temporal depth를 갖는 구조
3) C3D는 4개의 benchmarks에서 SOTA를 달성했고, 다른 2개의 benchmarks에서 현재 SOTA 방식과 비슷한 성능
Introduction
-
image based deep features는 motion modeling이 부족하기 때문에 video task에 적용하기 적합하지 않음
-
deep 3D ConvNet을 사용한 spatio-temporal features 학습 제안
다양한 video 분석 task에서 좋은 성능
-
기존에서 3D convolution을 사용한 방식들이 존재하였으나, C3D는 large-scale supervised training datasets과 modern deep architectures를 사용하여 좋은 성능을 보였다는 것이 중점
-
C3D의 특성 : generic, compact, simple, efficient
-
Contributions
1) 3D convolutional deep networks가 appearance와 motion을 동시에 modeling 하는 좋은 feature learning machines 임을 보여줌
2) 경험적으로, 모든 layer에 3x3x3 convolution kernel를 적용하는 것이 좋은 성능을 낸다는 것을 발견
3) simple linear model을 갖는 제안된 features가 4개의 task와 6개의 benchmarks에서 뛰어넘거나 비슷한 성능을 보임
compact and efficient
Learning Features with 3D ConvNets
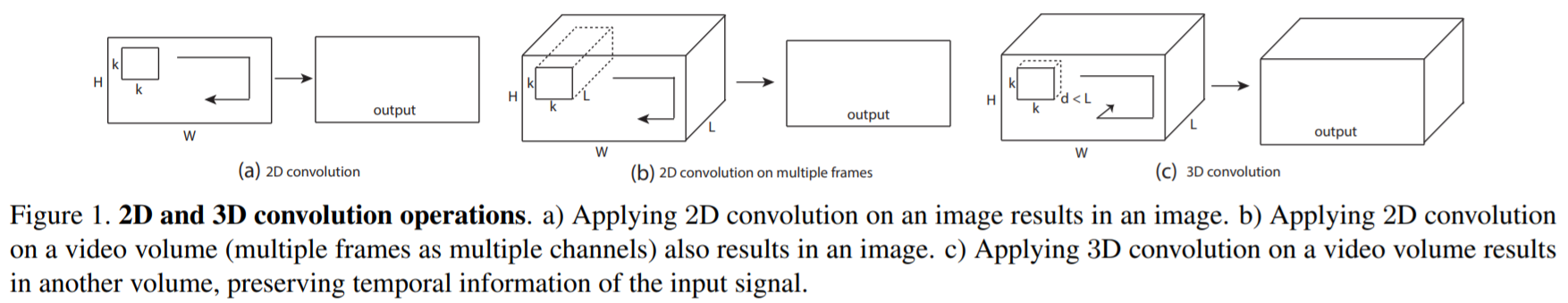
- 3.1 3D convolution and pooling
- 2D ConvNets은 convolution 연산 후에 temporal 정보를 잃어버림
input : 1개의 img -> output : 1개의 img
input : 여러개의 img -> output : 1개의 img
- 오직 3D convolution이 temporal 정보를 보존할 수 있음
input : 여러개의 img -> output : volume (2D, 3D pooling에서도 동일)
- Slow Fusion에서 3D convolutions을 이용하였으나, 여전히 3개의 convolution layer 이후에 temporal 정보를 잃어버린다는 문제가 존재
- 3D ConvNets을 위한 좋은 구조를 경험적으로 찾기 위해, 다양한 setting에서 성능을 평가
medium-scale dataset인 UCF 101을 사용하여 실험
2D ConvNet에서 좋은 성능을 보인 3x3으로 spatial receptive field를 고정시키고, temporal depth만 조절
- Notations
video clip size : c x l x h x w
c: channel / l : frame의 개수 / h : height / w : width
3D convolution과 pooling kernel size : d x k x k
d : temporal depth / k : spatial size
- Common network settings
input은 video clip이고 class labels(101개의 action 포함)을 예측
videos는 겹치지 않도록 16-frame clips으로 나눠져서 input으로 들어감
모든 frame은 128x171로 resize (UCF101 frames의 절반정도의 사이즈)
input dimensions : 3x16x128x171
학습과정에서 input clips을 3x16x112x112로 random crops을 진행 (jittering)
- network layer
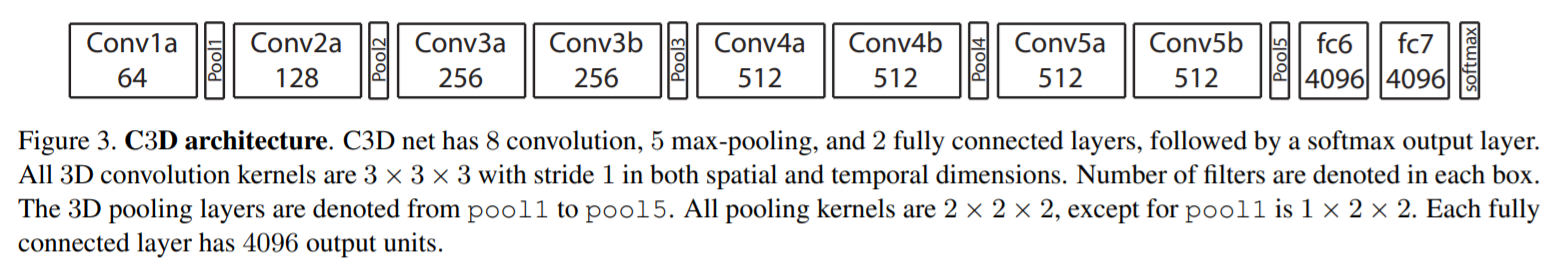
5개의 convolutoin layers와 5개의 pooling layers 그리고 2개의 fully-connected layers와 softmax loss layer(label 예측)로 구성
1) convolution layer
각 convolution layer 뒤에 pooling layer가 위치함
1-5 convolution layer의 filter 개수는 각각 64,128,256,256,256
모든 convolution kernel의 temporal depth(d)는 동일함
모든 convolution layers에 적절한 padding과 stride =1 을 적용
2) pooling layer
첫번째를 제외한 모든 pooling layers는 stride를 1로 하는 2x2x2 kernel 적용 (factor 8)
temporal 정보를 너무 빨리 합치지 않기 위해서, first pooling layer는 1x2x2 kernel을 적용함
3) fully-connected layer : 2048 output
- 30 clips을 mini-batches로 하고 초기 learning rate는 0.003으로 적용하며 4 epoch 마다 10으로 나누어줌 (총 16 epoch)
- Varying network architectures
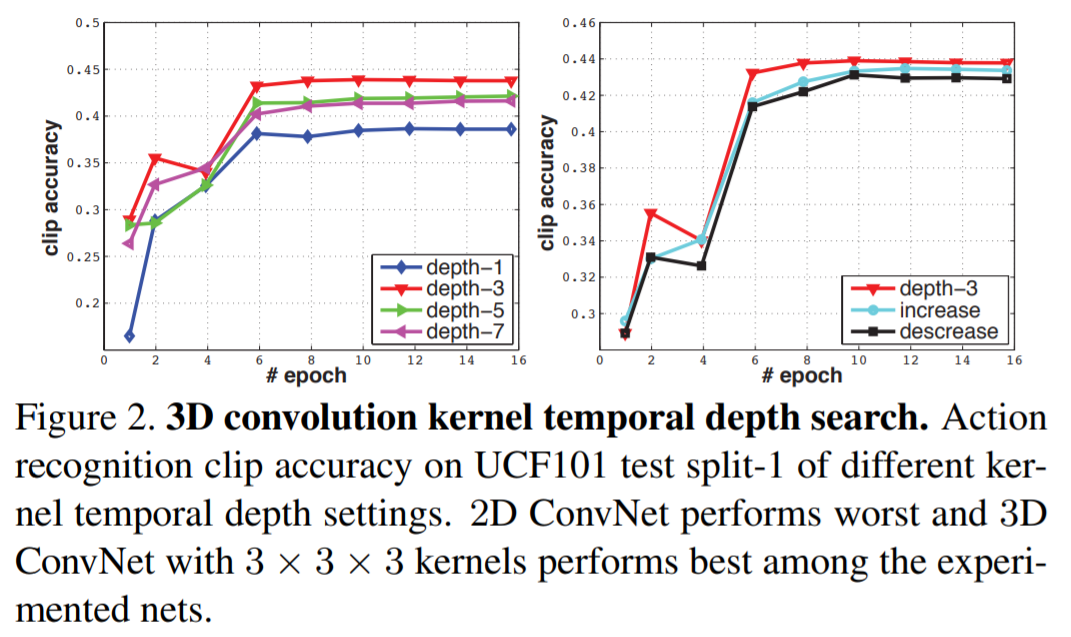
1) homogeneous temporal depth : 모든 convolution layers가 동일한 kernel temporal depth로 구성
depth-d : 1,3,5,7
depth-1은 frame을 1개만 고려하기 때문에 2D convolution과 동일
2) varying temporal depth : layer에 따라 다른 temporal depth로 구성
increasing : 3-3-5-5-7 / decreasing : 7-5-5-3-3
- 3.2 Exploring kernel temporal depth
network 별 parameter 차이는 크기 않으므로 신경쓰지 않아도 됨
depth-3이 가장 좋은 성능을 보임 (3x3x3 kernel이 best choice)
3D ConvNet의 효과 : video classification에서 2D ConvNet보다 일관성이 있으며, large-scale internal dataset(1380K)에서 일관성 있게 좋은 성능을 냄

Leave a comment